* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
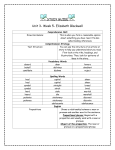
Download Phrases - Wando High School
Antisymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish pronouns wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Dutch grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
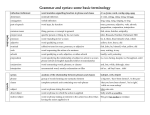
Grammar Review Sentence Parts and Phrases 1 Sentence Parts and Phrases • Subject – who or what the sentence is about – Must be a noun, pronoun, gerund, or infinitive – Can be an unspoken “you” – There and here are never the subject • Verb – action that takes place – Transitive: takes a direct object (I love grammar.) – Intransitive: no direct object (The ground shook.) – All linking verbs are intransitive: • is, am, are, was, were, be, being, been, appear, become, feel, grow, look, remain, seem, smell, sound, taste, stay, etc... 2 Sentence Parts and Phrases • Complement – completes the meaning of subject/verb – Direct Object (DO): noun or pronoun that follows an action verb, answers “what?” I like English. I like what? English – Indirect Object: noun or pronoun that comes before DO, answers “to or for whom or what” He gave me the paper. He gave the paper to whom? me 3 Sentence Parts and Phrases • Complement – completes the meaning of subject/verb (cont.) – Predicate Nominative: a noun or pronoun that follows linking verb and renames the subject (He is a nice guy.) – Predicate Adjective: an adjective that follows linking verb and describes the subject (He is gross.) 4 Sentence Parts and Phrases Phrase – a group of words that modify another • Appositive/Appositive Phrase - Noun or pronoun that follows and renames a noun or pronoun. – My son Beck likes trains. – Ashley, my daughter, loves to sing. Comma usage rules: – Restrictive: limits the meaning so it can’t be removed without changing the sentence – Unrestrictive: does not limit the meaning so it can be removed without changing the meaning 5 Sentence Parts and Phrases Phrase – a group of words that modify another • Preposition Phrase – a preposition followed by a noun or pronoun: gives position, relationship or direction – The key is under the rug Adjectivial - phrase functions like an adjective, describing a noun or pronoun Over Ed's head, the plane roared into the night sky. Adverbial - phrase functions like an adverb, describing a verb, adjective, or another adverb Over Ed's head, the plane roared into the night sky. – If there is no object, there is no preposition. (Please stand up. “Up” is an adverb) 6 Sentence Parts and Phrases • Gerund, Participle, or Infinitive Phrases – the gerund, participle or infinitive followed by its modifiers and objects – Writing long essays can be fun. (noun) – Running down the hall, he bumped into the principal. (adjective) – He likes to eat pepperoni pizza. (adverb) 7 Sentence Parts and Phrases • Introductory Phrase – consists of a noun/pronoun, a participle, and any related modifiers that modify a specific word, usually the subject. This phrase is set off by a comma. Bending at the waist, Emma stretched and touched her toes. Suffering from indigestion, Sean frequently took antacids. 8 Sentence Parts and Phrases • Absolute Phrase – consists of a noun/pronoun, a participle, and any related modifiers that modify the whole sentence rather than a specific word His homework finished, Matt headed for the baseball field. 9 Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Bill went home. Janey felt sick. Boozer, my dog, shook. I went to the store. I went home to run. Falling down isn’t fun. I bought myself some paper. Gasping for breath, I finally finished the marathon. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Direct object Indirect object Transitive verb Appositive (phrase) Prepositional Phrase Gerund Phrase Participle Phrase Infinitive 10 Review 1. C Bill went home. 2. A Janey felt sick. 3. D Boozer, my dog, shook. 4. E I went to the store. 5. H I went home to run. 6. F Falling down isn’t fun. 7. B I bought myself some paper. 8. G Gasping for breath, I finally finished the marathon. A. 2 Direct object B. 7 Indirect object C. 1 Transitive verb D. 3 Appositive (phrase) E. 4 Prepositional Phrase F. 6 Gerund Phrase G. 8 Participle Phrase H. 5 Infinitive 11