BIO 580 - Medical Microbiology - Unit One Part II
... and mucins (a group of large, heavily glycosylated proteins found in the body). ...
... and mucins (a group of large, heavily glycosylated proteins found in the body). ...
Topic 19 - Roslyn Public Schools
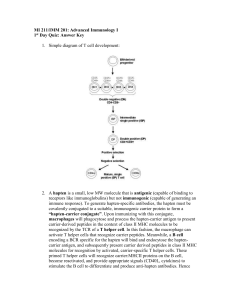
... • (a) B-cell – produce antibodies that destroy invading microbes or pathogens (including viruses, bacteria, and parasite) – each pathogen triggers a different response – there are millions of different pathogens so there are millions of different B-cells in the blood • (b) T-cells – there are two ty ...
... • (a) B-cell – produce antibodies that destroy invading microbes or pathogens (including viruses, bacteria, and parasite) – each pathogen triggers a different response – there are millions of different pathogens so there are millions of different B-cells in the blood • (b) T-cells – there are two ty ...
Slayt 1
... Complement inhibitors may be virus or host derived Assembling of C3 convertase is critical in all of three pathways Some viruses (HCMV) induce the expression of cellular Complement inhibitors like DAF, MCP Some viruses incorporate complement inhibitors into the viruses (HIV, HTLV). Glycoprotein C-1 ...
... Complement inhibitors may be virus or host derived Assembling of C3 convertase is critical in all of three pathways Some viruses (HCMV) induce the expression of cellular Complement inhibitors like DAF, MCP Some viruses incorporate complement inhibitors into the viruses (HIV, HTLV). Glycoprotein C-1 ...
Chapt07 Lecture 13ed Pt 2
... Inflammatory response • Increased blood flow also brings more white blood cells to an injured area, with __________ being the first scouts to kill pathogens. • This response can be short-lived, but if the neutrophils cannot control the damage, cytokines (chemicals) will call in more white blood cell ...
... Inflammatory response • Increased blood flow also brings more white blood cells to an injured area, with __________ being the first scouts to kill pathogens. • This response can be short-lived, but if the neutrophils cannot control the damage, cytokines (chemicals) will call in more white blood cell ...
Immune System Summmary
... entered the wound and has imbedded in the tissues and blood. The immune system can recognize the bacterium as an invader (non-self) because it displays different surface antigens from your own cells. The bacterium may encounter and be eaten by any of several different types of phagocytic leukocytes ...
... entered the wound and has imbedded in the tissues and blood. The immune system can recognize the bacterium as an invader (non-self) because it displays different surface antigens from your own cells. The bacterium may encounter and be eaten by any of several different types of phagocytic leukocytes ...
Innate Immunity
... ● Found on all phagocytes ● MARCO (macrophage receptor with collagenous struction) o binds bacterial cell walls but not yeast ...
... ● Found on all phagocytes ● MARCO (macrophage receptor with collagenous struction) o binds bacterial cell walls but not yeast ...
T cell-mediated immune response
... T cell-mediated immune response • Naive CD4+ T (helper) cells → effector cells (activation of macrophages for killing of ingested microbes, activation of B cells for production of antibodie, activation of other cells) - Th1 lymphocytes: production of IFN-g, activation of phagocytes, stimulation of ...
... T cell-mediated immune response • Naive CD4+ T (helper) cells → effector cells (activation of macrophages for killing of ingested microbes, activation of B cells for production of antibodie, activation of other cells) - Th1 lymphocytes: production of IFN-g, activation of phagocytes, stimulation of ...
Biochemistry of the immune system
... (small fragments of the pathogen) have been processed and presented in combination with a "self" receptor - a major histocompatibility system (MHC) molecule. ...
... (small fragments of the pathogen) have been processed and presented in combination with a "self" receptor - a major histocompatibility system (MHC) molecule. ...
sheet of notes
... • Defends against free bacteria, toxins, and viruses present in body fluids • The repeated subunits of these antigens bind simultaneously to a number of membrane antibodies on the B cell surface Cell-mediated immunity • Active against bacteria and viruses within infected body cells and against fungi ...
... • Defends against free bacteria, toxins, and viruses present in body fluids • The repeated subunits of these antigens bind simultaneously to a number of membrane antibodies on the B cell surface Cell-mediated immunity • Active against bacteria and viruses within infected body cells and against fungi ...
Humoral components and cellular mechanisms, such as
... The innate immune system consists of humoral components, such as complement, and cellular mechanisms, such as phagocytosis. This pathway directs the adaptive immune response. For example, the innate immune system mediates clearance of apoptotic cells without initiating adaptive immunity, a process w ...
... The innate immune system consists of humoral components, such as complement, and cellular mechanisms, such as phagocytosis. This pathway directs the adaptive immune response. For example, the innate immune system mediates clearance of apoptotic cells without initiating adaptive immunity, a process w ...
Type IV hypersensitivity
... of intracellular and other pathogens. • If the response is excessive it can damage host tissues • Subsequent exposure of the sensitised individual to the exogenous Ag results in the recruitment of specific T cells to the site and development of a local inflammatory ...
... of intracellular and other pathogens. • If the response is excessive it can damage host tissues • Subsequent exposure of the sensitised individual to the exogenous Ag results in the recruitment of specific T cells to the site and development of a local inflammatory ...
