Study Guide
... 18. The mixing of a gas or liquid cases heat transfer by___________________________________. 19. What occurs when electromagnetic waves transfer thermal energy ______________________. 20. The average kinetic energy of the molecules in an object is called ___________________________. 21. The transfer ...
... 18. The mixing of a gas or liquid cases heat transfer by___________________________________. 19. What occurs when electromagnetic waves transfer thermal energy ______________________. 20. The average kinetic energy of the molecules in an object is called ___________________________. 21. The transfer ...
What Is Energy Power Point
... – When you stretch a rubber band, it has the potential to snap back to its original shape. When you flick one across the room, you are transferring the elastic PE from the stretch into KE when you release it to make it fly. – When you squeeze a stress ball, it has the potential to decompress. Elasti ...
... – When you stretch a rubber band, it has the potential to snap back to its original shape. When you flick one across the room, you are transferring the elastic PE from the stretch into KE when you release it to make it fly. – When you squeeze a stress ball, it has the potential to decompress. Elasti ...
Chapter 5
... Draw a Bar Energy Chart A ball is dropped from rest from a bridge. As the ball falls through the air, it encounters a small amount of air resistance. The final state of the ball is the instant before it strikes the water. ...
... Draw a Bar Energy Chart A ball is dropped from rest from a bridge. As the ball falls through the air, it encounters a small amount of air resistance. The final state of the ball is the instant before it strikes the water. ...
Chapter 5.1 Energy Changes in Chemical and Nuclear Reactions
... average water molecule is moving slower • The total quantity of thermal energy is higher in the bathtub because there are mover water molecules in total ...
... average water molecule is moving slower • The total quantity of thermal energy is higher in the bathtub because there are mover water molecules in total ...
Energy - TeacherWeb
... substance • As a substance is warmed, some of its particles move faster • The average kinetic energy of the substances particles increases and so does the temperature of the substance ...
... substance • As a substance is warmed, some of its particles move faster • The average kinetic energy of the substances particles increases and so does the temperature of the substance ...
File
... How much work is required to lift a 100 kg crate uniformly through a vertical distance of 20 m? W = Fd First, we need to find the force. o Fw = mg o Fw = (100kg)(9.8m/s2) o Fw = 980 N Now, plug in Force into W=Fd o W = Fd o W = (980N)(20m) o W = 19,600 J ...
... How much work is required to lift a 100 kg crate uniformly through a vertical distance of 20 m? W = Fd First, we need to find the force. o Fw = mg o Fw = (100kg)(9.8m/s2) o Fw = 980 N Now, plug in Force into W=Fd o W = Fd o W = (980N)(20m) o W = 19,600 J ...
General
... This equation relates what two things (mass and energy) Einstein’s equation explains what two types of reactions (Fission and Fusion) In a frictionless environment the kinetic energy of a falling object will be _________ to the potential energy at the beginning of the fall. (Equal) The process of en ...
... This equation relates what two things (mass and energy) Einstein’s equation explains what two types of reactions (Fission and Fusion) In a frictionless environment the kinetic energy of a falling object will be _________ to the potential energy at the beginning of the fall. (Equal) The process of en ...
PHYSICS COURSE SYLLABUS Lucy C. Laney High School School
... SP1. Students will analyze the relationships between force, mass, gravity, and the motion of objects. a. Calculate average velocity, instantaneous velocity, and acceleration in a given frame of reference. b. Compare and contrast scalar and vector quantities. c. Compare graphically and algebraically ...
... SP1. Students will analyze the relationships between force, mass, gravity, and the motion of objects. a. Calculate average velocity, instantaneous velocity, and acceleration in a given frame of reference. b. Compare and contrast scalar and vector quantities. c. Compare graphically and algebraically ...
Name
... 3. Give an example where two people do the same amount of work, but one more powerful than the other. 4. Give an example where one person does more work than the other, but they are equally powerful. 5. In your own words, explain the relationship between work and energy. 6. Explain how potential and ...
... 3. Give an example where two people do the same amount of work, but one more powerful than the other. 4. Give an example where one person does more work than the other, but they are equally powerful. 5. In your own words, explain the relationship between work and energy. 6. Explain how potential and ...
Energy and Power - Reeths
... has mechanical energy. • Example 2- A guitars strings being plucked. ...
... has mechanical energy. • Example 2- A guitars strings being plucked. ...
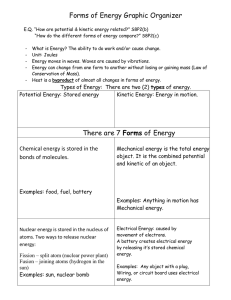
Forms of Energy
... What is Energy? The ability to do work and/or cause change. Unit: Joules Energy moves in waves. Waves are caused by vibrations. Energy can change from one form to another without losing or gaining mass (Law of Conservation of Mass). Heat is a byproduct of almost all changes in forms of energy. ...
... What is Energy? The ability to do work and/or cause change. Unit: Joules Energy moves in waves. Waves are caused by vibrations. Energy can change from one form to another without losing or gaining mass (Law of Conservation of Mass). Heat is a byproduct of almost all changes in forms of energy. ...
The BIG Idea— Energy is the ability to do work or make something
... The BIG Idea— Temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy or the molecular movement of a substance. Every energy conversion involves some conversion of energy to heat. Heat energy likes to spread out and be uniform. Here is my example of where heat can come from and how it moves. Heat Transfer Ex ...
... The BIG Idea— Temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy or the molecular movement of a substance. Every energy conversion involves some conversion of energy to heat. Heat energy likes to spread out and be uniform. Here is my example of where heat can come from and how it moves. Heat Transfer Ex ...
Forms of Energy Conversions
... Forms of Energy Conversions: use the back of this page for drawing if you need more room. There are six forms of energy: thermal (heat), electrical (moving electrons), electromagnetic (light), nuclear (energy that binds the nuclei of atoms), chemical and mechanical (a kind of kinetic energy of movin ...
... Forms of Energy Conversions: use the back of this page for drawing if you need more room. There are six forms of energy: thermal (heat), electrical (moving electrons), electromagnetic (light), nuclear (energy that binds the nuclei of atoms), chemical and mechanical (a kind of kinetic energy of movin ...
energy book content
... When there is a lot of heat energy, the particles move fast and there is high temperature When there is little heat energy, the particles move slower and there is low temperature HEAT LAW: DURING A TRANSFER, HEAT ALWAYS MOVE FROM WARMER OBJECT TO COLDER OBJECT SOURCES OF HEAT ENERGY: Sun, burning ma ...
... When there is a lot of heat energy, the particles move fast and there is high temperature When there is little heat energy, the particles move slower and there is low temperature HEAT LAW: DURING A TRANSFER, HEAT ALWAYS MOVE FROM WARMER OBJECT TO COLDER OBJECT SOURCES OF HEAT ENERGY: Sun, burning ma ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.