8.P.1.1Homework for Website
... 11. Which substance is an element? A. carbon dioxide C. water B. oxygen D. petroleum 12. How many atoms of oxygen are in a molecule of glucose, C6H12O6? A. 24 B. 12 C. 6 D. 1 13. Which BEST explains how atoms combine to form compounds? A. The atoms in the compound share electrons B. The atoms in th ...
... 11. Which substance is an element? A. carbon dioxide C. water B. oxygen D. petroleum 12. How many atoms of oxygen are in a molecule of glucose, C6H12O6? A. 24 B. 12 C. 6 D. 1 13. Which BEST explains how atoms combine to form compounds? A. The atoms in the compound share electrons B. The atoms in th ...
Wet Corrosion Conditions for Wet Corrosion Just as we live in an
... Electrochemical attack, the scientific name for wet corrosion, depends on three circumstances occurring simultaneously. This might seem restrictive, but the evidence of wet corrosion that we see all around us proves that these conditions are easily met. Rates of mass loss by wet corrosion may be tho ...
... Electrochemical attack, the scientific name for wet corrosion, depends on three circumstances occurring simultaneously. This might seem restrictive, but the evidence of wet corrosion that we see all around us proves that these conditions are easily met. Rates of mass loss by wet corrosion may be tho ...
Elements, mixtures and compounds lecture
... A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken down by chemical reactions: burning/acids/eating (but nucle ...
... A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken down by chemical reactions: burning/acids/eating (but nucle ...
L-5: Thermodynamics of Mixtures (Chapter 7)
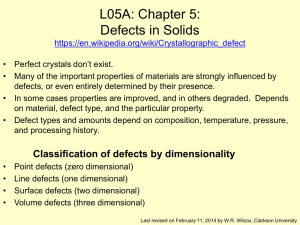
... • The factor of 2 comes about because there are two ions associated with each defect. ...
... • The factor of 2 comes about because there are two ions associated with each defect. ...
MATTER QUIZ: What to Study From: PHASE CHANGES
... Complete the graph below by marking the true statements with an X. ELEMENT ...
... Complete the graph below by marking the true statements with an X. ELEMENT ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
... • NH3(g) à nitrogen trihydride or ammonia • CH4(g) à carbon tetrahydride or methane • H2O2(l) à dihydrogen monoxide or water A MOLECULAR COMPOUND can contain what two combinations of elements? Non-‐metal + ...
... • NH3(g) à nitrogen trihydride or ammonia • CH4(g) à carbon tetrahydride or methane • H2O2(l) à dihydrogen monoxide or water A MOLECULAR COMPOUND can contain what two combinations of elements? Non-‐metal + ...
matter and its reactivity. Objects in the universe are composed of
... particles, stirring, temperature, and the amount of solute already dissolved. 3.1g Characteristic properties can be used to identify different materials, and separate a mixture of substances into its components. For example, iron can be removed from a mixture by means of a magnet. An insoluble subst ...
... particles, stirring, temperature, and the amount of solute already dissolved. 3.1g Characteristic properties can be used to identify different materials, and separate a mixture of substances into its components. For example, iron can be removed from a mixture by means of a magnet. An insoluble subst ...
lecture 13
... revolutionized human civilizations. The start of the Iron Age around 1300 B.C. marked the moment we learned to transform brittle iron ores to iron metal. This affected everything from how we grew food to how we waged wars. ...
... revolutionized human civilizations. The start of the Iron Age around 1300 B.C. marked the moment we learned to transform brittle iron ores to iron metal. This affected everything from how we grew food to how we waged wars. ...
non-metals - lchssci10weir
... Elements that rest on each side of the staircase. Have properties of both metals and non-metals. Example: Silicon – some ability to conduct electricity (used in transistors and chips). ...
... Elements that rest on each side of the staircase. Have properties of both metals and non-metals. Example: Silicon – some ability to conduct electricity (used in transistors and chips). ...
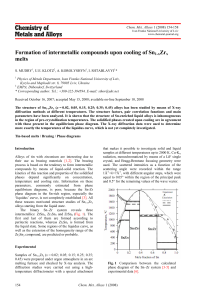
Formation of intermetallic compounds upon cooling of Sn1
... some changes in the heights and widths of the peaks. These changes were attributed to the difference in the phase fractions. From the results of the X-ray studies of liquid and solid Sn1-xZrx alloys one can conclude that the influence of structural features in the liquid at the starting stage of the ...
... some changes in the heights and widths of the peaks. These changes were attributed to the difference in the phase fractions. From the results of the X-ray studies of liquid and solid Sn1-xZrx alloys one can conclude that the influence of structural features in the liquid at the starting stage of the ...
Name Objective 1: Matter and Energy C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
... 5.32 g/cm3; germanium; metalloid 7.87 g/cm3; iron; metal 11.3 g/cm3; lead; metal 13.6 g/cm3; mercury; metal ...
... 5.32 g/cm3; germanium; metalloid 7.87 g/cm3; iron; metal 11.3 g/cm3; lead; metal 13.6 g/cm3; mercury; metal ...
Chemistry Unit Test Review
... before. What might have accounted for the mass being different after? ...
... before. What might have accounted for the mass being different after? ...
Lecture5
... The tin plate is an ideal material for food containers. Tin is not completely inert to all food. But corrosion and product chances are small if the proper choice of material is made. Among the many factors considered by can manufactures are: Chemical composition and physical properties of base plate ...
