1st Semester Review - Moore Public Schools
... 35. Practice writing at least 20 formulas given the name of compounds, and writing 20 names given the correct formulas. Have someone else make the formulas/ names for you to do. 36. Practice writing Lewis Structures, and identifying the electron domain geometry, molecular geometry, intermolecular fo ...
... 35. Practice writing at least 20 formulas given the name of compounds, and writing 20 names given the correct formulas. Have someone else make the formulas/ names for you to do. 36. Practice writing Lewis Structures, and identifying the electron domain geometry, molecular geometry, intermolecular fo ...
Chemistry 1 – Tollett Chapter 5 – Atomic Structure & The Periodic
... The atoms of any one element are different form those of any other element. ...
... The atoms of any one element are different form those of any other element. ...
Test 4
... electromagnetic radiation, emr, wavelength, frequency, photon, Bohr model, H atom emit light, principal energy levels, s, p, d, & f orbitals, probability map or density, Pauli Exclusion Principle, deBroglie matter wavelength, electron configuration, periodic properties, ionization energy, atomic siz ...
... electromagnetic radiation, emr, wavelength, frequency, photon, Bohr model, H atom emit light, principal energy levels, s, p, d, & f orbitals, probability map or density, Pauli Exclusion Principle, deBroglie matter wavelength, electron configuration, periodic properties, ionization energy, atomic siz ...
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
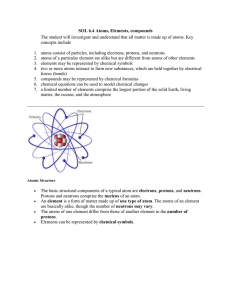
... The basic structural components of a typical atom are electrons, protons, and neutrons. Protons and neutrons comprise the nucleus of an atom. An element is a form of matter made up of one type of atom. The atoms of an element are basically alike, though the number of neutrons may vary. The atoms of ...
... The basic structural components of a typical atom are electrons, protons, and neutrons. Protons and neutrons comprise the nucleus of an atom. An element is a form of matter made up of one type of atom. The atoms of an element are basically alike, though the number of neutrons may vary. The atoms of ...
The History of Atomic Theory
... Described the atom as a small, incompressible sphere with an atmosphere of heat. ...
... Described the atom as a small, incompressible sphere with an atmosphere of heat. ...
The Atom
... 1) All elements are composed of atoms. 2) Atoms of one element are identical and different from those of any other element. 3) Atoms combine in whole number ratios to form compounds. 4) Chemical reactions rearrange atoms, but do not change them. ...
... 1) All elements are composed of atoms. 2) Atoms of one element are identical and different from those of any other element. 3) Atoms combine in whole number ratios to form compounds. 4) Chemical reactions rearrange atoms, but do not change them. ...
Ch 1.1 ppt
... • Certain chemical properties were repeated regularly. • These properties were related to the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom. ...
... • Certain chemical properties were repeated regularly. • These properties were related to the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom. ...
Note taker: ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE
... By _________, Bohr’s model of the atom no longer explained all observations. Bohr was correct about ______________________, but wrong about ___________________________. ...
... By _________, Bohr’s model of the atom no longer explained all observations. Bohr was correct about ______________________, but wrong about ___________________________. ...
Atomic Structure
... All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms II. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. III. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole number ...
... All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms II. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. III. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole number ...
Chemistry10AtomicTheory
... distinguished from one another by their respective relative weights. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form chemical compounds; a given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor des ...
... distinguished from one another by their respective relative weights. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form chemical compounds; a given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor des ...
- Chapter 7 - Periodic Properties of the Elements
... missing element underneath Si. He predicted a number of properties for this missing element (which he called eka-silicon or Germanium) with chemical properties similar to those of silicon. ...
... missing element underneath Si. He predicted a number of properties for this missing element (which he called eka-silicon or Germanium) with chemical properties similar to those of silicon. ...
