Electricity, Magnetism, and Motion
... Mechanical energy. Electricity produces motion! How can you make a loop of wire continue to spin? Current is reversed just as the loop gets to the vertical position. This reverses the direction of the movement of both sides of the loop. The current reverses after each half turn so the loop spins con ...
... Mechanical energy. Electricity produces motion! How can you make a loop of wire continue to spin? Current is reversed just as the loop gets to the vertical position. This reverses the direction of the movement of both sides of the loop. The current reverses after each half turn so the loop spins con ...
File
... 9. Walking converts what type of energy into mechanical energy? 10. Solar cells convert what type of energy into electrical energy? 11. Describe the changes in kinetic and potential energy for a pendulum as it swings. 12. Why are fossil fuels so widely used? 13. What is the SI unit for work and ener ...
... 9. Walking converts what type of energy into mechanical energy? 10. Solar cells convert what type of energy into electrical energy? 11. Describe the changes in kinetic and potential energy for a pendulum as it swings. 12. Why are fossil fuels so widely used? 13. What is the SI unit for work and ener ...
Cochise College
... An elevator and cable of mass 2600 kg contains a group of people of mass 500kg. An electric motor of 30% efficiency operates the elevator. (70% of the incoming electrical energy is lost in friction and heat.) If electrical energy costs the hotel 11 cents per kilowatthour, how much electrical energy ...
... An elevator and cable of mass 2600 kg contains a group of people of mass 500kg. An electric motor of 30% efficiency operates the elevator. (70% of the incoming electrical energy is lost in friction and heat.) If electrical energy costs the hotel 11 cents per kilowatthour, how much electrical energy ...
Work and Energy PPT - Aurora City Schools
... The net work done on an object (by a net force) is equal to a change in kinetic energy of the object ...
... The net work done on an object (by a net force) is equal to a change in kinetic energy of the object ...
Energy and Matter Notes
... 2. Two factors that determine the state of matter of a substance: _______________________ and the ___________________________________. 3. These two factors contribute to the ___________________ between the particles. 4. Substances _____________ _______________ when they overcome these attractions. 5 ...
... 2. Two factors that determine the state of matter of a substance: _______________________ and the ___________________________________. 3. These two factors contribute to the ___________________ between the particles. 4. Substances _____________ _______________ when they overcome these attractions. 5 ...
Energy Notes
... Energy - Ability to do work or cause change. Mechanical Energy - Energy an object has because of its motion or position. Potential Energy - Energy an object has because of its postion or shape. Kinetic Energy - Energy an object has because it is moving. Heat Energy - The energy related to the temper ...
... Energy - Ability to do work or cause change. Mechanical Energy - Energy an object has because of its motion or position. Potential Energy - Energy an object has because of its postion or shape. Kinetic Energy - Energy an object has because it is moving. Heat Energy - The energy related to the temper ...
TOPICS OBJECTIVES RESOURCES Temperature • Explain the
... Differentiate between thermal energy and temperature. Define “Heat” and “Calorie”. Differentiate between heat and temperature. Differentiate between heat and thermal energy. Explain how adding or removing heat from a system may result in a change of state. Define and give examples of conduction, con ...
... Differentiate between thermal energy and temperature. Define “Heat” and “Calorie”. Differentiate between heat and temperature. Differentiate between heat and thermal energy. Explain how adding or removing heat from a system may result in a change of state. Define and give examples of conduction, con ...
Energy - Reocities
... Energy defined as the capacity to do work, may exist in potential, kinetic, thermal, electrical, chemical, nuclear, or other various forms. There are, moreover, heat and work-i.e. energy in the process of transfer from one body to another. After it has been transferred, energy is always designated a ...
... Energy defined as the capacity to do work, may exist in potential, kinetic, thermal, electrical, chemical, nuclear, or other various forms. There are, moreover, heat and work-i.e. energy in the process of transfer from one body to another. After it has been transferred, energy is always designated a ...
Orbital Paths
... An orbit can only change if it gains/loses energy from another object, such as a gravitational encounter: ...
... An orbit can only change if it gains/loses energy from another object, such as a gravitational encounter: ...
Thermochemistry
... Measuring Energy Changes • calorie(c)-amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one Celsius degree. (Food you eat is measured in Kilocalories which is abbreviated C). • Joule (J)-the SI unit of energy • 1 c=4.184J ...
... Measuring Energy Changes • calorie(c)-amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one Celsius degree. (Food you eat is measured in Kilocalories which is abbreviated C). • Joule (J)-the SI unit of energy • 1 c=4.184J ...
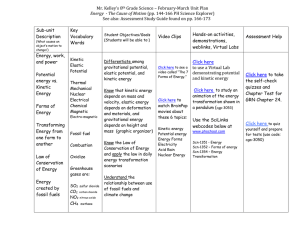
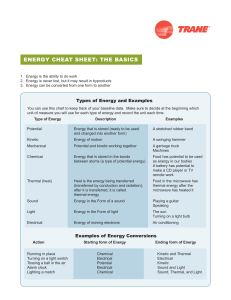
energy CheAt Sheet: the bASiCS
... You can use this chart to keep track of your baseline data. Make sure to decide at the beginning which unit of measure you will use for each type of energy and record the unit each time. ...
... You can use this chart to keep track of your baseline data. Make sure to decide at the beginning which unit of measure you will use for each type of energy and record the unit each time. ...
Energy and Work Section 10.1
... – KE = ½ (m)(v²) – Kinetic energy equals one half mass times velocity squared. ...
... – KE = ½ (m)(v²) – Kinetic energy equals one half mass times velocity squared. ...
What is Energy?
... • A form of energy whose source is the motion of molecules. When something is heated, the atoms or molecules in it begin to move faster. The hotter an object is, the quicker its molecules are moving. Heat can travel in 3 ways! ...
... • A form of energy whose source is the motion of molecules. When something is heated, the atoms or molecules in it begin to move faster. The hotter an object is, the quicker its molecules are moving. Heat can travel in 3 ways! ...
Chapter 13: Work and Energy - South Kingstown High School
... energy ALWAYS REMAINS THE SAME We know where it goes. Can’t always use the new energy form, but it is counted ...
... energy ALWAYS REMAINS THE SAME We know where it goes. Can’t always use the new energy form, but it is counted ...
Forces, Motion, Lithosphere, Hydrosphere and Atmosphere
... If the mass of an object doubles, how will this affect the components of mechanical energy? Both components of mechanical energy (potential energy and kinectic energy) would double ...
... If the mass of an object doubles, how will this affect the components of mechanical energy? Both components of mechanical energy (potential energy and kinectic energy) would double ...
Energy and Work - Stanley Teacher Prep
... Conservation of Energy • Law of conservation of energy: energy is neither created or destroyed, only changes state – As you move back and forth, energy is converted from kinetic to potential back to kinetic energy continuously – So why does the swing eventually stop? ...
... Conservation of Energy • Law of conservation of energy: energy is neither created or destroyed, only changes state – As you move back and forth, energy is converted from kinetic to potential back to kinetic energy continuously – So why does the swing eventually stop? ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.