* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Structure
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
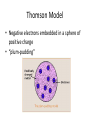
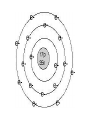
Atomic Structure Early Models of the Atom • Democritus (460 – 370 BCE) • Among first to suggest existence of atoms • Believed atoms were indivisible and indestructible • John Dalton (1766-1844) • Used experimental methods to observe atoms • Studied the ratios in which elements combine in chemical reactions • Formulated an atomic theory Dalton’s Atomic Theory I. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms II. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. III. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds IV. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element are never changed into atoms of another. Checkpoint: What happens to atoms in chemical reactions according to Dalton? JJ Thomson (1856-1940) • Discovered the electron as a negatively charged subatomic particle • Performed experiments that involved passing electric current through gases at low pressure (a cathode ray tube) and used a magnet to show particles with a charge Thomson Model • Negative electrons embedded in a sphere of positive charge • “plum-pudding” Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937) • Student of Thomson • Conducted the famous “goldfoil experiment” • Discovered the nucleus as a dense center to the atom • Electrons move around the nucleus Niels Bohr (1885-1962) • Student of Rutherford • Electrons moved in fixed circular paths around the nucleus • Each path was dependent upon the energy of the electron (the energy needed to move one electron from one energy level to the next is called a “quantum”) Erwin Shrödinger (1887-1961) • Focused his attention on the energy of electrons • Found electrons do not travel in fixed paths, but are randomly moving in certain areas around the nucleus • The quantum-mechanical model (electron-cloud model) is the current one we use today. – Predicts how likely an atom can be found in a certain location of the electron-cloud Today’s model • Electron-Cloud model/quantum-mechanical model • Nucleus: dense center with protons and neutrons • Electrons: moving randomly and rapidly around the nucleus in no fixed path but rather in probable areas. Left Page Activity • On a left page, you are going to create a timeline of the atom. Make sure to include the author of the model, a description, and a picture of each.