35.2 Defenses against Infection
... antibodies that circulate in the blood and lymph • The response is activated when antibodies on B cells bind to antigens on a pathogen. • Antibodies have two antigen binding sites on the prongs of the “Y” • These bind to specific antigens ...
... antibodies that circulate in the blood and lymph • The response is activated when antibodies on B cells bind to antigens on a pathogen. • Antibodies have two antigen binding sites on the prongs of the “Y” • These bind to specific antigens ...
Chapter 35- Infectious Diseases
... • Interferons- when viruses infect organism, certain cells produce protein that interferes with the viruses production of protein for reproduction. • This slows down how quickly viruses can reproduce and allows the body to start SPECIFIC DEFENSES. ...
... • Interferons- when viruses infect organism, certain cells produce protein that interferes with the viruses production of protein for reproduction. • This slows down how quickly viruses can reproduce and allows the body to start SPECIFIC DEFENSES. ...
Immune System - ilovebiology
... The immune system turns against itself The surface proteins on our own cells are viewed as foreign and the body makes antibodies to destroy the cells Not sure why the body turns against itself ...
... The immune system turns against itself The surface proteins on our own cells are viewed as foreign and the body makes antibodies to destroy the cells Not sure why the body turns against itself ...
Immune System Basics
... Due to their shape, each can bind to several antigens at once. Antigen/Antibody binding has three effects. ...
... Due to their shape, each can bind to several antigens at once. Antigen/Antibody binding has three effects. ...
Prentice Hall Biology - Valhalla High School
... •The immune system has the ability to recognize self and non-self – When the immune system makes a mistake and attacks its own cells, it produces an autoimmune disease • Examples – Type I diabetes – insulin-producing cells of the pancreas are destroyed – Multiple sclerosis – antibodies destroy the f ...
... •The immune system has the ability to recognize self and non-self – When the immune system makes a mistake and attacks its own cells, it produces an autoimmune disease • Examples – Type I diabetes – insulin-producing cells of the pancreas are destroyed – Multiple sclerosis – antibodies destroy the f ...
Groups of adhesive molecules
... Hemagglutination: Agglutination of red blood cells. Used to determine ABO blood types and to detect influenza and measles viruses. ...
... Hemagglutination: Agglutination of red blood cells. Used to determine ABO blood types and to detect influenza and measles viruses. ...
PATH_417_Case_2_Summary_SunnyChen
... Innate Response-Complement System • consists of various plasma proteins found in the blood • 3 main pathways: classical, alternative, mannose binding lectin – Initial enzyme generated-C3 convertase – Ultimately leads to the formation of C3a, C3b, C5a, C5b, and other associated complement proteins • ...
... Innate Response-Complement System • consists of various plasma proteins found in the blood • 3 main pathways: classical, alternative, mannose binding lectin – Initial enzyme generated-C3 convertase – Ultimately leads to the formation of C3a, C3b, C5a, C5b, and other associated complement proteins • ...
A. Immune hemolytic anemias
... taken and the RBCs are washed (removing the patient's own plasma) and then incubated with antihuman globulin (also known as "Coombs reagent"). If this produces agglutination of RBCs, the direct Coombs test is positive, a visual indication that antibodies (and/or complement proteins) are bound to the ...
... taken and the RBCs are washed (removing the patient's own plasma) and then incubated with antihuman globulin (also known as "Coombs reagent"). If this produces agglutination of RBCs, the direct Coombs test is positive, a visual indication that antibodies (and/or complement proteins) are bound to the ...
40 -2 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... of response. Specific Defense 3. Immune Response – A series of specific defenses designed to attack a particular pathogen. Antigen – A foreign protein ID) that triggers an immune response. Lymphocytes – WBCs in body that recognize and destroy antigens. B Cells & T Cells are produced in bone marrow. ...
... of response. Specific Defense 3. Immune Response – A series of specific defenses designed to attack a particular pathogen. Antigen – A foreign protein ID) that triggers an immune response. Lymphocytes – WBCs in body that recognize and destroy antigens. B Cells & T Cells are produced in bone marrow. ...
Immune Strategies to Infection
... Epithelial barriers offering physical and mechanical barriers Chemical factors: in response to microbes, macrophages and other cells secrete cytokines that mediate many of the cellular reactions of innate immunity (i.e.: inflammatory cytokines IL1, IL6, IL8, IL12, TNF-a). These activate vascul ...
... Epithelial barriers offering physical and mechanical barriers Chemical factors: in response to microbes, macrophages and other cells secrete cytokines that mediate many of the cellular reactions of innate immunity (i.e.: inflammatory cytokines IL1, IL6, IL8, IL12, TNF-a). These activate vascul ...
Immunology (A)
... It has two important characteristics: Immune response is highly specific for the antigen that triggered it and has memory to the antigen. Exposure to antigen creates an immunologic “memory.”(3’) 2.Complement: The complement system is an important component of innate immunity(2’). Complement was 1st ...
