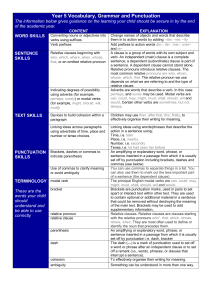
Year 5 Vocabulary Grammar and Punctuation
... A clause is a group of words with its own subject and verb. An independent (main) clause is a complete sentence; a dependent (subordinate) clause is part of a sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand alone. Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses. The most common relative pronouns are who, who ...
... A clause is a group of words with its own subject and verb. An independent (main) clause is a complete sentence; a dependent (subordinate) clause is part of a sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand alone. Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses. The most common relative pronouns are who, who ...
Try It Out - Cloudfront.net
... Preposition OR Adverb??? Most words that are used a prepositions can also be used as adverbs. If the word stands alone, it is an adverb. If that same word begins a prepositional phrase, it is a preposition. Try It Out ...
... Preposition OR Adverb??? Most words that are used a prepositions can also be used as adverbs. If the word stands alone, it is an adverb. If that same word begins a prepositional phrase, it is a preposition. Try It Out ...
HN English I Name_______________________________ Gerund
... on this second list with an equal sign [=] and the sentence still makes sense, the verb is almost always linking. ...
... on this second list with an equal sign [=] and the sentence still makes sense, the verb is almost always linking. ...
Parts of Speech: Definitions and other key points Phrase: A group of
... the dependent clause: If I go to the bank, I can deposit my check. (DC, IC) • If the dependent clause follows the independent clause, do not use a comma between the IC and the DC: I can deposit my check if I go to the bank. (IC DC) ...
... the dependent clause: If I go to the bank, I can deposit my check. (DC, IC) • If the dependent clause follows the independent clause, do not use a comma between the IC and the DC: I can deposit my check if I go to the bank. (IC DC) ...
Complements
... adjective to modify a noun or a pronoun. • An adjective clause almost always begins with a relative pronoun (who, whom, whose, which, what, and that) • Examples: 1. The girl who is sitting in the front row is my best friend. 2. The car that is bright red is speeding. ...
... adjective to modify a noun or a pronoun. • An adjective clause almost always begins with a relative pronoun (who, whom, whose, which, what, and that) • Examples: 1. The girl who is sitting in the front row is my best friend. 2. The car that is bright red is speeding. ...
Parts of Speech Test Review Sheet
... TARGET: I can use and identify a helping verb. I know how to use helping verbs. I can use modal auxiliaries (can, may, must) ...
... TARGET: I can use and identify a helping verb. I know how to use helping verbs. I can use modal auxiliaries (can, may, must) ...
Glossary Literacy L3 - Skills for Life Network
... between the inherent meaning of language (semantics) and the context where the language is used. predicate The part of a clause that is not the subject, e.g. Jo told me to come. prefix, suffix An item that has meaning, but can’t be a word by itself. Prefixes go at the beginning of words, e.g. unusua ...
... between the inherent meaning of language (semantics) and the context where the language is used. predicate The part of a clause that is not the subject, e.g. Jo told me to come. prefix, suffix An item that has meaning, but can’t be a word by itself. Prefixes go at the beginning of words, e.g. unusua ...
Year 5 Glossary
... space or in time. The most common prepositions are: "about," "above," "across," "after," "against," "along," "among," "around," "at," "before," "behind," "below," "beneath," "beside," "between," "beyond," "but," "by," "despite," "down," "during," "except," "for," "from," "in," "inside," "into," "lik ...
... space or in time. The most common prepositions are: "about," "above," "across," "after," "against," "along," "among," "around," "at," "before," "behind," "below," "beneath," "beside," "between," "beyond," "but," "by," "despite," "down," "during," "except," "for," "from," "in," "inside," "into," "lik ...
Clauses - North Pocono School District
... to the basic meaning of the sentence (usually follow proper nouns). Set these off with commas ...
... to the basic meaning of the sentence (usually follow proper nouns). Set these off with commas ...
Grammar_and_Usage_Student_Help_Desk
... A tornado destroyed the Kansas town of Coffeyville. o Demonstrative adjectives – This, that, these, and those are pronouns that can often be used as adjectives – This cartoon.. o Possessive adjectives – My, our, your, her, his, its, and their are possessive pronouns that may be used as adjectives – ...
... A tornado destroyed the Kansas town of Coffeyville. o Demonstrative adjectives – This, that, these, and those are pronouns that can often be used as adjectives – This cartoon.. o Possessive adjectives – My, our, your, her, his, its, and their are possessive pronouns that may be used as adjectives – ...
Phrases - Wando High School
... • Subject – who or what the sentence is about – Must be a noun, pronoun, gerund, or infinitive – Can be an unspoken “you” – There and here are never the subject ...
... • Subject – who or what the sentence is about – Must be a noun, pronoun, gerund, or infinitive – Can be an unspoken “you” – There and here are never the subject ...
