Mechanical & Thermal Energy Energy
... object is thermal energy. (most matter expands as its thermal energy increases) The faster molecules are moving, the more thermal energy they have; which is why balls go farther in warm weather than cold. ...
... object is thermal energy. (most matter expands as its thermal energy increases) The faster molecules are moving, the more thermal energy they have; which is why balls go farther in warm weather than cold. ...
Energy - Maples Elementary School
... Kinetic Energy: the energy of motion Potential Energy: stored energy ...
... Kinetic Energy: the energy of motion Potential Energy: stored energy ...
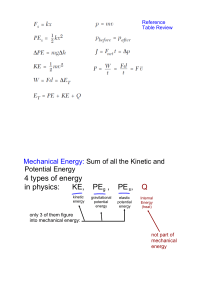
4 types of energy in physics: KE, PEg , PEs, Q
... What is its kinetic energy just as it reaches the ground? ...
... What is its kinetic energy just as it reaches the ground? ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy Notes
... • Kinetic to potential – skateboarding to the top of the ramp and doing a stall • Potential to kinetic – standing on a diving board then jumping off • Light energy to chemical – photosynthesis in plants • Chemical to kinetic – eating breakfast and using that energy to walk, run, kick, etc. ...
... • Kinetic to potential – skateboarding to the top of the ramp and doing a stall • Potential to kinetic – standing on a diving board then jumping off • Light energy to chemical – photosynthesis in plants • Chemical to kinetic – eating breakfast and using that energy to walk, run, kick, etc. ...
Energy - Office Mix
... Calculate Kinetic Energy Distinguish between kinetic energy and Potential energy • Classify different types of potential Energy • Calculate Potential energy associated with an object ...
... Calculate Kinetic Energy Distinguish between kinetic energy and Potential energy • Classify different types of potential Energy • Calculate Potential energy associated with an object ...
Chapter-9-Energy-notes
... Work is done when a force _______ causes an object to ____________. The force must act against _________________ or __________________. The motion has to be the same ___________________ as the force. Is the female walking up the stairs a force against friction or against gravity? Write an example of ...
... Work is done when a force _______ causes an object to ____________. The force must act against _________________ or __________________. The motion has to be the same ___________________ as the force. Is the female walking up the stairs a force against friction or against gravity? Write an example of ...
Work, Energy and Forces (1)
... energy mgh and zero kinetic energy. At the bottom it has kinetic energy mv2 /2 = mgh and no potential energy. ...
... energy mgh and zero kinetic energy. At the bottom it has kinetic energy mv2 /2 = mgh and no potential energy. ...
Environmental Systems
... Forms of Energy • Joule: basic unit of energy (J) • Energy and Power a. energy-ability to do work power-rate at which work is done therefore, energy = power X time power = energy / time ...
... Forms of Energy • Joule: basic unit of energy (J) • Energy and Power a. energy-ability to do work power-rate at which work is done therefore, energy = power X time power = energy / time ...
Kinetic Energy
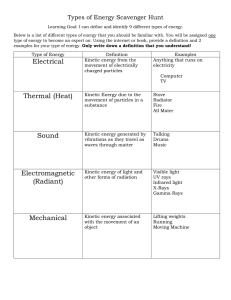
... Types of Energy Scavenger Hunt Learning Goal: I can define and identify 9 different types of energy. Below is a list of different types of energy that you should be familiar with. You will be assigned one type of energy to become an expert on. Using the internet or book, provide a definition and 2 e ...
... Types of Energy Scavenger Hunt Learning Goal: I can define and identify 9 different types of energy. Below is a list of different types of energy that you should be familiar with. You will be assigned one type of energy to become an expert on. Using the internet or book, provide a definition and 2 e ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy Problems
... On a separate sheet of paper, answer the following questions. You must show your work to get full credit for the answer. 1) What is the gravitational constant on Earth? 2) What is the Potential Energy of a 10 N (pay attention to the unit, Newtons, here) book that is placed on a shelf that is 2.5 met ...
... On a separate sheet of paper, answer the following questions. You must show your work to get full credit for the answer. 1) What is the gravitational constant on Earth? 2) What is the Potential Energy of a 10 N (pay attention to the unit, Newtons, here) book that is placed on a shelf that is 2.5 met ...
Mechanical energy
... Electrical energy light, thermal energy, sound Chemical energy kinetic energy to move a car, ...
... Electrical energy light, thermal energy, sound Chemical energy kinetic energy to move a car, ...
Introduction to Physics (in a nutshell) Based on the Physics Worktext
... Galileo Galilei – studied the behavior of falling bodies and experimented with pendulums Isaac Newton – formulated the laws of motion, gravity, discovered the nature and composition of light Aristotle – believed that all things are made of four elements: earth, air, fire, and water Johannes Kepler – ...
... Galileo Galilei – studied the behavior of falling bodies and experimented with pendulums Isaac Newton – formulated the laws of motion, gravity, discovered the nature and composition of light Aristotle – believed that all things are made of four elements: earth, air, fire, and water Johannes Kepler – ...
Chapter 2
... created nor destroyed but can be changed from one form to another. The quantity of energy remains the same. E = mc2 ...
... created nor destroyed but can be changed from one form to another. The quantity of energy remains the same. E = mc2 ...
Week 3 CCA Review
... 3. Metalloids are elements that have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. They are found on the stair step line on the Periodic Table. Metalloids are semiconductors, which means they can conduct electricity at high temperatures. 4. Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can ...
... 3. Metalloids are elements that have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. They are found on the stair step line on the Periodic Table. Metalloids are semiconductors, which means they can conduct electricity at high temperatures. 4. Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can ...
Name: Period:______ Date:______ Infinite Potential Forms of
... 14. What is power and what is its unit? Power is the rate at which work is performed, or how much work in how much time. Its unit is the watt (W) 15. Where did the term horsepower come from? The term horsepower was first used as a way of comparing the power of early steam engines to that of horses. ...
... 14. What is power and what is its unit? Power is the rate at which work is performed, or how much work in how much time. Its unit is the watt (W) 15. Where did the term horsepower come from? The term horsepower was first used as a way of comparing the power of early steam engines to that of horses. ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.