Body Planes, Sections, and Cavitites
... Opening within body which protects internal organs, and allows transfer of materials/information ...
... Opening within body which protects internal organs, and allows transfer of materials/information ...
Chapter 1 Test Study Guide
... 18. Place the 4 abdominopelvic quadrants in the correct boxes. Also name an organ that would be found in each quadrant. ...
... 18. Place the 4 abdominopelvic quadrants in the correct boxes. Also name an organ that would be found in each quadrant. ...
Intro Notes (new)
... -_______________- ability to sense changes in the environment and respond to them. ! - ___________ Digestion- breakdown of ingested foods. ! - _______________ - all the chemical reactions that occur in the body ! - ______________- removal of wastes from the body ! - ______________- cellular and orga ...
... -_______________- ability to sense changes in the environment and respond to them. ! - ___________ Digestion- breakdown of ingested foods. ! - _______________ - all the chemical reactions that occur in the body ! - ______________- removal of wastes from the body ! - ______________- cellular and orga ...
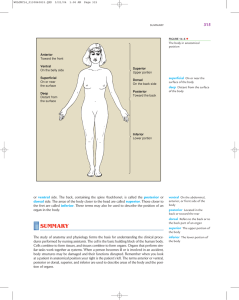
Anterior Toward the front Ventral On the belly side Superficial On or
... The study of anatomy and physiology forms the basis for understanding the clinical procedures performed by nursing assistants. The cell is the basic building block of the human body. Cells combine to form tissues, and tissues combine to form organs. Organs that perform similar tasks work together as ...
... The study of anatomy and physiology forms the basis for understanding the clinical procedures performed by nursing assistants. The cell is the basic building block of the human body. Cells combine to form tissues, and tissues combine to form organs. Organs that perform similar tasks work together as ...
Medical)Terminology) !Anatomy) !Physiology
... Medical)Terminology) • Words made from parts – Root: pnea-Breath, arthr-joint – Root with combining form: therm-o + meter = thermometer – Prefix: dys (pain)-pnea, tachy (fast)-pnea – Suffix: arthr-itis (inflammation of), hemophiliac (pertaining to certain disease) ...
... Medical)Terminology) • Words made from parts – Root: pnea-Breath, arthr-joint – Root with combining form: therm-o + meter = thermometer – Prefix: dys (pain)-pnea, tachy (fast)-pnea – Suffix: arthr-itis (inflammation of), hemophiliac (pertaining to certain disease) ...
bodysystemsterms
... ! SECTION – cut made through the body in the direction of a certain plane ! SAGITTAL PLANE – divides the body into right and left parts ! CORONAL (FRONTAL) PLANE – vertical cut at right angles to saggital plane, divides the body into anterior and posterior portions ! TRANSVERSE PLANE – cross-section ...
... ! SECTION – cut made through the body in the direction of a certain plane ! SAGITTAL PLANE – divides the body into right and left parts ! CORONAL (FRONTAL) PLANE – vertical cut at right angles to saggital plane, divides the body into anterior and posterior portions ! TRANSVERSE PLANE – cross-section ...
General Body and Directional Terms
... • Cells are the basic unit of life • Cells of similar function join together to form tissue • Groups of tissue join together to form organs ...
... • Cells are the basic unit of life • Cells of similar function join together to form tissue • Groups of tissue join together to form organs ...
HospitalLawsandRules
... authorized person (by the patient) can read the medical record. The doctor should be there during the reading of the record. The medical record can not be removed from the department as it is the property of the hospital. Copies can be made though. The head of each department gives the guidelines fo ...
... authorized person (by the patient) can read the medical record. The doctor should be there during the reading of the record. The medical record can not be removed from the department as it is the property of the hospital. Copies can be made though. The head of each department gives the guidelines fo ...
review ch 1 anatomy human body orientation
... 22. The Arm would be located in the _____________ body area. 23. The elbow would be located in the_________ body area 24. The armpit would be located in the _______ body area. 25. The _____________ would be located in the abdominal body area 26. The ____________ system includes the pancreas, adrenal ...
... 22. The Arm would be located in the _____________ body area. 23. The elbow would be located in the_________ body area 24. The armpit would be located in the _______ body area. 25. The _____________ would be located in the abdominal body area 26. The ____________ system includes the pancreas, adrenal ...
