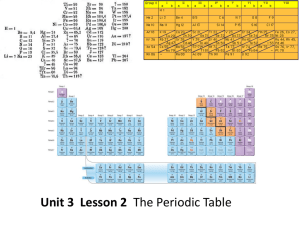
Periodic Trends Handout
... Periodic Trends Periodic Law • Properties of elements repeat themselves periodically as they are placed in order by atomic number. Mendeleev’s Periodic Table (1869) • Arrange elements in order of increasing atomic mass. • Arrange elements in columns so that elements with similar properties are in th ...
... Periodic Trends Periodic Law • Properties of elements repeat themselves periodically as they are placed in order by atomic number. Mendeleev’s Periodic Table (1869) • Arrange elements in order of increasing atomic mass. • Arrange elements in columns so that elements with similar properties are in th ...
Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table
... 4. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about valence electrons and chemical bonding. a. Most atoms are less stable when they have eight valence electrons. b. Atoms with eight valence electrons easily form compounds. c. Having eight valence electrons makes atoms very reactive. d. Atoms wi ...
... 4. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about valence electrons and chemical bonding. a. Most atoms are less stable when they have eight valence electrons. b. Atoms with eight valence electrons easily form compounds. c. Having eight valence electrons makes atoms very reactive. d. Atoms wi ...
File
... halogens in its properties Ans 9)Hydrogen has single electron in its valence shell and forms a positively charged this is similar to alkali metals such as sodium .There fore hydrogen resembles alkali metals.However its chemical properties are not similar to alkali metals.Hydrogen is gaseous and form ...
... halogens in its properties Ans 9)Hydrogen has single electron in its valence shell and forms a positively charged this is similar to alkali metals such as sodium .There fore hydrogen resembles alkali metals.However its chemical properties are not similar to alkali metals.Hydrogen is gaseous and form ...
document
... • Mass Number- the sum of the number of protons plus the number of neutrons • Atomic Number- the number of protons in the nucleus of an element • Symbol for an atomic nucleus- The element symbol with the mass number as a superscript on the left and the atomic number as a subscript on the left. ...
... • Mass Number- the sum of the number of protons plus the number of neutrons • Atomic Number- the number of protons in the nucleus of an element • Symbol for an atomic nucleus- The element symbol with the mass number as a superscript on the left and the atomic number as a subscript on the left. ...
Final Exam Review
... 4. What is the periodic law? THE PROPERTIES OF THE ELEMENTS REPEAT PERIODICALLY 5. What is a period? How many are there in the periodic table? A HORIZONTAL ROW IN THE PERIODIC TABLE; 7 6. What is a group (also called a family)? How many are there in the periodic table? A VERTICAL COLUMN IN THE PERIO ...
... 4. What is the periodic law? THE PROPERTIES OF THE ELEMENTS REPEAT PERIODICALLY 5. What is a period? How many are there in the periodic table? A HORIZONTAL ROW IN THE PERIODIC TABLE; 7 6. What is a group (also called a family)? How many are there in the periodic table? A VERTICAL COLUMN IN THE PERIO ...
Chapter 7-8 Power Point - Kawameeh Middle School
... (electrons) and reasoned that they must have a positive charge that balances them out. ...
... (electrons) and reasoned that they must have a positive charge that balances them out. ...
Understanding the Atom PP
... (electrons) and reasoned that they must have a positive charge that balances them out. ...
... (electrons) and reasoned that they must have a positive charge that balances them out. ...
The Periodic Table
... • Elements in group 2 are known as the alkaline earth metals. • Group 2 metals are harder, denser and stronger than alkali metals, and have higher melting points. • Less reactive than group 1, but still too reactive to be found in nature as free elements. ...
... • Elements in group 2 are known as the alkaline earth metals. • Group 2 metals are harder, denser and stronger than alkali metals, and have higher melting points. • Less reactive than group 1, but still too reactive to be found in nature as free elements. ...
periodic table
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
Periodic trends
... Malleable – hammered into sheets All solid at room temperature (except Hg- Mercury) Conductors of heat and electricity ...
... Malleable – hammered into sheets All solid at room temperature (except Hg- Mercury) Conductors of heat and electricity ...
2013 The Periodic Table
... have some chemical and physical properties of metals and other properties of nonmetals. In the periodic table, the metalloids lie along the border between metals and nonmetals. ...
... have some chemical and physical properties of metals and other properties of nonmetals. In the periodic table, the metalloids lie along the border between metals and nonmetals. ...
(halogens group) 4-write down the electronic configuration
... …………to…………inside the same group. 4-the highest element in electro negativity is…….while the most metallic element is ……… 5- in the group , by increasing the atomic number , the electro negativity………… . 6-as the atomic number increases in the same period ,the non metallic property…………. 7-each period ...
... …………to…………inside the same group. 4-the highest element in electro negativity is…….while the most metallic element is ……… 5- in the group , by increasing the atomic number , the electro negativity………… . 6-as the atomic number increases in the same period ,the non metallic property…………. 7-each period ...
WILF 1 - GCSE Chemistry Help
... If elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number, the problems with elements like tellurium and iodine are solved. Elements in the same group have the same number of outer shell electrons. It is the number of outer shell electrons which determines how the element behaves. Chlorine ...
... If elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number, the problems with elements like tellurium and iodine are solved. Elements in the same group have the same number of outer shell electrons. It is the number of outer shell electrons which determines how the element behaves. Chlorine ...
