Outline12 CNS - Napa Valley College
... a. Cerebral gray matter and white matter gray matter cerebral cortex basal ganglia and nuclei of the limbic system white matter association fibers – connect areas within the same cerebral hemisphere commissural fibers (corpus callosum) – connect R and L cerebral hemispheres projection fibers – conne ...
... a. Cerebral gray matter and white matter gray matter cerebral cortex basal ganglia and nuclei of the limbic system white matter association fibers – connect areas within the same cerebral hemisphere commissural fibers (corpus callosum) – connect R and L cerebral hemispheres projection fibers – conne ...
Chapter 15 - Austin Community College
... • The BBB is absent in some places of the 3rd and 4th ventricles at patches called circumventricular organs where some substances may pass into the brain tissue. ...
... • The BBB is absent in some places of the 3rd and 4th ventricles at patches called circumventricular organs where some substances may pass into the brain tissue. ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... neural fibers (myelinated axons, or white matter) connecting the two hemispheres ...
... neural fibers (myelinated axons, or white matter) connecting the two hemispheres ...
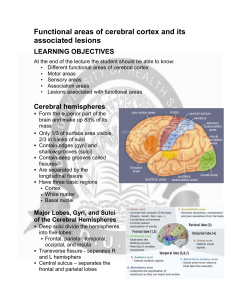
Functional areas of cerebral cortex and its associated lesions
... Area 43 (inferior end of postcentral gyrus) Olfactory Area ...
... Area 43 (inferior end of postcentral gyrus) Olfactory Area ...
PSY 437 Sensation and Perception Knapp Study Guide 11 Primary
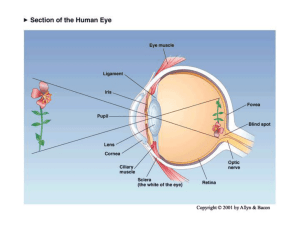
... Today we’ll trace the pathway from the retina to the primary visual cortex. We’ll also see how primary visual cortex is organized and some things it can do.. 1. What sources does each LGN receive information from and why would it be important to receive information from these sources? 2. What type o ...
... Today we’ll trace the pathway from the retina to the primary visual cortex. We’ll also see how primary visual cortex is organized and some things it can do.. 1. What sources does each LGN receive information from and why would it be important to receive information from these sources? 2. What type o ...
Chapter 2 STUDY GUIDE
... *The spinal cord is a column of nerves that transmit information between the brain and the peripheral nervous system. *A spinal reflex is controlled at the level of the spinal cord that may involve as few as one or two neurons; Spinal reflexes are UNLEARNED! *The thalamus is a relay station that pla ...
... *The spinal cord is a column of nerves that transmit information between the brain and the peripheral nervous system. *A spinal reflex is controlled at the level of the spinal cord that may involve as few as one or two neurons; Spinal reflexes are UNLEARNED! *The thalamus is a relay station that pla ...
Blue= rods Green = Cones
... – the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and then the primary visual cortex (V1, area 17): more to come… ...
... – the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and then the primary visual cortex (V1, area 17): more to come… ...
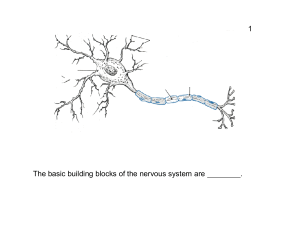
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
Structure of the Brain
... - CAT or Computerized Axial Tomography (x-rays are passed through the head - rCBF or Regional Cerebral Bloodflow (uses radioactive isotopes injected into the blood. When a region of the brain is activated, more blood is sent to the area and the isotopes track this blood. The isotopes are measure by ...
... - CAT or Computerized Axial Tomography (x-rays are passed through the head - rCBF or Regional Cerebral Bloodflow (uses radioactive isotopes injected into the blood. When a region of the brain is activated, more blood is sent to the area and the isotopes track this blood. The isotopes are measure by ...
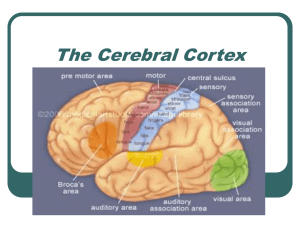
The Cerebral Cortex
... Fingers & mouth occupy the greatest amount of motor cortical space b/c they require precise control (Foerster & Penfield) 2004, USDA approved 1st clinical trial of neural prosthetics with paralyzed humans ...
... Fingers & mouth occupy the greatest amount of motor cortical space b/c they require precise control (Foerster & Penfield) 2004, USDA approved 1st clinical trial of neural prosthetics with paralyzed humans ...