PHA 321 - Biosciences II
... B) show induration because of an influx of sensitized T cells and macrophages C) peak at 4 to six hours after exposure to antigen D) depend on the activities of the Fc portion of antibodies E) are characterized by a wheal and flare reaction ...
... B) show induration because of an influx of sensitized T cells and macrophages C) peak at 4 to six hours after exposure to antigen D) depend on the activities of the Fc portion of antibodies E) are characterized by a wheal and flare reaction ...
MLAB 1315- Hematology Fall 2007 Keri Brophy
... Seasonal hemolytic anemia during the winter months. Usually not severe. RBC’s agglutinate at room temperature and will be seen as clumps on a peripheral smear. ...
... Seasonal hemolytic anemia during the winter months. Usually not severe. RBC’s agglutinate at room temperature and will be seen as clumps on a peripheral smear. ...
Unit 4 - Immunology and Public Health
... C or airways ____________act as a physical barrier to pathogens. D or non-specific 3. This is an example of _____________defence. ...
... C or airways ____________act as a physical barrier to pathogens. D or non-specific 3. This is an example of _____________defence. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - I. Introduction to class
... ACTIVITY OF OTHER CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM. • DEFENSE AGAINST: • BACTERIA AND VIRUSES THAT ARE INSIDE HOST CELLS AND ARE INACCESSIBLE TO ANTIBODIES. • FUNGI, PROTOZOA, AND WORMS ...
... ACTIVITY OF OTHER CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM. • DEFENSE AGAINST: • BACTERIA AND VIRUSES THAT ARE INSIDE HOST CELLS AND ARE INACCESSIBLE TO ANTIBODIES. • FUNGI, PROTOZOA, AND WORMS ...
Lec.2 Dr.Maysem M.Alwash Hypersensitivity Reaction s (cont.)
... antigens are either killed (negative selection) or rendered harmless during their maturation in central (generative) lymphoid organs (i.e., in the thymus for T cells and in the bone ...
... antigens are either killed (negative selection) or rendered harmless during their maturation in central (generative) lymphoid organs (i.e., in the thymus for T cells and in the bone ...
Primary immune response
... b) V-D rearrangement – V-D-J joining c) transcription if V-D-J product is readable, then splicing (V-D-J-C joining) d) translation in protein (H chain) ...
... b) V-D rearrangement – V-D-J joining c) transcription if V-D-J product is readable, then splicing (V-D-J-C joining) d) translation in protein (H chain) ...
AP Biology Chapter 43
... AP Bio Bellringer 1/11 • If you did the homework please get it out so I can pick it up. • Question: As animals are heterotrophic organisms, the ability to move and find food is important. Movement on earth, for animals, occurs basically in three different environments (Air, land, or water). Each env ...
... AP Bio Bellringer 1/11 • If you did the homework please get it out so I can pick it up. • Question: As animals are heterotrophic organisms, the ability to move and find food is important. Movement on earth, for animals, occurs basically in three different environments (Air, land, or water). Each env ...
Types of Immunoglobulins
... i. Monomer ii. 1st fetal Ig to be made iii. 1st Ig produce by virgin B lymphocytes after exposed to antigen b. Secreted i. Pentameric 7. Increase level indicates a. Recent infection 8. Involved in Acute Inflmtn-agglutination ...
... i. Monomer ii. 1st fetal Ig to be made iii. 1st Ig produce by virgin B lymphocytes after exposed to antigen b. Secreted i. Pentameric 7. Increase level indicates a. Recent infection 8. Involved in Acute Inflmtn-agglutination ...
immunology2
... 3- acute phase protein.. A* originated from the liver. B* present in blood. C* nature : its group of proteins produce by hepatic cells in low level in healthy body. D* function : in case of infection , macrophage ingest bacteria secrete cytokines ώ activate hepatic cell to secrete large amount of a ...
... 3- acute phase protein.. A* originated from the liver. B* present in blood. C* nature : its group of proteins produce by hepatic cells in low level in healthy body. D* function : in case of infection , macrophage ingest bacteria secrete cytokines ώ activate hepatic cell to secrete large amount of a ...
GROWTH MEDIA OCULAR INFECTION
... • Chronic inflammation • Released factors up regulate VEGF leads to choroidal neovascularization ...
... • Chronic inflammation • Released factors up regulate VEGF leads to choroidal neovascularization ...
Complement system
The complement system is a part of the immune system that helps or complements the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear pathogens from an organism. It is part of the innate immune system, which is not adaptable and does not change over the course of an individual's lifetime. However, it can be recruited and brought into action by the adaptive immune system.The complement system consists of a number of small proteins found in the blood, in general synthesized by the liver, and normally circulating as inactive precursors (pro-proteins). When stimulated by one of several triggers, proteases in the system cleave specific proteins to release cytokines and initiate an amplifying cascade of further cleavages. The end-result of this activation cascade is massive amplification of the response and activation of the cell-killing membrane attack complex. Over 30 proteins and protein fragments make up the complement system, including serum proteins, serosal proteins, and cell membrane receptors. They account for about 5% of the globulin fraction of blood serum and can serve as opsonins.Three biochemical pathways activate the complement system: the classical complement pathway, the alternative complement pathway, and the lectin pathway.