The Immune System - Blue Valley School District
... dilation in the surrounding capillaries and indirectly the four symptoms of inflammation: 1. Swelling 2. Reddness 3. Warmth 4. Pain ...
... dilation in the surrounding capillaries and indirectly the four symptoms of inflammation: 1. Swelling 2. Reddness 3. Warmth 4. Pain ...
abstract
... Southwestern Medical Center, 5323 Harry Hines Blvd, Dallas, TX 75390-9148 The presence of DNA and aberrant RNA in the cytoplasm is a danger signal that alerts the host immune system to eliminate microbial infections and malignant cells, but inappropriate activation of these pathways can also lead to ...
... Southwestern Medical Center, 5323 Harry Hines Blvd, Dallas, TX 75390-9148 The presence of DNA and aberrant RNA in the cytoplasm is a danger signal that alerts the host immune system to eliminate microbial infections and malignant cells, but inappropriate activation of these pathways can also lead to ...
Lecture 7: The body`s defenses
... Precipitation of soluble antigens The above enhance phagocytosis ...
... Precipitation of soluble antigens The above enhance phagocytosis ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 M.Sc. BI 3951 - IMMUNOTECHNOLOGY
... 2. What are the features of Dendritic cells? 3. Mention the source and function of plasma cells. 4. Give the expansion NALT and one of its function. 5. What do you mean by Lymph nodes? 6. What do you understand by HLA? 7. Write two functional features of Haplotyping 8. Define the process phagocytosi ...
... 2. What are the features of Dendritic cells? 3. Mention the source and function of plasma cells. 4. Give the expansion NALT and one of its function. 5. What do you mean by Lymph nodes? 6. What do you understand by HLA? 7. Write two functional features of Haplotyping 8. Define the process phagocytosi ...
Immune System - Mayfield City Schools
... Autoimmune diseases (A disease in which the immune system attacks the organism’s own cells; ex: rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, multiple sclerosis) Cancer (A disease in which the cells begin dividing at an uncontrolled rate and become invasive) AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome); When ...
... Autoimmune diseases (A disease in which the immune system attacks the organism’s own cells; ex: rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, multiple sclerosis) Cancer (A disease in which the cells begin dividing at an uncontrolled rate and become invasive) AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome); When ...
Antibodies - blobs.org
... regions and the Fc region. The Fab regions are the fragment antigen-binding regions, which are the bits which connect to enemy proteins and which are different in different antibodies. The Fc region is the fragment crystallisable region, which is the bit which connects to normal human immune cells, ...
... regions and the Fc region. The Fab regions are the fragment antigen-binding regions, which are the bits which connect to enemy proteins and which are different in different antibodies. The Fc region is the fragment crystallisable region, which is the bit which connects to normal human immune cells, ...
11 Acut inflammation BA
... – vasoactive amines (histamine, serotonin), C3a and C5a (complement system), bradykinin, leukotrienes (LT), PAF Chemotactic leukocyte activation – C3a, C5a, LTB4, chemokines (e.g. IL-8) Fever • IL-1, IL-6, TNFα, PGE2 ...
... – vasoactive amines (histamine, serotonin), C3a and C5a (complement system), bradykinin, leukotrienes (LT), PAF Chemotactic leukocyte activation – C3a, C5a, LTB4, chemokines (e.g. IL-8) Fever • IL-1, IL-6, TNFα, PGE2 ...
L12 nonspecificdefense 7e
... • NOD-like receptors (NLRs) – Cytoplasmic proteins detect bacterial parts ...
... • NOD-like receptors (NLRs) – Cytoplasmic proteins detect bacterial parts ...
IMMUNOLOGICAL ASPECT OF BACTERIAL INFECTION
... 1. Activate the alternative pathway (properdin) of complement in the absence of antibody. 2. Activate the Classical pathway of complement via mannose binding protein (MBP). 3. Recognize by Pattern-recognized receptors including Toll-Like receptors on Macrophage and Dendritic cells—activate the prote ...
... 1. Activate the alternative pathway (properdin) of complement in the absence of antibody. 2. Activate the Classical pathway of complement via mannose binding protein (MBP). 3. Recognize by Pattern-recognized receptors including Toll-Like receptors on Macrophage and Dendritic cells—activate the prote ...
Atypical Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome associated with a CD46
... presentation was negative. This led us to investigate for aHUS. GENETIC AND FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS: Genetic analysis revealed a mutation in the complement regulatory protein CD46 (c.286+2T>G). Functional analysis demonstrated a nonsecreted protein. In individuals with mutations in complement genes, inc ...