Rexed`s Lamina
... second order neuron occurs in spinal cord Third order neurons arise in thalamus and continue to cerebral cortex ...
... second order neuron occurs in spinal cord Third order neurons arise in thalamus and continue to cerebral cortex ...
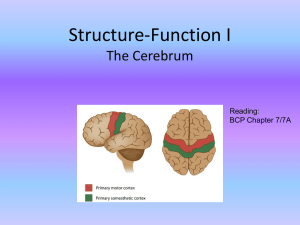
Structure-Function I
... layers differ in thickness, cell density and type pyramidal cells (output neurons; excitatory) vs stellate cells (local circuit; both excitatory and inhibitory) vertical axons and dendrites give rise to columnar organization layer thickness differs from brain area to area ...
... layers differ in thickness, cell density and type pyramidal cells (output neurons; excitatory) vs stellate cells (local circuit; both excitatory and inhibitory) vertical axons and dendrites give rise to columnar organization layer thickness differs from brain area to area ...
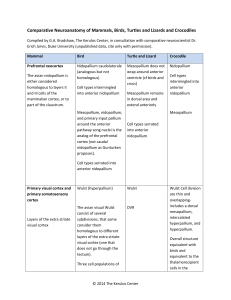
Comparative Neuroanatomy of Mammals, Birds, Turtles and Lizards
... cortex of mammals; The DVR (dorsal ventricular ridge ; primary sensory regions ( L2, Entopallium, and Basorostralis) mixed with nidopallium (cf Birds) contains a population of cells equivalent to the thalamorecipient cells in the somatosensory cortex; the core nucleus of the dorsal ventricular ridge ...
... cortex of mammals; The DVR (dorsal ventricular ridge ; primary sensory regions ( L2, Entopallium, and Basorostralis) mixed with nidopallium (cf Birds) contains a population of cells equivalent to the thalamorecipient cells in the somatosensory cortex; the core nucleus of the dorsal ventricular ridge ...
fahime_sheikhzadeh
... NEOCORTEX: Laminar Cortical Circuits for Vision and Cognition”, Stephen Grossberg, Boston University. Invited article to appear in: Book Title: “Computational Neuroscience: From Neurons to Theory and Back Again”, Editors: Paul Cisek, Trevor Drew, and John ...
... NEOCORTEX: Laminar Cortical Circuits for Vision and Cognition”, Stephen Grossberg, Boston University. Invited article to appear in: Book Title: “Computational Neuroscience: From Neurons to Theory and Back Again”, Editors: Paul Cisek, Trevor Drew, and John ...
Slide ()
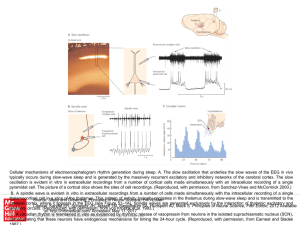
... oscillation is evident in vitro in extracellular recordings from a number of cortical cells made simultaneously with an intracellular recording of a single pyramidal cell. The picture of a cortical slice shows the sites of cell recordings. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanchez-Vives and McCormi ...
... oscillation is evident in vitro in extracellular recordings from a number of cortical cells made simultaneously with an intracellular recording of a single pyramidal cell. The picture of a cortical slice shows the sites of cell recordings. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanchez-Vives and McCormi ...
Brumberg - QC Queens College
... The function of an electronic device such as a transistor radio can be explained based on its identifiable circuit elements; resistors, capacitors and transistors. Similarly, understanding the individual elements of a cortical circuit and how they interact brings us a step closer to understanding th ...
... The function of an electronic device such as a transistor radio can be explained based on its identifiable circuit elements; resistors, capacitors and transistors. Similarly, understanding the individual elements of a cortical circuit and how they interact brings us a step closer to understanding th ...
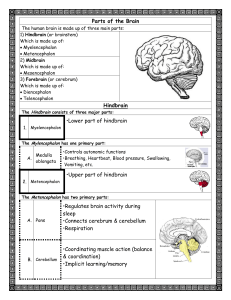
Parts of the Brain Hindbrain •Lower part of hindbrain •Upper part of
... •Wrinkled outer layer of the brain •Controls mostly sense & motor functions •Wrinkled - increase surface of the brain (15 square feet) •Gyri: ridges •Sulci: valleys •2mm to 4mm thick •20-23 billion neurons •2/3 of body’s neurons in cerebral cortex ...
