Atoms and Molecules
... • Matter is made of atoms • Atoms are made of protons, neutrons and electrons • Elements are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom ...
... • Matter is made of atoms • Atoms are made of protons, neutrons and electrons • Elements are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom ...
Chapter 2 Lect. 1
... 1. Becquerel (1896) discovered that uranium produced an image on photographic film in the absence of light 2. This spontaneous emission of radiation was called radioactivity 3. Three types of radioactive emission were eventually discovered a. Gamma rays (g) = high energy light wave b. Beta particles ...
... 1. Becquerel (1896) discovered that uranium produced an image on photographic film in the absence of light 2. This spontaneous emission of radiation was called radioactivity 3. Three types of radioactive emission were eventually discovered a. Gamma rays (g) = high energy light wave b. Beta particles ...
Periodic_Table
... - comes from idea of “Earth”, materials unable to light on fire - reactive metallic elements with two electrons in the outermost energy level - harder, denser, stronger and have higher melting points, lower reactivity than alkali ex. Be, Ca, Mg ...
... - comes from idea of “Earth”, materials unable to light on fire - reactive metallic elements with two electrons in the outermost energy level - harder, denser, stronger and have higher melting points, lower reactivity than alkali ex. Be, Ca, Mg ...
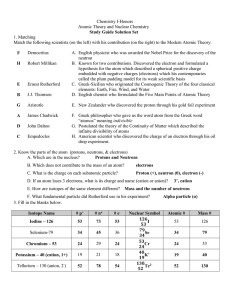
Study Guide - Honors Chemistry
... one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may ...
... one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei by force (an alpha particle is used to break it up) one nucleus is broken into multiple (2 in this case) nuclei on its own. No force is needed. one nucleus is transformed into another nucleus by bombarding a particle into it. A particle may ...
Ch. 5 Outline Notes
... a. Hypothesized _________________ using experiments B. __________________ Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made of ________________ 2. Atoms are _______________________ and cannot be __________________ into smaller particles (later proved _______________) 3. All atoms of one element are exactly ______ ...
... a. Hypothesized _________________ using experiments B. __________________ Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made of ________________ 2. Atoms are _______________________ and cannot be __________________ into smaller particles (later proved _______________) 3. All atoms of one element are exactly ______ ...
Organizing the Elements (Use pages 500
... atomic mass for most elements listed as a whole number and a decimal fraction? symbol, atomic mass, atomic number, name, average of all the different masses of different weight atoms (isotopes) for a given element 9. What are columns and rows called in the periodic table? Groups are also named what? ...
... atomic mass for most elements listed as a whole number and a decimal fraction? symbol, atomic mass, atomic number, name, average of all the different masses of different weight atoms (isotopes) for a given element 9. What are columns and rows called in the periodic table? Groups are also named what? ...
Scientists timeline
... modern discovery process about atoms • Transformed Democritus’s theories on atoms into an actual scientific theory ...
... modern discovery process about atoms • Transformed Democritus’s theories on atoms into an actual scientific theory ...
I. Historical Atomic Models - Hobbs Freshman High School
... 1. 1st energy level (K) can hold up to 2 e-. 2. 2nd energy level (L) can hold up to 8 e-. 3. 3rd energy level (M) can hold up to 18 e- IF it is NOT the outermost energy level. 4. 4th energy level (N) can hold up to 32 e- IF it is NOT the outermost energy level. C. The # of energy levels of an atom d ...
... 1. 1st energy level (K) can hold up to 2 e-. 2. 2nd energy level (L) can hold up to 8 e-. 3. 3rd energy level (M) can hold up to 18 e- IF it is NOT the outermost energy level. 4. 4th energy level (N) can hold up to 32 e- IF it is NOT the outermost energy level. C. The # of energy levels of an atom d ...
Elements - Heartland
... Only 1 in 8000 alpha particles is scattered. Scattering occurs when an alpha particle encounters a gold nuclei. A nucleus is very small and contains both the protons and the neutrons. Thus, it contains almost all of the mass of an atom. This very dense center is surrounded by the electron cloud, whi ...
... Only 1 in 8000 alpha particles is scattered. Scattering occurs when an alpha particle encounters a gold nuclei. A nucleus is very small and contains both the protons and the neutrons. Thus, it contains almost all of the mass of an atom. This very dense center is surrounded by the electron cloud, whi ...
Chapter 9: The Atom
... Chapter 9.2 Objectives and Vocabulary Use the periodic table to obtain information about the elements. Explain the relationship between an element's placement on the periodic table and its chemical properties. Understand a simple model of electron arrangement. ...
... Chapter 9.2 Objectives and Vocabulary Use the periodic table to obtain information about the elements. Explain the relationship between an element's placement on the periodic table and its chemical properties. Understand a simple model of electron arrangement. ...