... presentation was negative. This led us to investigate for aHUS. GENETIC AND FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS: Genetic analysis revealed a mutation in the complement regulatory protein CD46 (c.286+2T>G). Functional analysis demonstrated a nonsecreted protein. In individuals with mutations in complement genes, inc ...
File - The Building Blocks For Learning
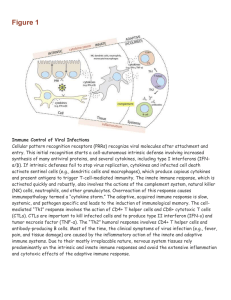
... Immune Control of Viral Infections Cellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize viral molecules after attachment and entry. This initial recognition starts a cell-autonomous intrinsic defense involving increased synthesis of many antiviral proteins, and several cytokines, including type I ...
... Immune Control of Viral Infections Cellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize viral molecules after attachment and entry. This initial recognition starts a cell-autonomous intrinsic defense involving increased synthesis of many antiviral proteins, and several cytokines, including type I ...
Bacteria vs. Viruses
... pathogen (foreign invader), your immune system works faster to fight it. WHY? ...
... pathogen (foreign invader), your immune system works faster to fight it. WHY? ...
Immunology Lecture 6 Feb 12 2013
... The smaller complement components C3a, C4a and C5a are known as anaphylatoxins Anaphylatoxins induce anaphylaxis, an acute systemic inflammatory response Order of potency: C5a > C3a > C4a ...
... The smaller complement components C3a, C4a and C5a are known as anaphylatoxins Anaphylatoxins induce anaphylaxis, an acute systemic inflammatory response Order of potency: C5a > C3a > C4a ...
Type of Innate immune
... although they can react with existing antibodies. Such substances need to be coupled to carrier molecule in order to have sufficient epitopes to be antigenic. For some chemicals, such as drugs, the carrier may be a host (auto) protein. The tertiary structure as well as the amino acid sequence, is im ...
... although they can react with existing antibodies. Such substances need to be coupled to carrier molecule in order to have sufficient epitopes to be antigenic. For some chemicals, such as drugs, the carrier may be a host (auto) protein. The tertiary structure as well as the amino acid sequence, is im ...
final exam of medical immunology
... 16 In Class I MHC molecules,peptide-binding site consist of A α1 and α2 domains B α1 and α3 domains C α1 and β1 domains D β2m 17 Biological role of the MHC proteins do not contribute to A A fundamental role in regulating immune responses. B Ag presentation C Self-MHC restriction. D Control of B cell ...
... 16 In Class I MHC molecules,peptide-binding site consist of A α1 and α2 domains B α1 and α3 domains C α1 and β1 domains D β2m 17 Biological role of the MHC proteins do not contribute to A A fundamental role in regulating immune responses. B Ag presentation C Self-MHC restriction. D Control of B cell ...
Bacterial Evasion of Host Immune Responses - Assets
... antibacterial protection comes from individuals with deficiencies in individual complement genes (Table 4.2). Such genetic deficiencies can be broadly divided into seven categories: (i) classical pathway genes, (ii) mannose-binding lectin, (iii) alternative pathway genes, (iv) C3, (v) genes encoding ...
... antibacterial protection comes from individuals with deficiencies in individual complement genes (Table 4.2). Such genetic deficiencies can be broadly divided into seven categories: (i) classical pathway genes, (ii) mannose-binding lectin, (iii) alternative pathway genes, (iv) C3, (v) genes encoding ...
THE PEARLS OF WISDOM - OSW
... that respond early and nonspecifically to infection Lymphoid progenitor cells develop into lymphocytes ...
... that respond early and nonspecifically to infection Lymphoid progenitor cells develop into lymphocytes ...
Complement system
The complement system is a part of the immune system that helps or complements the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear pathogens from an organism. It is part of the innate immune system, which is not adaptable and does not change over the course of an individual's lifetime. However, it can be recruited and brought into action by the adaptive immune system.The complement system consists of a number of small proteins found in the blood, in general synthesized by the liver, and normally circulating as inactive precursors (pro-proteins). When stimulated by one of several triggers, proteases in the system cleave specific proteins to release cytokines and initiate an amplifying cascade of further cleavages. The end-result of this activation cascade is massive amplification of the response and activation of the cell-killing membrane attack complex. Over 30 proteins and protein fragments make up the complement system, including serum proteins, serosal proteins, and cell membrane receptors. They account for about 5% of the globulin fraction of blood serum and can serve as opsonins.Three biochemical pathways activate the complement system: the classical complement pathway, the alternative complement pathway, and the lectin pathway.