... The tin plate is an ideal material for food containers. Tin is not completely inert to all food. But corrosion and product chances are small if the proper choice of material is made. Among the many factors considered by can manufactures are: Chemical composition and physical properties of base plate ...
CHEMISTRY EXAM 2 REVIEW
... My child completed this review and studied for at least 30 minutes. Define the following chemistry terms: [Chemistry Dictionary] 1. alloy a mixture of metals 2. brittleness the property of matter that is how easily the substance breaks or shatters when force is applied to it. 3. compound a substance ...
... My child completed this review and studied for at least 30 minutes. Define the following chemistry terms: [Chemistry Dictionary] 1. alloy a mixture of metals 2. brittleness the property of matter that is how easily the substance breaks or shatters when force is applied to it. 3. compound a substance ...
Chemistry Notes with Blanks
... The combination of carbon and water contains the same _________ as sugar. Elements: can’t be broken into _________ substances (atoms.) (Carbon is an element) Sugar + water…would you drink this? Ash + water…would you drink this? Why? They contain the same elements don’t they? Why don’t you get sugar ...
... The combination of carbon and water contains the same _________ as sugar. Elements: can’t be broken into _________ substances (atoms.) (Carbon is an element) Sugar + water…would you drink this? Ash + water…would you drink this? Why? They contain the same elements don’t they? Why don’t you get sugar ...
Naming Ionic Compounds
... o write down the symbols for the elements in the order they appear in the compound name – the metal will always be first and the non metal second e.g. calcium chloride…. write down CaCl o figure out the ionic charge of each element from the periodic table – normally metals have a positive charge and ...
... o write down the symbols for the elements in the order they appear in the compound name – the metal will always be first and the non metal second e.g. calcium chloride…. write down CaCl o figure out the ionic charge of each element from the periodic table – normally metals have a positive charge and ...
ch22 lecture 7e
... – The inorganic cycle involves slow weathering of phosphatecontaining rocks, which causes PO43– to leach into the rivers and seas. – The land-based biological cycle involves incorporation of PO43– into organisms and its release through excretion and ...
... – The inorganic cycle involves slow weathering of phosphatecontaining rocks, which causes PO43– to leach into the rivers and seas. – The land-based biological cycle involves incorporation of PO43– into organisms and its release through excretion and ...
PHASE COMPOSITION AND MICROSTRUCTURE OF Ti-6Al
... quantities by many metals as well as can be easily removed at high-temperature processing in vacuum. This allows using hydrogen as a temporary alloying element in metallic materials at a given stage of manufacture of semi-finished and finished products including those of titanium alloys. Historicall ...
... quantities by many metals as well as can be easily removed at high-temperature processing in vacuum. This allows using hydrogen as a temporary alloying element in metallic materials at a given stage of manufacture of semi-finished and finished products including those of titanium alloys. Historicall ...
4 hon chem classifying matter b
... Theory – an explanation of observations i.e. Darwin’s Theory of Evolution Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
... Theory – an explanation of observations i.e. Darwin’s Theory of Evolution Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
Metals and non-metals III IMPORTANT POINTS Non-metals
... c. In the reactivity series, Metal X is placed below zinc but above copper i. What happens when the hydroxide of copper is heated? ii. What products would you expect to obtain when the hydroxide of X is heated in a dry test tube? iii. Metal X forms the X2+ ion. Write a balanced equation, using X as ...
... c. In the reactivity series, Metal X is placed below zinc but above copper i. What happens when the hydroxide of copper is heated? ii. What products would you expect to obtain when the hydroxide of X is heated in a dry test tube? iii. Metal X forms the X2+ ion. Write a balanced equation, using X as ...
The production and use of metals
... The more reactive a metal, the more stable are it’s compounds and therefore the more difficult they are to extract. Iron is a fairly reactive metal. It is found as an ore called haematite which is mainly iron oxide mixed with impurities. Iron is extracted in the Blast Furnace (Port Talbot Steelwork ...
... The more reactive a metal, the more stable are it’s compounds and therefore the more difficult they are to extract. Iron is a fairly reactive metal. It is found as an ore called haematite which is mainly iron oxide mixed with impurities. Iron is extracted in the Blast Furnace (Port Talbot Steelwork ...
Alloy

An alloy is a mixture of metals or a mixture of a metal and another element. Alloys are defined by metallic bonding character. An alloy may be a solid solution of metal elements (a single phase) or a mixture of metallic phases (two or more solutions). Intermetallic compounds are alloys with a defined stoichiometry and crystal structure. Zintl phases are also sometimes considered alloys depending on bond types (see also: Van Arkel-Ketelaar triangle for information on classifying bonding in binary compounds).Alloys are used in a wide variety of applications. In some cases, a combination of metals may reduce the overall cost of the material while preserving important properties. In other cases, the combination of metals imparts synergistic properties to the constituent metal elements such as corrosion resistance or mechanical strength. Examples of alloys are steel, solder, brass, pewter, duralumin, phosphor bronze and amalgams.The alloy constituents are usually measured by mass. Alloys are usually classified as substitutional or interstitial alloys, depending on the atomic arrangement that forms the alloy. They can be further classified as homogeneous (consisting of a single phase), or heterogeneous (consisting of two or more phases) or intermetallic.