Major Parts of the Brain:
... depressions called? _________________ deep grooves called? _____________________ ...
... depressions called? _________________ deep grooves called? _____________________ ...
chapter 3 study guide
... Neurons: Identify and locate the fundamental components and functions that form the biological bases of communication and behavior within the nervous system, including: ...
... Neurons: Identify and locate the fundamental components and functions that form the biological bases of communication and behavior within the nervous system, including: ...
CORTEX I. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS a. Cerebral cortex = grey
... 2. Function = gustatory, auton; ?consequences of actions (risky decision)? iv. Everything grows around insula (fixed) hemispheres become C-shaped ...
... 2. Function = gustatory, auton; ?consequences of actions (risky decision)? iv. Everything grows around insula (fixed) hemispheres become C-shaped ...
Ocular Dominance Columns
... Neuronal survival is mediated by competition for targetderived trophic factors. Similarly, cortical organization is mediated by activitydependent competition early in life (i.e. during the critical period). This activity-dependent competition appears to be mediated by trophic factors. ...
... Neuronal survival is mediated by competition for targetderived trophic factors. Similarly, cortical organization is mediated by activitydependent competition early in life (i.e. during the critical period). This activity-dependent competition appears to be mediated by trophic factors. ...
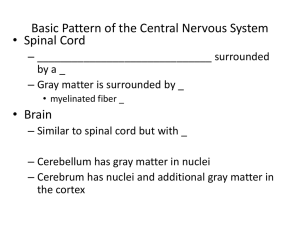
Basic Pattern of the Central Nervous System
... • Deep sulci divide the hemispheres into five lobes: ...
... • Deep sulci divide the hemispheres into five lobes: ...
Cortical and subcortical anatomy: basics and applied
... accumbens) and temporal lobes). to the pontine nuclei. Corticospinal and Corticobulbar fibres from frontal and anterior parietal cortex. ...
... accumbens) and temporal lobes). to the pontine nuclei. Corticospinal and Corticobulbar fibres from frontal and anterior parietal cortex. ...
A.P. Psychology 3-B (C)
... Located at front of parietal lobes Registers and processes body touch and movement sensations (Input) ...
... Located at front of parietal lobes Registers and processes body touch and movement sensations (Input) ...
Cerebral Cortex
... Located at front of parietal lobes Registers and processes body touch and movement sensations (Input) ...
... Located at front of parietal lobes Registers and processes body touch and movement sensations (Input) ...
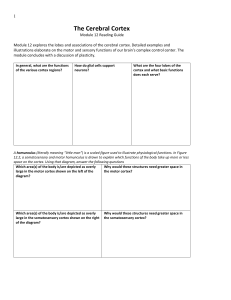
The Cerebral Cortex
... module concludes with a discussion of plasticity. In general, what are the functions of the various cortex regions? ...
... module concludes with a discussion of plasticity. In general, what are the functions of the various cortex regions? ...
Chapter 2 Notes
... Hemispheric specialization: Some cortical functions are localized to a particular hemisphere of the brain ...
... Hemispheric specialization: Some cortical functions are localized to a particular hemisphere of the brain ...
04 Physiology of large hemispheres, cerebellum
... The 3 deep nuclei are: – (1) fastigial - concerned with balance; sends information mainly to the vestibular and reticular nuclei – (2) dentate and (3) interposed - both concerned with voluntary movement; send axons mainly to the thalamus and red nucleus All 3 receive inputs from sensory afferent tra ...
... The 3 deep nuclei are: – (1) fastigial - concerned with balance; sends information mainly to the vestibular and reticular nuclei – (2) dentate and (3) interposed - both concerned with voluntary movement; send axons mainly to the thalamus and red nucleus All 3 receive inputs from sensory afferent tra ...
Brain Anatomy PPT
... Each consist of cerebral cortex overlying white matter and basal nuclei (regions of gray matter inside brain) – centers for planning and learning movement sequences Left cerebral hemisphere Corpus callosum ...
... Each consist of cerebral cortex overlying white matter and basal nuclei (regions of gray matter inside brain) – centers for planning and learning movement sequences Left cerebral hemisphere Corpus callosum ...
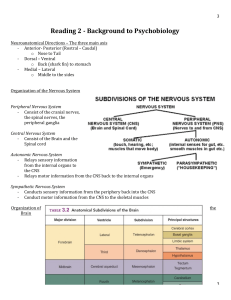
Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... - Corpus Callosum – Principal commissure connecting the left and right hemisphere together - Gyrus (plural) – The bumps created by two sulci - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matte ...
... - Corpus Callosum – Principal commissure connecting the left and right hemisphere together - Gyrus (plural) – The bumps created by two sulci - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matte ...
Central Nervous System Part 2
... primary somatic motor cortex: axons from the primary motor area in the frontal lobe form major voluntary motor tract which descends into the cord, paths are crossed and body is represented upside down. Most neurons are dedicated to fine motor control of face, moth and hands. premotor cortex primary ...
... primary somatic motor cortex: axons from the primary motor area in the frontal lobe form major voluntary motor tract which descends into the cord, paths are crossed and body is represented upside down. Most neurons are dedicated to fine motor control of face, moth and hands. premotor cortex primary ...
Nervous system slides
... ¾Function: site of prominent neural processing & integrating centers ¾Made up of: the epithalamus, hypothalamus, & thalamus ¾ Thalamus: directs neural input from the body to specific areas of the cerebral cortex (the outer, gray area) ¾Hypothalamus: produces hormones : regulates - survival mechanis ...
