Element Symbol
... mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that they cannot be easily seen. 11. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a solution. ...
... mixed and cannot be visibly distinguished. The particles of the substances are so small that they cannot be easily seen. 11. Another name for a homogeneous mixture is a solution. ...
Ferrous Metallurgy: The Chemistry and Structure of Iron and Steel
... Has a face-centre cubic (FCC) crystal structure. This material is important in that it is the structure from which other structures are formed when the material cools from elevated temperatures. Often known as iron. Not present at room temperatures. ...
... Has a face-centre cubic (FCC) crystal structure. This material is important in that it is the structure from which other structures are formed when the material cools from elevated temperatures. Often known as iron. Not present at room temperatures. ...
Technical terms-3
... Eutectic reaction A reaction wherein, upon cooling, a liquid phase transforms isothermally and reversibly into two intimately mixed solid phases. Eutectic structure A two-phase microstructure resulting from the solidification of a liquid having the eutectic composition; the phases exist as lamellae ...
... Eutectic reaction A reaction wherein, upon cooling, a liquid phase transforms isothermally and reversibly into two intimately mixed solid phases. Eutectic structure A two-phase microstructure resulting from the solidification of a liquid having the eutectic composition; the phases exist as lamellae ...
Ferrous Metallurgy - Marcellus Independent Technical Solutions
... Has a face-centre cubic (FCC) crystal structure. This material is important in that it is the structure from which other structures are formed when the material cools from elevated temperatures. Often known as iron. Not present at room temperatures. ...
... Has a face-centre cubic (FCC) crystal structure. This material is important in that it is the structure from which other structures are formed when the material cools from elevated temperatures. Often known as iron. Not present at room temperatures. ...
g - Santa Rosa Junior College
... – The inorganic cycle involves slow weathering of phosphatecontaining rocks, which causes PO43- to leach into the rivers and seas. – The land-based biological cycle involves incorporation of PO43- into organisms and its release through excretion and ...
... – The inorganic cycle involves slow weathering of phosphatecontaining rocks, which causes PO43- to leach into the rivers and seas. – The land-based biological cycle involves incorporation of PO43- into organisms and its release through excretion and ...
1.5 Modern and smart materials
... Ability to change colour in response to UV or an applied voltage Replaces the need for separate reading and sunglasses ...
... Ability to change colour in response to UV or an applied voltage Replaces the need for separate reading and sunglasses ...
Environmental Embrittlement Characteristics of the AlFe and AlCuFe
... Firstly, more crystallographic phases are commonly obtained (see Figure 2d). Furthermore, it can be observed in Figure 4 that the degradation time increase with the increment of the number of crystalline phases formed. Now, in the case of the B2-Al60 Fe40 composition, there is an appreciable decreme ...
... Firstly, more crystallographic phases are commonly obtained (see Figure 2d). Furthermore, it can be observed in Figure 4 that the degradation time increase with the increment of the number of crystalline phases formed. Now, in the case of the B2-Al60 Fe40 composition, there is an appreciable decreme ...
ch22_lecture_6e_final
... – The inorganic cycle involves slow weathering of phosphatecontaining rocks, which causes PO43- to leach into the rivers and seas. – The land-based biological cycle involves incorporation of PO43- into organisms and its release through excretion and ...
... – The inorganic cycle involves slow weathering of phosphatecontaining rocks, which causes PO43- to leach into the rivers and seas. – The land-based biological cycle involves incorporation of PO43- into organisms and its release through excretion and ...
NICKEL
... Nickel is produced by nuclear fusion in stars and has been identified in supernovae. 62Ni is the most stable nucleide of all the elements and 78Ni is thought to play an important role in the synthesis of elements heavier that iron in supernovae explosions. Most of the Earth’s nickel is in the core a ...
... Nickel is produced by nuclear fusion in stars and has been identified in supernovae. 62Ni is the most stable nucleide of all the elements and 78Ni is thought to play an important role in the synthesis of elements heavier that iron in supernovae explosions. Most of the Earth’s nickel is in the core a ...