IE 1
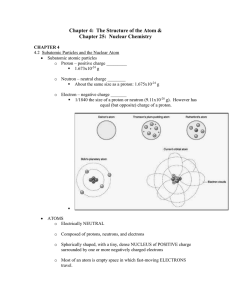
... 1.2 Fundamental particles of an atom An atom is the smallest unit quantity of an element that is capable of existence, either alone or in chemical combination with other atoms of the same or another element. The fundamental particles of which atoms are composed are the proton , electron and neutron ...
... 1.2 Fundamental particles of an atom An atom is the smallest unit quantity of an element that is capable of existence, either alone or in chemical combination with other atoms of the same or another element. The fundamental particles of which atoms are composed are the proton , electron and neutron ...
CHAPTER 18 NOTES
... • atoms of the same element with different #s of neutrons example – hydrogen has 3 isotopes 0, 1, or 2 • 2 ways to show difference between isotopes: 1. name of element followed by mass # 2. write the symbol with the mass # and atomic # ...
... • atoms of the same element with different #s of neutrons example – hydrogen has 3 isotopes 0, 1, or 2 • 2 ways to show difference between isotopes: 1. name of element followed by mass # 2. write the symbol with the mass # and atomic # ...
We know now that it is composed of protons and neutrons.
... But other models were made after Rutherford´s model to explain better the properties of atoms. ...
... But other models were made after Rutherford´s model to explain better the properties of atoms. ...
MID-TERM EXAM REVIEW! Unit 1 Convert the following: 1.) 2.02 x
... 39.) Effective nuclear charge 40.) Shielding effect ...
... 39.) Effective nuclear charge 40.) Shielding effect ...
levels of organization and the atom
... Build a table that describes the parts of an atom, and that includes the: name, electrical charge, mass, place found, and function, of each sub-atomic particle. ...
... Build a table that describes the parts of an atom, and that includes the: name, electrical charge, mass, place found, and function, of each sub-atomic particle. ...
Chapter 4 and 5 Powerpoint - School District of La Crosse
... • A.ALKALI METALS (Group 1) • 1 soft high reactive metals. • 2.When mixed with water they form a slippery solution ...
... • A.ALKALI METALS (Group 1) • 1 soft high reactive metals. • 2.When mixed with water they form a slippery solution ...
California Chemistry Standards Test
... 1. proteins, nucleic acids, and starch are made up of repetitive combinations 2. hydrocarbons and polymers 3. amino acids building blocks of matter Nuclear Processes-(2) 1. protons and neutrons in the nucleus (forces) 2. fusion and fission 3. isotopes of elements are radioactive 4. radioactive decay ...
... 1. proteins, nucleic acids, and starch are made up of repetitive combinations 2. hydrocarbons and polymers 3. amino acids building blocks of matter Nuclear Processes-(2) 1. protons and neutrons in the nucleus (forces) 2. fusion and fission 3. isotopes of elements are radioactive 4. radioactive decay ...
Name: Period
... a. Ionic Solids b. Metallic Solids c. Network Solids 7. How are ionic compounds and molecular compounds different? Ionic Compounds ...
... a. Ionic Solids b. Metallic Solids c. Network Solids 7. How are ionic compounds and molecular compounds different? Ionic Compounds ...
34.) Write out the set of four quantum numbers for the last electron
... 17.) Making salt from sodium and chlorine 18.) Sprinkling salt on french fries * In what group (give number) are each of the following elements found in the Periodic Table? 19.) alkali metals 20.) alkaline earth metals 21.) transition elements 22.) halogens 23.) noble gases Unit 3 * Tell scientist w ...
... 17.) Making salt from sodium and chlorine 18.) Sprinkling salt on french fries * In what group (give number) are each of the following elements found in the Periodic Table? 19.) alkali metals 20.) alkaline earth metals 21.) transition elements 22.) halogens 23.) noble gases Unit 3 * Tell scientist w ...
Lecture 1: Basic Concepts: Atoms and Bonding
... an electron than others. Each electron does, however, have a specific energy. Must solve wave equation for specific states! • The combination of the energy and probability gives rise to the current understanding for electron distributions, which are referred to as electron orbitals; these orbital ...
... an electron than others. Each electron does, however, have a specific energy. Must solve wave equation for specific states! • The combination of the energy and probability gives rise to the current understanding for electron distributions, which are referred to as electron orbitals; these orbital ...
The New Alchemy
... Protons – one of the parts of an atom. Protons have a (+) charge and are found in the nucleus. Neutrons – one of the parts of an atom. Neutrons have no charge and are found in the nucleus. Nucleus – found in the center of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Nuclei is the plural of nucleus. Nu ...
... Protons – one of the parts of an atom. Protons have a (+) charge and are found in the nucleus. Neutrons – one of the parts of an atom. Neutrons have no charge and are found in the nucleus. Nucleus – found in the center of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Nuclei is the plural of nucleus. Nu ...