... ¾Function: site of prominent neural processing & integrating centers ¾Made up of: the epithalamus, hypothalamus, & thalamus ¾ Thalamus: directs neural input from the body to specific areas of the cerebral cortex (the outer, gray area) ¾Hypothalamus: produces hormones : regulates - survival mechanis ...
L6. Thalamus (László Acsády) All cortical areas receive thalamic
... All cortical areas receive thalamic inputs and no cortical area is functional without intact thalamocortical connections. The thalamus has multiple functions. It may be thought of as a kind of hub of information. The thalamus is generally believed to act as a relay between different subcortical area ...
... All cortical areas receive thalamic inputs and no cortical area is functional without intact thalamocortical connections. The thalamus has multiple functions. It may be thought of as a kind of hub of information. The thalamus is generally believed to act as a relay between different subcortical area ...
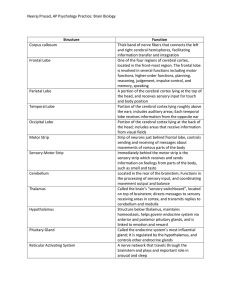
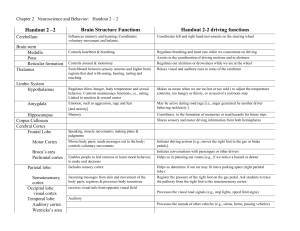
Handout 2 –2 Brain Structure Functions Handout 2-2 driving
... Frontal Lobe Motor Cortex Broca’s area Prefrontal cortex ...
... Frontal Lobe Motor Cortex Broca’s area Prefrontal cortex ...
Neuroscience 14b – Organisation of the Cerebral Cortex
... cord and corpus striatum. 6. Fusiform layer VI, which contains few large pyramidal neurons and many small spindle-like pyramidal and fusiform neurones; it sends efferent fibers to the thalamus, establishing a very precise reciprocal interconnection between the cortex and the thalamus. All the layers ...
... cord and corpus striatum. 6. Fusiform layer VI, which contains few large pyramidal neurons and many small spindle-like pyramidal and fusiform neurones; it sends efferent fibers to the thalamus, establishing a very precise reciprocal interconnection between the cortex and the thalamus. All the layers ...
Slide ()
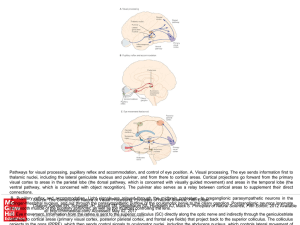
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
Unit 01 Biology and the Brain_Part 2
... Hippocampus • Involved in the processing and storage of memories. ...
... Hippocampus • Involved in the processing and storage of memories. ...
The Cerebral Cortex and Its Functions
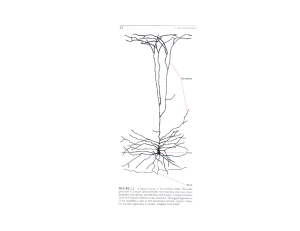
... The human brain hemispheres are covered in its greater part by an external layer of gray color called cerebral cortex. A deep cut into the brain would show that this gray surface has a thickness varying from 1 to 4 mm. Its largest part is composed by nerve cells (neurons) which receive impulses from ...
... The human brain hemispheres are covered in its greater part by an external layer of gray color called cerebral cortex. A deep cut into the brain would show that this gray surface has a thickness varying from 1 to 4 mm. Its largest part is composed by nerve cells (neurons) which receive impulses from ...
Module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
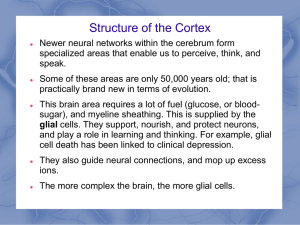
... glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and thinking. For example, glial cell death has been linked to clinical depression. They also guide neural connections, and mop up excess ions. The more complex the brain, the more glial cells. ...
... glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and thinking. For example, glial cell death has been linked to clinical depression. They also guide neural connections, and mop up excess ions. The more complex the brain, the more glial cells. ...
Cerebral cortex

The cerebral cortex is the cerebrum's (brain) outer layer of neural tissue in humans and other mammals. It is divided into two cortices, along the sagittal plane: the left and right cerebral hemispheres divided by the medial longitudinal fissure. The cerebral cortex plays a key role in memory, attention, perception, awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. The human cerebral cortex is 2 to 4 millimetres (0.079 to 0.157 in) thick.In large mammals, the cerebral cortex is folded, giving a much greater surface area in the confined volume of the skull. A fold or ridge in the cortex is termed a gyrus (plural gyri) and a groove or fissure is termed a sulcus (plural sulci). In the human brain more than two-thirds of the cerebral cortex is buried in the sulci.The cerebral cortex is gray matter, consisting mainly of cell bodies (with astrocytes being the most abundant cell type in the cortex as well as the human brain as a whole) and capillaries. It contrasts with the underlying white matter, consisting mainly of the white myelinated sheaths of neuronal axons. The phylogenetically most recent part of the cerebral cortex, the neocortex (also called isocortex), is differentiated into six horizontal layers; the more ancient part of the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, has at most three cellular layers. Neurons in various layers connect vertically to form small microcircuits, called cortical columns. Different neocortical regions known as Brodmann areas are distinguished by variations in their cytoarchitectonics (histological structure) and functional roles in sensation, cognition and behavior.