... It has two important characteristics: Immune response is highly specific for the antigen that triggered it and has memory to the antigen. Exposure to antigen creates an immunologic “memory.”(3’) 2.Complement: The complement system is an important component of innate immunity(2’). Complement was 1st ...
Micro 532 Exam 96
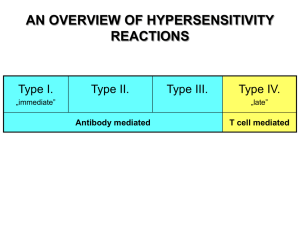
... For the next five questions - Pick the most appropriate answer from the following list. Each answer may be used more than once. A. Atopic hypersensitivity B. Cytotoxic hypersensitivity C. Toxic complex hypersensitivity D. Cell-mediated hypersensitivity E. B and C ...
... For the next five questions - Pick the most appropriate answer from the following list. Each answer may be used more than once. A. Atopic hypersensitivity B. Cytotoxic hypersensitivity C. Toxic complex hypersensitivity D. Cell-mediated hypersensitivity E. B and C ...
At the heart of the immune response is the ability to distinguish
... from their surfaces. One of the remarkable things about the immune system is its ability to recognize many millions of distinctive non-self molecules, and to respond by producing molecules such as these antibodies—and also cells—that can match and counteract each one of the non-self molecules. Any s ...
... from their surfaces. One of the remarkable things about the immune system is its ability to recognize many millions of distinctive non-self molecules, and to respond by producing molecules such as these antibodies—and also cells—that can match and counteract each one of the non-self molecules. Any s ...
Introduction to Immunity worksheet (LE)
... (1) From the word bank, assign each term to the immunity heading with which it is associated. Some terms may fit more than one category and should be placed in all categories that apply. antibodies in breast milk lymphocytes stomach acid, saliva, tears complement first line of defense ...
... (1) From the word bank, assign each term to the immunity heading with which it is associated. Some terms may fit more than one category and should be placed in all categories that apply. antibodies in breast milk lymphocytes stomach acid, saliva, tears complement first line of defense ...
Complexity and the Immune System
... which are able to quickly split into lots of effector cells and more memory cells • After an attack, have more memory cells, and they’re more coordinated ...
... which are able to quickly split into lots of effector cells and more memory cells • After an attack, have more memory cells, and they’re more coordinated ...
Adaptive or acquired immune system
... 1. Physical barriers (skin, mucus lining of gastrointestinal, respiratory and genitourinary tracts) 2. Phagocytic cells – neutrophils, macrophages 3. Protective chemicals – acid pH of stomach, lipids on skin surface 4. Enzymes – lysozyme in saliva, intestinal secretions; digests cell walls of bacter ...
... 1. Physical barriers (skin, mucus lining of gastrointestinal, respiratory and genitourinary tracts) 2. Phagocytic cells – neutrophils, macrophages 3. Protective chemicals – acid pH of stomach, lipids on skin surface 4. Enzymes – lysozyme in saliva, intestinal secretions; digests cell walls of bacter ...
Innate immunity/ cont…II.Second line: 2.Phagocytosis:
... debris, and produce inflammatory molecules which regulate other components of the immune system. They express a wide range of surface receptors that allow them to identify microorganisms. Also, phagocytosis can be enhanced by antibodies, complement and acute phase proteins (all called opsonins and a ...
... debris, and produce inflammatory molecules which regulate other components of the immune system. They express a wide range of surface receptors that allow them to identify microorganisms. Also, phagocytosis can be enhanced by antibodies, complement and acute phase proteins (all called opsonins and a ...
01_innate - WordPress.com
... • Infected or altered self (transformed) cell downregulated MHC • NK does not receive inhibitory signal • Signals kill infected cell ...
... • Infected or altered self (transformed) cell downregulated MHC • NK does not receive inhibitory signal • Signals kill infected cell ...
Presentation
... Sources and Impacts of Emerging Contaminants Nancy Denslow, Ph.D. Center for Environmental and Human Toxicology, UF ...
... Sources and Impacts of Emerging Contaminants Nancy Denslow, Ph.D. Center for Environmental and Human Toxicology, UF ...
Complement system
The complement system is a part of the immune system that helps or complements the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear pathogens from an organism. It is part of the innate immune system, which is not adaptable and does not change over the course of an individual's lifetime. However, it can be recruited and brought into action by the adaptive immune system.The complement system consists of a number of small proteins found in the blood, in general synthesized by the liver, and normally circulating as inactive precursors (pro-proteins). When stimulated by one of several triggers, proteases in the system cleave specific proteins to release cytokines and initiate an amplifying cascade of further cleavages. The end-result of this activation cascade is massive amplification of the response and activation of the cell-killing membrane attack complex. Over 30 proteins and protein fragments make up the complement system, including serum proteins, serosal proteins, and cell membrane receptors. They account for about 5% of the globulin fraction of blood serum and can serve as opsonins.Three biochemical pathways activate the complement system: the classical complement pathway, the alternative complement pathway, and the lectin pathway.