Levels of Organization and Anatomical Terms
... • Landmarks around the body create a map for orientation • Based on Latin or Greek words used by ancient anatomists ...
... • Landmarks around the body create a map for orientation • Based on Latin or Greek words used by ancient anatomists ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
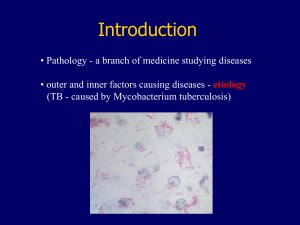
... Introduction • how and why - development - pathogenesis (infectious endocarditis - thrombembolism - multiple abscesses) • related disciplines: anatomy, histology, microbiology, clinical chemistry, hematology, laboratory medicine ...
... Introduction • how and why - development - pathogenesis (infectious endocarditis - thrombembolism - multiple abscesses) • related disciplines: anatomy, histology, microbiology, clinical chemistry, hematology, laboratory medicine ...
Anatomy 1 * The Anatomical Position
... Anatomists have agreed on a standardised position for the human body in all cases. It is known as the anatomical position. ...
... Anatomists have agreed on a standardised position for the human body in all cases. It is known as the anatomical position. ...
Allied Health I
... relationship of one body part to another. Physiology studies the function of each body part and how the functions of the various body parts coordinate to form a complete living organism. For our purposes in this unit it is the study of directions, positions, planes, sections, cavities, and abdominal ...
... relationship of one body part to another. Physiology studies the function of each body part and how the functions of the various body parts coordinate to form a complete living organism. For our purposes in this unit it is the study of directions, positions, planes, sections, cavities, and abdominal ...
Language of Anatomy
... Used when talking about the arms and legs Closest part of the arm or leg to the attachment point on the body The elbow is proximal to the wrist (it is closer to the attachment point of the arm to the body) ...
... Used when talking about the arms and legs Closest part of the arm or leg to the attachment point on the body The elbow is proximal to the wrist (it is closer to the attachment point of the arm to the body) ...
Cytoplasm The gel-like substance that surrounds the nucleus of a
... A pathological state, usually febrile, resulting from the presence of micro-organisms or their products in the bloodstream Supportive Producing or associated with generation of pus Endoscopy A visual examination of a cavity or canal using a specialized lighted instrument called an endoscope Le ...
... A pathological state, usually febrile, resulting from the presence of micro-organisms or their products in the bloodstream Supportive Producing or associated with generation of pus Endoscopy A visual examination of a cavity or canal using a specialized lighted instrument called an endoscope Le ...
NUR101ModA
... hypochondriac region, and the epigastric region lie above an imaginary line across the abdomen at the level of the ninth rib cartilages Middle regions: right and left lumbar region, and the umbilical region lie below an imaginary line across the abdomen at the level of the top of the hip bones. Lowe ...
... hypochondriac region, and the epigastric region lie above an imaginary line across the abdomen at the level of the ninth rib cartilages Middle regions: right and left lumbar region, and the umbilical region lie below an imaginary line across the abdomen at the level of the top of the hip bones. Lowe ...
medical terminology and abbreviations
... Is a flexible connective tissue found in many parts of the body. It can bend a bit, but resists stretching. It main function is to connect bones together ...
... Is a flexible connective tissue found in many parts of the body. It can bend a bit, but resists stretching. It main function is to connect bones together ...
Key Terms - Fall River Public Schools
... Being or located near, on, or toward the back or posterior part of the human body The distinguishing character or personality of an individual Situated below and closer to the feet than another and especially another similar part of an upright body especially of a human being Of or relating to the s ...
... Being or located near, on, or toward the back or posterior part of the human body The distinguishing character or personality of an individual Situated below and closer to the feet than another and especially another similar part of an upright body especially of a human being Of or relating to the s ...
Introduction to Forensic Science
... Provides services to county and municipal agencies Financed by local government Individual police departments ...
... Provides services to county and municipal agencies Financed by local government Individual police departments ...
Anatomical Terminology
... is often used to describe the relationship between structures, often with reference to the body. e.g. The lungs are found anterior to the heart. Ventral is often considered the same as Anterior Posterior: refers to the back of the body is often used to describe the relationship between str ...