Performing an Autopsy
... • Small hospitals usually have to send bodies out to be autopsied, while larger hospitals keep a pathologist on staff. • An autopsy is normally performed by a team of three; a diener, a prosector, and the pathologist. – The diener is often a person who is in college planning on going into the medica ...
... • Small hospitals usually have to send bodies out to be autopsied, while larger hospitals keep a pathologist on staff. • An autopsy is normally performed by a team of three; a diener, a prosector, and the pathologist. – The diener is often a person who is in college planning on going into the medica ...
BASIC ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY ANATOMICAL POSITION
... 1. Sagittal plane- vertical plane that divides the body or an organ into right and left sides Midsagittal/ Median plane- equal right and left Parasagittal- unequal right and left 2. Frontal or Coronal- divides the body or an organ into anterior and posterior portions 3. Transverse/ Cross section ...
... 1. Sagittal plane- vertical plane that divides the body or an organ into right and left sides Midsagittal/ Median plane- equal right and left Parasagittal- unequal right and left 2. Frontal or Coronal- divides the body or an organ into anterior and posterior portions 3. Transverse/ Cross section ...
Unit 1 Review Intro and Tissues
... LT #11. Provide the appropriate anatomical term for major body regions. 12, 13 and 14. Draw a stick person and label the dorsal cavity and the 2 parts. Label the ventral cavity and its 4 cavities. ...
... LT #11. Provide the appropriate anatomical term for major body regions. 12, 13 and 14. Draw a stick person and label the dorsal cavity and the 2 parts. Label the ventral cavity and its 4 cavities. ...
Forensic Autopsy Cadaver Demonstration Distance Learning
... properties and principles of matter and energy structures of, functions of, and relationships among human body systems principles of movement and physical fitness methods used to assess health, reduce risk factors, and avoid high risk behaviors (such as violence, tobacco, alcohol and other drug use) ...
... properties and principles of matter and energy structures of, functions of, and relationships among human body systems principles of movement and physical fitness methods used to assess health, reduce risk factors, and avoid high risk behaviors (such as violence, tobacco, alcohol and other drug use) ...
Dr. Robert C. Bux - El Paso County, Colorado
... Determine the cause and manner of death Positively identify the deceased Determine the time of death Collect evidence from the body Document injuries and natural diseases Provide expert testimony in court ...
... Determine the cause and manner of death Positively identify the deceased Determine the time of death Collect evidence from the body Document injuries and natural diseases Provide expert testimony in court ...
CHAPTER ONE - Hollidaysburg Area School District
... The human body is divided up into two major cavities. Those two cavities are then subdivided . The purposes of the cavities are to: let the organs __________ independently of the body ...
... The human body is divided up into two major cavities. Those two cavities are then subdivided . The purposes of the cavities are to: let the organs __________ independently of the body ...
Postmortem Forensic Toxicology - BIOL-104: Forensic Biology
... • The act of ending ones own life. • These autopsies often easily identify source, cause, and other factors of the death. • Suicide is often identified in the forensic autopsy as a cause of toxic, firearms, blunt force trauma, etc. ...
... • The act of ending ones own life. • These autopsies often easily identify source, cause, and other factors of the death. • Suicide is often identified in the forensic autopsy as a cause of toxic, firearms, blunt force trauma, etc. ...
Autopsy

An autopsy—also known as a post-mortem examination, necropsy, autopsia cadaverum, or obduction—is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present. It is usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist.The word “autopsy” means to study and directly observe the body (Adkins and Barnes, 317). This includes an external examination of the deceased and the removal and dissection of the brain, kidneys, lungs and heart. When a coroner receives a body, he or she must first review the circumstances of the death and all evidence, then decide what type of autopsy should be performed if any. If an autopsy is recommended, the coroner can choose between an external autopsy (the deceased is examined, fingerprinted, and photographed but not opened; blood and fluid samples are taken), an external and partial internal autopsy (the deceased is opened but only affected organs are removed and examined), or a full external and internal autopsy.Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. For example, a forensic autopsy is carried out when the cause of death may be a criminal matter, while a clinical or academic autopsy is performed to find the medical cause of death and is used in cases of unknown or uncertain death, or for research purposes. Autopsies can be further classified into cases where external examination suffices, and those where the body is dissected and internal examination is conducted. Permission from next of kin may be required for internal autopsy in some cases. Once an internal autopsy is complete the body is reconstituted by sewing it back together.