* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Complements
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Dutch grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
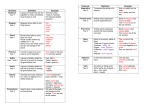
Grammar Complements, Phrases, & Clauses SED 340 Complements • A complement is a word or group of words that completes the meaning begun by the subject and verb. • Four kinds: direct objects, indirect objects, predicate nominatives, and predicate adjectives • Two are affected by the action of the verb • Predicate nominatives and predicate adjectives are both called subject complements. Direct Objects • The direct object receives the action expressed by the verb or names the result of the action. • Examples: 1. She drank the soda. 2. I signed the check. Indirect Objects • Indirect objects precede the direct object and tell to whom or what or for whom or what the action of the verb is done. • Examples: 1. My mom gave me a present. 2. Bob sent us the memo on Thursday. Subject Complements • A subject complement is a word which follows a linking verb and refers to (explains or describes) the subject. • Two kinds: predicate nominatives and predicate adjectives Predicate Nominatives • Predicate nominatives are nouns or pronouns. • Examples: 1. She is a secretary. 2. It was him. Predicate Adjectives • Predicate adjectives are adjectives which modify the subject. • Examples: 1. She is pretty. 2. My dog is lazy. Complements Complements Direct Objects Indirect Objects Subject Complements Predicate Nominatives Predicate Adjectives Phrases • A phrase is a group of related words that is used as a single part of speech and does not contain a verb and its subject. • Five kinds: prepositional, adjective, adverb, verbal, and appositive Prepositional Phrases • A prepositional phrase is a group of words that begin with a preposition and usually ends with a noun or pronoun. • Examples: 1. Please put the paper in the basket. 2. I found ten apples under the tree. Adjective Phrases • An adjective phrase is a prepositional phrase that modifies a noun or a pronoun. • Examples: 1. That girl in the car is my sister. 2. The disk on the table is his. Adverb Phrases • An adverb phrase is a prepositional phrase that modifies a verb, an adjective, or an adverb. • Examples: 1. The pine tree was planted in the back yard. 2. I ran from the dog. Verbals and Verbal Phrases • A verbal is a word that is formed from a verb but it is used in a sentence as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. • A verbal phrase is a group of related words that contains a verbal. • Three kinds: participles, gerunds and infinitives Participles and Participial Phrases • A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective. • A participial phrase is a group of related words that contains a participle and that acts as an adjective. • Examples: 1. Running through the forest, the girl enjoyed the crisp air. 2. Swimming to the surface, the fish swallowed the worm. Gerunds and Gerund Phrases • A gerund is a verb form ending in –ing that is used as a noun. • A gerund phrase is a group of related words that includes the gerund. • Examples: 1. Swimming is my favorite thing to do in the summer. 2. Washing the dishes is my daily chore. Infinitives and Infinitive Phrases • An infinitive is a verb form that can be used as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. • An infinitive has the word to directly before the base form of the verb. • An infinitive phrase is a group of related words that includes the infinitive. • Examples: 1. I would like to go to Europe. 2. He needs to read the whole book by tomorrow. Appositives and Appositive Phrases • An appositive is a noun or pronoun that explains the noun or pronoun it follows. • An appositive phrase is made up of an appositive and its modifiers. • Most of the time set apart from the rest of the sentence with commas, but if the appositive is necessary to the meaning of the sentence or is closely related to the word it follows, no commas are necessary • Examples: 1. Susan, the girl in the front row, is reading a book. 2. The movie Lord of the Rings is his favorite. Phrases Phrases Appositive Prepositional Adjective Adverb Verbal Infinitive Gerund Participial Clauses • A clause is a group of words containing a subject and a verb which forms part of a sentence. • Independent or dependent (subordinate) • Three kinds: adjective, adverb, and noun Independent and Dependent Clauses • An independent clause expresses a complete thought and can stand by itself as a sentence. • A dependent clause or subordinate clause does not express a complete thought and cannot stand alone. Adjective Clauses • An adjective clause is a subordinate clause used as an adjective to modify a noun or a pronoun. • An adjective clause almost always begins with a relative pronoun (who, whom, whose, which, what, and that) • Examples: 1. The girl who is sitting in the front row is my best friend. 2. The car that is bright red is speeding. Adverb Clauses • An adverb clause is a subordinate clause used as an adverb. • Examples: 1. When I smiled at him he waved. 2. Because she wakes up early, she is always on time. Noun Clauses • A noun clause is a subordinate clause used as a noun. • Can be used as a subject, a complement, or an object of the preposition • Examples: 1. They asked who won. 2. My friend asked whoever was able to please stand. Clauses Clauses Independent Dependent Adjective Noun Adverb Questions??? Grammar Web Sites • • • • http://englishplus.com/grammar/ http://www.ucl.ac.uk/internet-grammar/ http://a4esl.org/q/j/ http://www.ucalgary.ca/UofC/eduweb/grammar Grammar Books • Prentice Hall Reference Guide to Grammar Usage (5th Ed.) By: Muriel Harris • The Writer’s Pocket Handbook By: Alfred Rosa and Paul Eschholz • Guide to Rapid Revision (8th Ed.) By: Daniel Pearlman and Paula Pearlman • English Grammar: Language as Human Behavior (2nd Ed.) By: Anita K. Barry More Grammar Books • Painless Grammar By: Rebecca Elliott, Ph.D. • Nitty-Gritty Grammar & More Nitty-Gritty Grammar By: Edith H. Fine & Judith P. Josephson • Essentials of English Grammar (2nd Ed.) By: L. Sue Baugh