LITERARY TERMS 1. onomatopoeia: The use of words whose
... (and, but, or, so, yet, for) or a semicolon (;). Example: The enormous dog ran away quickly, and he yelped as he ran into the tree. Complex Sentence: a complete sentence (independent clause) and a dependent clause. A dependent clause begins with a subordinating conjunction or a relative pronoun. Exa ...
... (and, but, or, so, yet, for) or a semicolon (;). Example: The enormous dog ran away quickly, and he yelped as he ran into the tree. Complex Sentence: a complete sentence (independent clause) and a dependent clause. A dependent clause begins with a subordinating conjunction or a relative pronoun. Exa ...
Morphology and Syntax - University of Edinburgh
... Jane was upset because an unexpected problem with the manual’s availability implied that the risk in case of a fire was very high. upset = a state, but not a verb availability = not a ‘person, place or thing’, but is a noun implied = not an ‘action, process or state’, but is a verb fire = process o ...
... Jane was upset because an unexpected problem with the manual’s availability implied that the risk in case of a fire was very high. upset = a state, but not a verb availability = not a ‘person, place or thing’, but is a noun implied = not an ‘action, process or state’, but is a verb fire = process o ...
wordclasses_24.09.13
... Degree adverbs: specify the extent of some action, process, or property extremely, very, somewhat Manner adverb: describe the manner of some action or process or property Slowly, delicately Temporal adverbs: describe the time that some action or event took place Yesterday, Monday ...
... Degree adverbs: specify the extent of some action, process, or property extremely, very, somewhat Manner adverb: describe the manner of some action or process or property Slowly, delicately Temporal adverbs: describe the time that some action or event took place Yesterday, Monday ...
Parts of Speech Review - jaguar-language-arts
... themselves. If you want to go on vacation, you can leave some food and water for your cat, and it will be okay. A cat can sleep on your bed and keep you warm at night. I think these things make cats good ...
... themselves. If you want to go on vacation, you can leave some food and water for your cat, and it will be okay. A cat can sleep on your bed and keep you warm at night. I think these things make cats good ...
Grammar Final Study Guide
... Interrogative - An interrogative sentence asks a question. An interrogative sentence ends with a question mark. Example: How did you find the card? ...
... Interrogative - An interrogative sentence asks a question. An interrogative sentence ends with a question mark. Example: How did you find the card? ...
Chapter 14
... Present tense is used in advertising Present participle (the –ing form) is not generally used. Present perfect tense is used in public relations writing. ...
... Present tense is used in advertising Present participle (the –ing form) is not generally used. Present perfect tense is used in public relations writing. ...
Developing
... asked, saved, dealt, eaten, seen “The puppies, exhausted, collapsed in the grass.” ...
... asked, saved, dealt, eaten, seen “The puppies, exhausted, collapsed in the grass.” ...
SENTENCE PARTS AND TYPES
... Abstract nouns name something that cannot be touched or seen, such as an idea, doctrine, thought, theory, concept, condition, or feeling: joy ...
... Abstract nouns name something that cannot be touched or seen, such as an idea, doctrine, thought, theory, concept, condition, or feeling: joy ...
Parts of Speech
... Can tell about place: Our classroom is on the third floor. Please sit in your chair. Can tell about direction: He went to Little Rock. Examples: in, on, at, around, for, to, from. There are many, many more. ...
... Can tell about place: Our classroom is on the third floor. Please sit in your chair. Can tell about direction: He went to Little Rock. Examples: in, on, at, around, for, to, from. There are many, many more. ...
CHAPTER 14: The Phrase
... – **It is possible to have an infinitive with the to omitted. • I’ll help you [to] do your homework. • Cats like to purr and [to] eat all day. ...
... – **It is possible to have an infinitive with the to omitted. • I’ll help you [to] do your homework. • Cats like to purr and [to] eat all day. ...
Gerund
... A participle is a verbal that functions as an adjective to modify a noun or pronoun. Verb + d, ed, or ing that is now an adjective. A participle requires a comma to set off an introductory participle or participial phrase. WALKING through the park, I saw a bear. A present participle ends in ing. Usi ...
... A participle is a verbal that functions as an adjective to modify a noun or pronoun. Verb + d, ed, or ing that is now an adjective. A participle requires a comma to set off an introductory participle or participial phrase. WALKING through the park, I saw a bear. A present participle ends in ing. Usi ...
Because you know you love my sentence structure lectures, here is
... Appositive phrases •An appositive is usually a noun that renames another noun; it also adds new information about the noun it follows. •An appositive phrase also includes modifiers. •Appositives and appositive phrases sometimes begin with that is, such as, for example, or in other words. Examples: ...
... Appositive phrases •An appositive is usually a noun that renames another noun; it also adds new information about the noun it follows. •An appositive phrase also includes modifiers. •Appositives and appositive phrases sometimes begin with that is, such as, for example, or in other words. Examples: ...