COS 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3
... around a nucleus, marked by a constant distance from the nucleus • Closer to nucleus, lower energy level of electrons • Further from nucleus, more energy electrons have • Number of filled energy levels an atom has depends on number of electrons ...
... around a nucleus, marked by a constant distance from the nucleus • Closer to nucleus, lower energy level of electrons • Further from nucleus, more energy electrons have • Number of filled energy levels an atom has depends on number of electrons ...
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... SUBATOMIC PARTICLES OF AN ATOM? WHAT ARE THEIR CHARGES, LOCATIONS, AND MASS? ...
... SUBATOMIC PARTICLES OF AN ATOM? WHAT ARE THEIR CHARGES, LOCATIONS, AND MASS? ...
John Dalton William Crookes J.J. Thomson Ernest Rutherford
... together to form new substances and taking them apart chemists discovered that ALL matter is made of elements) ...
... together to form new substances and taking them apart chemists discovered that ALL matter is made of elements) ...
A review of Atoms
... nucleus.Here it is shown as a small dot circling the nucleus. There are the same number of electrons and protons in a neutral atom. ...
... nucleus.Here it is shown as a small dot circling the nucleus. There are the same number of electrons and protons in a neutral atom. ...
K has two shells (n=4 vs n=2) more than Li, so it
... K has two shells (n=4 vs n=2) more than Li, so it would be much larger. ...
... K has two shells (n=4 vs n=2) more than Li, so it would be much larger. ...
ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
... A. Electrons travel around the nucleus in the electron cloud. B. Electrons follow paths called energy levels or energy shells. C. All elements have at least 1 energy level. D. The period number (or the rows) on the Periodic Table tells you the number of occupied energy shells that element has. E. El ...
... A. Electrons travel around the nucleus in the electron cloud. B. Electrons follow paths called energy levels or energy shells. C. All elements have at least 1 energy level. D. The period number (or the rows) on the Periodic Table tells you the number of occupied energy shells that element has. E. El ...
Section 3 The Periodic Table
... Electrons are placed in energy levels. Energy levels nearer the nucleus have lower energy than those levels that are farther away. ...
... Electrons are placed in energy levels. Energy levels nearer the nucleus have lower energy than those levels that are farther away. ...
CHAPTER 3: The Building Blocks of Matter
... I. Early Atomic Theory□Democritus (400 B.C.)- suggested that the world was made of two things: -empty space and -tiny, indivisible particles called ‘____________’. □Dalton (early 1800s)- using the experimental observations of others, including Lavoisier and Proust, he proposed□Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
... I. Early Atomic Theory□Democritus (400 B.C.)- suggested that the world was made of two things: -empty space and -tiny, indivisible particles called ‘____________’. □Dalton (early 1800s)- using the experimental observations of others, including Lavoisier and Proust, he proposed□Dalton’s Atomic Theory ...
Ch 3 studentElements Ions Isotopes
... 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical 3. different elements have different atoms 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements ...
... 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical 3. different elements have different atoms 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements ...
Radioisotopes
... • Isotopes are any of the different types of atoms (Nuclides) of the same chemical element, each having a different atomic mass (mass number) • Isotopes of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons. • Therefore, isotopes have di ...
... • Isotopes are any of the different types of atoms (Nuclides) of the same chemical element, each having a different atomic mass (mass number) • Isotopes of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons. • Therefore, isotopes have di ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure I. History of the Atom A. Democritus (400
... 1. Ground state: All the electrons in an atom have the lowest possible energy a. Stable 2. Excited state: An electron moves to an orbital of higher energy a. Less stable Chapter 5 Periodic Table I. Organizing the elements A. Mendeleev’s Periodic Table 1. Arranged in rows by increasing atomic mass 2. ...
... 1. Ground state: All the electrons in an atom have the lowest possible energy a. Stable 2. Excited state: An electron moves to an orbital of higher energy a. Less stable Chapter 5 Periodic Table I. Organizing the elements A. Mendeleev’s Periodic Table 1. Arranged in rows by increasing atomic mass 2. ...