ALKALI EARTH METALS Introduction Properties Beryllium
... The word “earth” was used for the oxides of group 2A by the ancient scientists. Alkaline earth metals, after the alkali metals, are secondary metals with strong metallic properties. The group 2A elements are less active than those of 1A, but more active than those of group 3A. Except Be, all form io ...
... The word “earth” was used for the oxides of group 2A by the ancient scientists. Alkaline earth metals, after the alkali metals, are secondary metals with strong metallic properties. The group 2A elements are less active than those of 1A, but more active than those of group 3A. Except Be, all form io ...
Chemistry Test Study Guide
... mixed together but not chemically combined. 3. Pure substance - a homogeneous composition that cannot be broken down or separated using physical means. ...
... mixed together but not chemically combined. 3. Pure substance - a homogeneous composition that cannot be broken down or separated using physical means. ...
Application of grain boundary engineering concepts
... crack before it reaches a critical length Lcrit at which failure occurs. For example, a component of 1 mm thickness having a conventional grain size of 50 /zm possesses approximately 20 triple junctions as possible sites for crack arrest across its entire thickness (Fig. 1 (a)). On the contrary, if ...
... crack before it reaches a critical length Lcrit at which failure occurs. For example, a component of 1 mm thickness having a conventional grain size of 50 /zm possesses approximately 20 triple junctions as possible sites for crack arrest across its entire thickness (Fig. 1 (a)). On the contrary, if ...
Document
... strengthened, and together they form a “solid solution”. Different alloying elements can be used to cause either a substitutional or an interstitial solid solution. Precipitation hardening is a process where impure particles are distributed throughout the metal. This is achieved by first heating t ...
... strengthened, and together they form a “solid solution”. Different alloying elements can be used to cause either a substitutional or an interstitial solid solution. Precipitation hardening is a process where impure particles are distributed throughout the metal. This is achieved by first heating t ...
Study Guide Answers
... 17. Does every atom of the same element have the same number of protons? Why or Why not? Yes, every atom of the same element has to have the same number of protons. The number of protons determines the type of atom. Example, all hydrogen atoms have 1 proton and all helium atoms have 2 protons. 18. ...
... 17. Does every atom of the same element have the same number of protons? Why or Why not? Yes, every atom of the same element has to have the same number of protons. The number of protons determines the type of atom. Example, all hydrogen atoms have 1 proton and all helium atoms have 2 protons. 18. ...
prediction of room temperature mechanical properties in aluminium
... structural parts, such as brake valves and callipers which are traditionally made of cast iron and steels. The most significant barrier to the acceptance of cast aluminium in many structural applications has been its reputation for variability in mechanical properties. Anything that may help predict ...
... structural parts, such as brake valves and callipers which are traditionally made of cast iron and steels. The most significant barrier to the acceptance of cast aluminium in many structural applications has been its reputation for variability in mechanical properties. Anything that may help predict ...
The Second Political Party System: 1856 - 1896
... usually with limestone as a flux. Pig iron has a very high carbon content, typically 3.5–4.5%, which makes it very brittle and not that useful as a material except for limited applications. ...
... usually with limestone as a flux. Pig iron has a very high carbon content, typically 3.5–4.5%, which makes it very brittle and not that useful as a material except for limited applications. ...
Matter
... Compound • Individual atoms lose their original properties after bonding • Composition is fixed • can be decomposed / broken down ...
... Compound • Individual atoms lose their original properties after bonding • Composition is fixed • can be decomposed / broken down ...
Balancing Single Replacement Reactions - Kossmann
... Name: __________________________ Class: ____________________ Date: _____________ ...
... Name: __________________________ Class: ____________________ Date: _____________ ...
A New Breakthrough in Thermoelectric Materials A joint South
... TE alloys are special because the metals have an incredibly high melting point. Instead of melting the metals to fuse them, they are combined through a process called sintering which uses heat and/or pressure to join the small, metallic granules. The joint team, including IBS researchers, used a pro ...
... TE alloys are special because the metals have an incredibly high melting point. Instead of melting the metals to fuse them, they are combined through a process called sintering which uses heat and/or pressure to join the small, metallic granules. The joint team, including IBS researchers, used a pro ...