... •Wrinkled outer layer of the brain •Controls mostly sense & motor functions •Wrinkled - increase surface of the brain (15 square feet) •Gyri: ridges •Sulci: valleys •2mm to 4mm thick •20-23 billion neurons •2/3 of body’s neurons in cerebral cortex ...
the cerebral cortex
... My investigations showed that the functional superiority of the human brain is intimately bound up with the prodigious abundance and unusual wealth of forms of the so-called neurons with the short axons. S. R. y Cajal: Recuerdos de mi vida. 1917. ...
... My investigations showed that the functional superiority of the human brain is intimately bound up with the prodigious abundance and unusual wealth of forms of the so-called neurons with the short axons. S. R. y Cajal: Recuerdos de mi vida. 1917. ...
Neural coding in the primary olfactory cortex
... The primary olfactory (piriform) cortex is a phylogenetically-ancient three-layered structure that is the first cortical destination of olfactory information. The comparatively simple architecture of the piriform cortex (PC) suggests that it may be a valuable model system for the study of cortical s ...
... The primary olfactory (piriform) cortex is a phylogenetically-ancient three-layered structure that is the first cortical destination of olfactory information. The comparatively simple architecture of the piriform cortex (PC) suggests that it may be a valuable model system for the study of cortical s ...
11-5_TheMulti-CenterAspectOfMotorControl. _NagyD
... controlling these voluntary movements is the motor cortex. The motor cortex is located in the rear portion of the frontal lobe, just before the central sulcus (furrow) that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe. The motor cortex is divided into two main areas, Area 4 and Area 6. Area 4, ...
... controlling these voluntary movements is the motor cortex. The motor cortex is located in the rear portion of the frontal lobe, just before the central sulcus (furrow) that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe. The motor cortex is divided into two main areas, Area 4 and Area 6. Area 4, ...
Cerebral cortex and thalamus lecture
... association cortex – so important for sensation - Integration of auditory, visual and somatic sensory information ...
... association cortex – so important for sensation - Integration of auditory, visual and somatic sensory information ...
THE CEREBRAL CORTEX
... My investigations showed that the functional superiority of the human brain is intimately bound up with the prodigious abundance and unusual wealth of forms of the so-called neurons with the short axons. S. R. y Cajal: Recuerdos de mi vida. 1917. ...
... My investigations showed that the functional superiority of the human brain is intimately bound up with the prodigious abundance and unusual wealth of forms of the so-called neurons with the short axons. S. R. y Cajal: Recuerdos de mi vida. 1917. ...
Lecture 5 - Brain I - Linn
... Composed of distinctive cell groups: e.g. Caudate & lentiform Play a role in motor control, may be involved with attention and cognition. Disorders of the basal nuclei show up as too much or too little movement such as Huntington’s or Parkinson’s diseases. ...
... Composed of distinctive cell groups: e.g. Caudate & lentiform Play a role in motor control, may be involved with attention and cognition. Disorders of the basal nuclei show up as too much or too little movement such as Huntington’s or Parkinson’s diseases. ...
Cerebral cortex

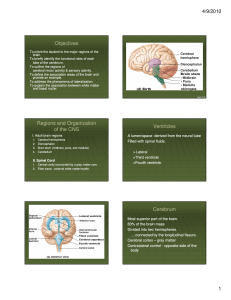
The cerebral cortex is the cerebrum's (brain) outer layer of neural tissue in humans and other mammals. It is divided into two cortices, along the sagittal plane: the left and right cerebral hemispheres divided by the medial longitudinal fissure. The cerebral cortex plays a key role in memory, attention, perception, awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. The human cerebral cortex is 2 to 4 millimetres (0.079 to 0.157 in) thick.In large mammals, the cerebral cortex is folded, giving a much greater surface area in the confined volume of the skull. A fold or ridge in the cortex is termed a gyrus (plural gyri) and a groove or fissure is termed a sulcus (plural sulci). In the human brain more than two-thirds of the cerebral cortex is buried in the sulci.The cerebral cortex is gray matter, consisting mainly of cell bodies (with astrocytes being the most abundant cell type in the cortex as well as the human brain as a whole) and capillaries. It contrasts with the underlying white matter, consisting mainly of the white myelinated sheaths of neuronal axons. The phylogenetically most recent part of the cerebral cortex, the neocortex (also called isocortex), is differentiated into six horizontal layers; the more ancient part of the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, has at most three cellular layers. Neurons in various layers connect vertically to form small microcircuits, called cortical columns. Different neocortical regions known as Brodmann areas are distinguished by variations in their cytoarchitectonics (histological structure) and functional roles in sensation, cognition and behavior.