* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
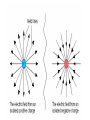
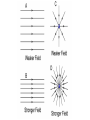
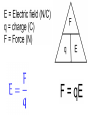
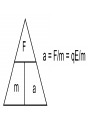
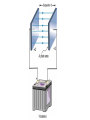
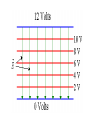
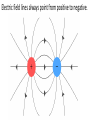
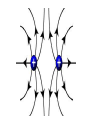
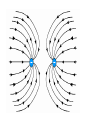
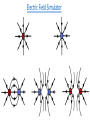
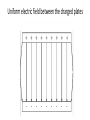
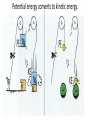
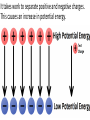
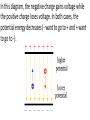
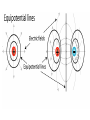
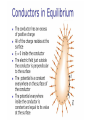
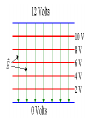
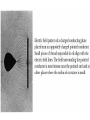
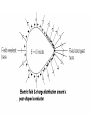
Parallel Plate Capacitor Capacitor with power supply Electric field lines always point from positive to negative. Electric Field Simulator Uniform electric field between the charged plates Electric field inside conductor is zero. Faraday cage The electric field inside a Faraday cage is zero. Kinetic Energy - Energy of motion Potential Energy - Energy of position If an object is in a location where it really doesn't want to be, it has a lot of potential energy. In order for the object to be located in this position, work must be done. Work = (Force)(distance) W = Fd (1 Joule = 1Newton-meter) Potential energy converts to kinetic energy. It takes work to separate positive and negative charges. This causes an increase in potential energy. Electric Potential = Electric Potential Energy per charge V = PE/q 1 volt = 1 Joule/coulomb Electric Potential is also called voltage. Example: If 0.05 C of charge has a PE of 30 J, then its voltage is ? V = PE/q = 30J/0.05C = 600V In this diagram, the negative charge gains voltage while the positive charge loses voltage. In both cases, the potential energy decreases (- want to go to + and + want to go to -). Faraday cages can block reception