Name: Date: Pod: Name: Date: Pod: Name: Date: Pod: Do Now
... Which of the following explains the total amount of kinetic What is the rolling motion of boiling water an example of? energy contained in the particles of a substance? a. Conduction a. Temperature b. Convection b. Heat c. Radiation c. Thermal energy d. Insulation d. Kinetic energy Label the parts o ...
... Which of the following explains the total amount of kinetic What is the rolling motion of boiling water an example of? energy contained in the particles of a substance? a. Conduction a. Temperature b. Convection b. Heat c. Radiation c. Thermal energy d. Insulation d. Kinetic energy Label the parts o ...
File
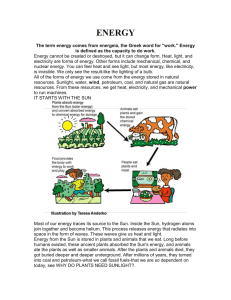
... We get our ability to do things from our food. Our food is our source of energy. A fire gets its ability to do something (that is, heat other things up or burn things) from the wood. The wood is the source of the energy. Plants make their food by photosynthesis. The energy they need comes from the S ...
... We get our ability to do things from our food. Our food is our source of energy. A fire gets its ability to do something (that is, heat other things up or burn things) from the wood. The wood is the source of the energy. Plants make their food by photosynthesis. The energy they need comes from the S ...
Blank Jeopardy
... “Inputs of energy are equal to all outputs of energy after all conversions” is an example of this law. ...
... “Inputs of energy are equal to all outputs of energy after all conversions” is an example of this law. ...
Energy - Hudson Falls Central School District
... Elastic PE is found in a stretched or compressed elastic object (springs) If a spring is not stretched or compressed, then there is no elastic potential energy ...
... Elastic PE is found in a stretched or compressed elastic object (springs) If a spring is not stretched or compressed, then there is no elastic potential energy ...
HeatTransfer
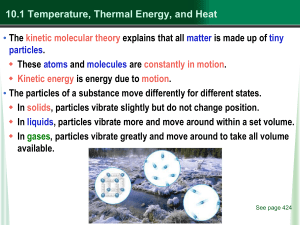
... • The kinetic molecular theory explains that all matter is made up of tiny particles. These atoms and molecules are constantly in motion. Kinetic energy is energy due to motion. • The particles of a substance move differently for different states. In solids, particles vibrate slightly but do n ...
... • The kinetic molecular theory explains that all matter is made up of tiny particles. These atoms and molecules are constantly in motion. Kinetic energy is energy due to motion. • The particles of a substance move differently for different states. In solids, particles vibrate slightly but do n ...
How is Work and Power Related? Chapter 5 Work and Power
... multiply force OR distance Increasing force or distance are at the expense of the other variable Energy is conserved in an ideal situation no friction Work in would equal Work out in another words F x d (in) = F x d (out) Work in is done on the machine and Work out is done by the machine ...
... multiply force OR distance Increasing force or distance are at the expense of the other variable Energy is conserved in an ideal situation no friction Work in would equal Work out in another words F x d (in) = F x d (out) Work in is done on the machine and Work out is done by the machine ...
924 Lecture, Energy
... Laws of Thermodynamics 1. Conservation of energy: Energy is neither created nor destroyed; it is transformed. you can't take out of a system more than you put in. you can't win 2. The entropy of the universe is continually increasing. perpetual motion and a heat engine with 100% efficiency are both ...
... Laws of Thermodynamics 1. Conservation of energy: Energy is neither created nor destroyed; it is transformed. you can't take out of a system more than you put in. you can't win 2. The entropy of the universe is continually increasing. perpetual motion and a heat engine with 100% efficiency are both ...
Slide 1
... G. Potential Energy- the energy an object has because of its position or shape. It has energy because work has been already done to it. ...
... G. Potential Energy- the energy an object has because of its position or shape. It has energy because work has been already done to it. ...
Energy Transformations
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
Energy and Forces
... During this unit, we will address the following Maine Learning Results: D3h Describe several different types of energy forms including heat energy, chemical energy, and mechanical energy D3i Use examples of energy transformations from one form to another to explain that energy cannot be created or d ...
... During this unit, we will address the following Maine Learning Results: D3h Describe several different types of energy forms including heat energy, chemical energy, and mechanical energy D3i Use examples of energy transformations from one form to another to explain that energy cannot be created or d ...
Energy & Its Conservation
... If Cal lifts a 2 kg textbook from The floor to a shelf 2.1 m above The floor. What is the book’s Potential energy relative to the Floor? What is the potential energy Relative to his head if he is 1.65 m tall? 41.2 J ...
... If Cal lifts a 2 kg textbook from The floor to a shelf 2.1 m above The floor. What is the book’s Potential energy relative to the Floor? What is the potential energy Relative to his head if he is 1.65 m tall? 41.2 J ...
Chapter 15
... given the objects mass and velocity Analyze how potential energy is related to an object’s position and give examples of gravitational and elastic potential energy Solve equations that relate an object’s gravitational potential energy to its mass and height Give examples of the major forms of energy ...
... given the objects mass and velocity Analyze how potential energy is related to an object’s position and give examples of gravitational and elastic potential energy Solve equations that relate an object’s gravitational potential energy to its mass and height Give examples of the major forms of energy ...
Additional Energy Terms
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.