... is often used to describe the relationship between structures, often with reference to the body. e.g. The lungs are found anterior to the heart. Ventral is often considered the same as Anterior Posterior: refers to the back of the body is often used to describe the relationship between str ...
Acting Internship Description
... clinical reasoning in this decision. In addition, describe possible adverse outcomes (e.g., potential miscarriage of justice, risk to public health, incorrect determination of cause and manner of death) when the decision of whether or not to perform an autopsy is made incorrectly. 10. Based upon med ...
... clinical reasoning in this decision. In addition, describe possible adverse outcomes (e.g., potential miscarriage of justice, risk to public health, incorrect determination of cause and manner of death) when the decision of whether or not to perform an autopsy is made incorrectly. 10. Based upon med ...
Page 61
... Body Symmetry: bilateral with head end & tail end, left and right side Body Plan: long, narrow without legs – flat and soft as jelly Tissue/ organs/ organ systems: Respiratory & circulatory: not needed – body thin Nervous: interprets info and directs animals response Brain: knot of nerve tissue in h ...
... Body Symmetry: bilateral with head end & tail end, left and right side Body Plan: long, narrow without legs – flat and soft as jelly Tissue/ organs/ organ systems: Respiratory & circulatory: not needed – body thin Nervous: interprets info and directs animals response Brain: knot of nerve tissue in h ...
Forensic Science - alistawatkins
... Pictures of markings are put into the IBIS system and matched with other bullets from the same gun ...
... Pictures of markings are put into the IBIS system and matched with other bullets from the same gun ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide Answers Section 1: Identify the area or
... 1. This type of anatomy traces structural changes throughout life. ___developmental_______ anatomy 2. A __tissue_____ is a group of similar cells that have a common function. 3. In a homeostatic feedback mechanism when the response enhances the initial stimulus, the mechanism is called a __positive_ ...
... 1. This type of anatomy traces structural changes throughout life. ___developmental_______ anatomy 2. A __tissue_____ is a group of similar cells that have a common function. 3. In a homeostatic feedback mechanism when the response enhances the initial stimulus, the mechanism is called a __positive_ ...
Internal – inside the body
... b. VENTRAL CAVITY – located on the anterior/ ventral surface of the body which contains the chest and abdomen. i. Thoracic Cavity – the portion of ventral cavity superior to the diaphragm 1. Pleural cavities – spaces surrounding each lung 2. Mediastinum – a broad middle tissue mass of the thoracic c ...
... b. VENTRAL CAVITY – located on the anterior/ ventral surface of the body which contains the chest and abdomen. i. Thoracic Cavity – the portion of ventral cavity superior to the diaphragm 1. Pleural cavities – spaces surrounding each lung 2. Mediastinum – a broad middle tissue mass of the thoracic c ...
Medical Terminology
... Structure of the Body Cell – fundamental unit of all living things Different types of cells include muscle cells, epithelial cells (skin), nerve cells, fat cells. Cells are specialized throughout the body to carry out their individual functions ...
... Structure of the Body Cell – fundamental unit of all living things Different types of cells include muscle cells, epithelial cells (skin), nerve cells, fat cells. Cells are specialized throughout the body to carry out their individual functions ...
Chapter 1 Jeopardy A and P
... This is the layer of the serous membrane that touches the inside of the abdominal wall ...
... This is the layer of the serous membrane that touches the inside of the abdominal wall ...
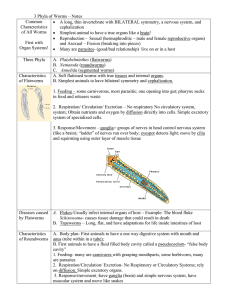
3 Phyla of Worms – Notes - Effingham County Schools
... system; Obtain nutrients and oxygen by diffusion directly into cells. Simple excretory system of specialized cells. 3. Response/Movement – ganglia= groups of nerves in head control nervous system (like a brain); “ladder” of nerves run over body; eyespot detects light; move by cilia and squirming usi ...
... system; Obtain nutrients and oxygen by diffusion directly into cells. Simple excretory system of specialized cells. 3. Response/Movement – ganglia= groups of nerves in head control nervous system (like a brain); “ladder” of nerves run over body; eyespot detects light; move by cilia and squirming usi ...
