the law of conservation of energy
... A car launched up the hill at a given speed will never go higher than a certain point. A car rolling downhill will only reach a certain speed. Why? The answer is that nature keeps an exact balance of energy: the law of conservation of energy Speed uses one form of energy and height uses another. Thi ...
... A car launched up the hill at a given speed will never go higher than a certain point. A car rolling downhill will only reach a certain speed. Why? The answer is that nature keeps an exact balance of energy: the law of conservation of energy Speed uses one form of energy and height uses another. Thi ...
Energy Test Study Guide
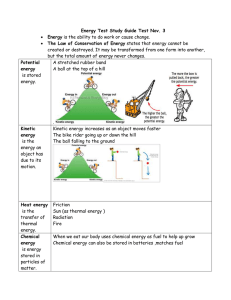
... Energy Test Study Guide Test Nov. 3 Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It may be transformed from one form into another, but the total amount of energy never changes. A stretched rubber band A ball at ...
... Energy Test Study Guide Test Nov. 3 Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It may be transformed from one form into another, but the total amount of energy never changes. A stretched rubber band A ball at ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... life scenarios and calculate the amount of work done and power used. We will also study the types of energy involved in doing work (potential and kinetic, as well as other forms) and how work is done to transform that energy from one form to another. Again, we will look at real life scenarios and ca ...
... life scenarios and calculate the amount of work done and power used. We will also study the types of energy involved in doing work (potential and kinetic, as well as other forms) and how work is done to transform that energy from one form to another. Again, we will look at real life scenarios and ca ...
Mechanical Energy - Miss Burnett`s 6th grade Classroom
... Mechanical Energy The energy of motion that does the work ...
... Mechanical Energy The energy of motion that does the work ...
Potential Energy
... Kinetic Energy • Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity. • Common units of kinetic energy: Joules – An object with mass of 1 kg, moving at 1 m/s, has a kinetic energy of 0.5 Joule. ...
... Kinetic Energy • Kinetic energy is a scalar quantity. • Common units of kinetic energy: Joules – An object with mass of 1 kg, moving at 1 m/s, has a kinetic energy of 0.5 Joule. ...
Technology Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology
... Chemical energy: energy stored within a chemical substance. Electrical energy: energy associated with electrons moving along a conductor. Energy: the ability to do work. Exhaustible energy resources: materials that cannot be replaced. Fission: the process of splitting atoms to release vast quantitie ...
... Chemical energy: energy stored within a chemical substance. Electrical energy: energy associated with electrons moving along a conductor. Energy: the ability to do work. Exhaustible energy resources: materials that cannot be replaced. Fission: the process of splitting atoms to release vast quantitie ...
hw1
... you done in ft⋅lbs? In joules? (b)If you push a cart along a horizontal surface with a force of ten Newtons, and the cart moves 3 meters, how much work have you done in joules? 4. Since energy is conserved, where has the energy gone in question 3? (a)Where did it come from? (b)What is the kinetic en ...
... you done in ft⋅lbs? In joules? (b)If you push a cart along a horizontal surface with a force of ten Newtons, and the cart moves 3 meters, how much work have you done in joules? 4. Since energy is conserved, where has the energy gone in question 3? (a)Where did it come from? (b)What is the kinetic en ...
16: Work, Power, and Energy
... • Displacement: The quantity that describes the change in location of an object which includes its direction of motion. Displacement is a vector quantity. • Acceleration: Rate at which an object’s velocity changes with time; this change may in speed, direction, or both. • Vector: A quantity that rep ...
... • Displacement: The quantity that describes the change in location of an object which includes its direction of motion. Displacement is a vector quantity. • Acceleration: Rate at which an object’s velocity changes with time; this change may in speed, direction, or both. • Vector: A quantity that rep ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 1. Elastic Collision…one where the total kinetic energy of the system is conserved. 2. Inelastic Collision…one where the total kinetic energy is not conserved. -momentum is conserved in both types of collisions Conditions for elastic collisions: 1. collision must be oblique (initially objects collid ...
... 1. Elastic Collision…one where the total kinetic energy of the system is conserved. 2. Inelastic Collision…one where the total kinetic energy is not conserved. -momentum is conserved in both types of collisions Conditions for elastic collisions: 1. collision must be oblique (initially objects collid ...
Chapter 15 Notes - Valdosta State University
... type of wall. A wall that allows heat flow is called a diathermal wall. One that does not is said to be adiabatic. The state of a system is described by specifying factors that affect the internal energy of the system. In the case of a gas this would be temperature, pressure, volume, and mass. There ...
... type of wall. A wall that allows heat flow is called a diathermal wall. One that does not is said to be adiabatic. The state of a system is described by specifying factors that affect the internal energy of the system. In the case of a gas this would be temperature, pressure, volume, and mass. There ...
Law of Conservation of Energy
... suddenly starts moving…potential energy gets transferred into kinetic energy! ...
... suddenly starts moving…potential energy gets transferred into kinetic energy! ...
What is Energy?
... • Power is the rate at which work is done • Power is therefore the rate at which energy is transferred • Power = Energy Transferred time ...
... • Power is the rate at which work is done • Power is therefore the rate at which energy is transferred • Power = Energy Transferred time ...
Forms of Energy
... Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic. ...
... Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic. ...
Answers
... Next,you are familiar with both of these: Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy. According to the text written below the heading “Gravitational Potential Energy” on this page, Gravitational Potential Energy is The energy stored in an object as the result of its vertical position or height. The energy ...
... Next,you are familiar with both of these: Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy. According to the text written below the heading “Gravitational Potential Energy” on this page, Gravitational Potential Energy is The energy stored in an object as the result of its vertical position or height. The energy ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.