8th Science LF Sept 7-11
... Color the periodic table to distinguish location of metals, non-metals, and metalloids. Think Pair Share – Identify Periodic Table Trends Discover that Element Game from Discovery Education (print pgs. 2 and 10) Quick Write – See Critical Writing Prompt ...
... Color the periodic table to distinguish location of metals, non-metals, and metalloids. Think Pair Share – Identify Periodic Table Trends Discover that Element Game from Discovery Education (print pgs. 2 and 10) Quick Write – See Critical Writing Prompt ...
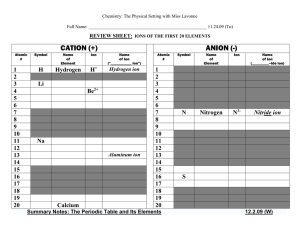
IONS OF THE FIRST 20 ELEMENTS
... The alkaline earth elements are metallic elements found in the second group of the periodic table. All alkaline earth elements have an oxidation number of +2, making them very reactive. Because of their reactivity, the alkaline metals are not found free in nature. The Alkaline Earth Metals are: Bery ...
... The alkaline earth elements are metallic elements found in the second group of the periodic table. All alkaline earth elements have an oxidation number of +2, making them very reactive. Because of their reactivity, the alkaline metals are not found free in nature. The Alkaline Earth Metals are: Bery ...
Core Chemistry Term 3 Final Exam 2007-08 S2
... 93. In what kind of reaction do two or more substances combine to form a new compound? a. decomposition reaction c. double-replacement reaction b. ionic reaction d. synthesis reaction 94. The equation AX A + X is the general (variable) equation for a a. synthesis reaction c. combustion reaction b. ...
... 93. In what kind of reaction do two or more substances combine to form a new compound? a. decomposition reaction c. double-replacement reaction b. ionic reaction d. synthesis reaction 94. The equation AX A + X is the general (variable) equation for a a. synthesis reaction c. combustion reaction b. ...
C1 - Powerpoint - tonyconnett.com
... 2. Group 1 atoms want to loose an electron, do you think it would be easier to remove an electron from Lithium or Cs? 3. What is the most reactive element in group 1? 4. Group 7 atoms want to gain an electron, which atom would most strongly attract an electron to the ‘gap’ in the outer shell? 5. Whi ...
... 2. Group 1 atoms want to loose an electron, do you think it would be easier to remove an electron from Lithium or Cs? 3. What is the most reactive element in group 1? 4. Group 7 atoms want to gain an electron, which atom would most strongly attract an electron to the ‘gap’ in the outer shell? 5. Whi ...
Review guide for Chemistry`s First Semester Exam Unit 1 Thinking
... Know the value for the density of water 8. Write the value of density for pure water Know what makes one substance more dense than a different substance 9. If you have 1 kg of lead and 1 kg of cotton, which takes up more space? 10. If you have a volume of 10 cm3 of lead and another volume of 10 cm3 ...
... Know the value for the density of water 8. Write the value of density for pure water Know what makes one substance more dense than a different substance 9. If you have 1 kg of lead and 1 kg of cotton, which takes up more space? 10. If you have a volume of 10 cm3 of lead and another volume of 10 cm3 ...
Atomic Structure - RHS Encore Academy
... 16. What are metalloids? (page 136) 17. What major change occurs as you move from left to right across the periodic table? (page 138) 18. What is a valence electron? Draw a SQUARE around each valence electron in the picture! (page 139) ...
... 16. What are metalloids? (page 136) 17. What major change occurs as you move from left to right across the periodic table? (page 138) 18. What is a valence electron? Draw a SQUARE around each valence electron in the picture! (page 139) ...
Periodic Table Notes 2
... showed similar patterns of chemical behavior were placed into groups. His chart was incomplete at the time, but Mendeleev predicted that new elements were yet to be discovered, so he left blank spaces in his first version of the periodic table. Over the years, modified versions of the original perio ...
... showed similar patterns of chemical behavior were placed into groups. His chart was incomplete at the time, but Mendeleev predicted that new elements were yet to be discovered, so he left blank spaces in his first version of the periodic table. Over the years, modified versions of the original perio ...
Periodic Table Name: Practice Review H
... grouped in A) periods C) horizontal rows E) horizontal families ...
... grouped in A) periods C) horizontal rows E) horizontal families ...
Unit 1: Introduction to Chemistry
... malleable = able to be hammered into thin sheets; ductile = able to be drawn into fine wire 3. List three properties of nonmetals. has a low density, low melting point, and is a poor conductor of heat and electricity 4. Solid nonmetals, such as _carbon_ and _sulfur_, have a _dull_ appearance. They _ ...
... malleable = able to be hammered into thin sheets; ductile = able to be drawn into fine wire 3. List three properties of nonmetals. has a low density, low melting point, and is a poor conductor of heat and electricity 4. Solid nonmetals, such as _carbon_ and _sulfur_, have a _dull_ appearance. They _ ...
Atomic radii generally decrease along each period (row) of the
... the outermost level is completely filled; therefore, the additional electron that the following alkali metal (Group I) possesses will go into the next principal energy level, accounting for the increase in the atomic radius. Therefore, atomic size, or radius, increases as one moves down a group in t ...
... the outermost level is completely filled; therefore, the additional electron that the following alkali metal (Group I) possesses will go into the next principal energy level, accounting for the increase in the atomic radius. Therefore, atomic size, or radius, increases as one moves down a group in t ...