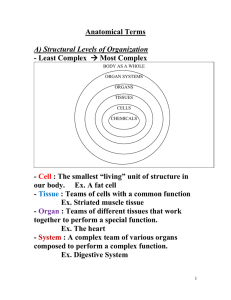
Anatomical Terms - Winston Knoll Collegiate
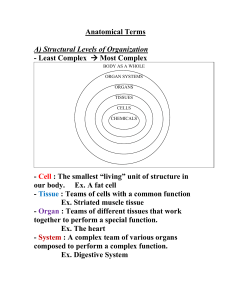
... our body. Ex. A fat cell - Tissue : Teams of cells with a common function Ex. Striated muscle tissue - Organ : Teams of different tissues that work together to perform a special function. Ex. The heart - System : A complex team of various organs composed to perform a complex function. Ex. Digestive ...
... our body. Ex. A fat cell - Tissue : Teams of cells with a common function Ex. Striated muscle tissue - Organ : Teams of different tissues that work together to perform a special function. Ex. The heart - System : A complex team of various organs composed to perform a complex function. Ex. Digestive ...
Anatomical Terms - Mr. Lesiuk
... our body. Ex. A fat cell - Tissue : Teams of cells with a common function Ex. Striated muscle tissue - Organ : Teams of different tissues that work together to perform a special function. Ex. The heart - System : A complex team of various organs composed to perform a complex function. Ex. Digestive ...
... our body. Ex. A fat cell - Tissue : Teams of cells with a common function Ex. Striated muscle tissue - Organ : Teams of different tissues that work together to perform a special function. Ex. The heart - System : A complex team of various organs composed to perform a complex function. Ex. Digestive ...
Is Autopsy Useful? - Société Française de Médecine Légale
... In agreement with previous studies (3,4), the new information provided by the autopsy could have influenced treatment decisions in some cases. In Cases 12 (unrecognized intraperitoneal abscess), 13 (unrecognized intraperitoneal hematoma), and 14 (unrecognized necrosis of the small bowel), early surg ...
... In agreement with previous studies (3,4), the new information provided by the autopsy could have influenced treatment decisions in some cases. In Cases 12 (unrecognized intraperitoneal abscess), 13 (unrecognized intraperitoneal hematoma), and 14 (unrecognized necrosis of the small bowel), early surg ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology I
... Directional Terms: Superior (cephalic or cranial) – toward the head, upper, or above. Inferior (caudal) – toward the feet, under or below ...
... Directional Terms: Superior (cephalic or cranial) – toward the head, upper, or above. Inferior (caudal) – toward the feet, under or below ...
Anatomical Planes of Dissections File
... Medical professionals often refer to sections of the body in terms of anatomical planes (flat surfaces). These planes are imaginary lines – vertical or horizontal – drawn through an upright body. The terms are used to describe a specific body part. Coronal – front and back Sagittal – left and right ...
... Medical professionals often refer to sections of the body in terms of anatomical planes (flat surfaces). These planes are imaginary lines – vertical or horizontal – drawn through an upright body. The terms are used to describe a specific body part. Coronal – front and back Sagittal – left and right ...
Autopsy

An autopsy—also known as a post-mortem examination, necropsy, autopsia cadaverum, or obduction—is a highly specialized surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse to determine the cause and manner of death and to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present. It is usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist.The word “autopsy” means to study and directly observe the body (Adkins and Barnes, 317). This includes an external examination of the deceased and the removal and dissection of the brain, kidneys, lungs and heart. When a coroner receives a body, he or she must first review the circumstances of the death and all evidence, then decide what type of autopsy should be performed if any. If an autopsy is recommended, the coroner can choose between an external autopsy (the deceased is examined, fingerprinted, and photographed but not opened; blood and fluid samples are taken), an external and partial internal autopsy (the deceased is opened but only affected organs are removed and examined), or a full external and internal autopsy.Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. For example, a forensic autopsy is carried out when the cause of death may be a criminal matter, while a clinical or academic autopsy is performed to find the medical cause of death and is used in cases of unknown or uncertain death, or for research purposes. Autopsies can be further classified into cases where external examination suffices, and those where the body is dissected and internal examination is conducted. Permission from next of kin may be required for internal autopsy in some cases. Once an internal autopsy is complete the body is reconstituted by sewing it back together.