Ch 1: Engineering materials
... Classifications & Specifications of Metallic Materials Major characteristics of metallic materials are crystallinity, conductivity to heat and electricity and relatively high strength & toughness. Classification: systematic arrangement or division of materials into group on the basis of some common ...
... Classifications & Specifications of Metallic Materials Major characteristics of metallic materials are crystallinity, conductivity to heat and electricity and relatively high strength & toughness. Classification: systematic arrangement or division of materials into group on the basis of some common ...
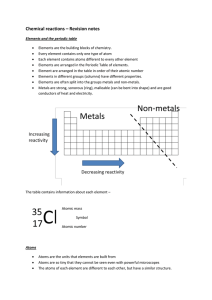
Chemical reactions revision
... The atoms of elements can be joined together to form compounds Once the atoms are joined in a compound, they are difficult to separate. Reactions are written as chemical equations – (element + element -> compound) ...
... The atoms of elements can be joined together to form compounds Once the atoms are joined in a compound, they are difficult to separate. Reactions are written as chemical equations – (element + element -> compound) ...
personal_and_public_transport
... face centred cubic (FCC) austenite to body centred cubic (BCC) ferrite is not given enough time to occur fully and the steel becomes trapped in between as Body Centred Tetragonal (BCT) martensite. This new structure can be exceedingly hard but quite brittle. Air Hardening If steel has nickel and chr ...
... face centred cubic (FCC) austenite to body centred cubic (BCC) ferrite is not given enough time to occur fully and the steel becomes trapped in between as Body Centred Tetragonal (BCT) martensite. This new structure can be exceedingly hard but quite brittle. Air Hardening If steel has nickel and chr ...
Material Selection - Web Services Overview
... – If considerable machining is required, it may well be more economical to choose a more expensive material with higher machinability rating than a lower cost material with lower machinability. – Some materials can not be machined at all (ceramics). – A “non-common” metal may require more lead time, ...
... – If considerable machining is required, it may well be more economical to choose a more expensive material with higher machinability rating than a lower cost material with lower machinability. – Some materials can not be machined at all (ceramics). – A “non-common” metal may require more lead time, ...
Class Notes
... composed of compounds formed between carbon and hydrogen. When carbon and hydrogen bond together, the compounds they form have completely different properties than either elemental carbon or ...
... composed of compounds formed between carbon and hydrogen. When carbon and hydrogen bond together, the compounds they form have completely different properties than either elemental carbon or ...
Polymers composed of a large number of repeating units. Isomers
... Monel metal A nickel-copper alloy with high fatigue strength and excellent corrosion resistance in a range of media Nichrome is a 80% nickel and 20% chromium non-magnetic alloy usually used as a resistance wire. Patented in 1905, it is the oldest documented form of resistance heating alloy ...
... Monel metal A nickel-copper alloy with high fatigue strength and excellent corrosion resistance in a range of media Nichrome is a 80% nickel and 20% chromium non-magnetic alloy usually used as a resistance wire. Patented in 1905, it is the oldest documented form of resistance heating alloy ...
Alloy

An alloy is a mixture of metals or a mixture of a metal and another element. Alloys are defined by metallic bonding character. An alloy may be a solid solution of metal elements (a single phase) or a mixture of metallic phases (two or more solutions). Intermetallic compounds are alloys with a defined stoichiometry and crystal structure. Zintl phases are also sometimes considered alloys depending on bond types (see also: Van Arkel-Ketelaar triangle for information on classifying bonding in binary compounds).Alloys are used in a wide variety of applications. In some cases, a combination of metals may reduce the overall cost of the material while preserving important properties. In other cases, the combination of metals imparts synergistic properties to the constituent metal elements such as corrosion resistance or mechanical strength. Examples of alloys are steel, solder, brass, pewter, duralumin, phosphor bronze and amalgams.The alloy constituents are usually measured by mass. Alloys are usually classified as substitutional or interstitial alloys, depending on the atomic arrangement that forms the alloy. They can be further classified as homogeneous (consisting of a single phase), or heterogeneous (consisting of two or more phases) or intermetallic.