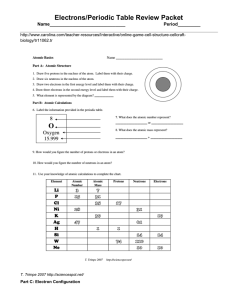
Electrons/Periodic Table Review Packet Name______________________________ Period_________
... b. metals with unpredictable properties c. a halogen d. make good semiconductors e. alkali metals f. ...
... b. metals with unpredictable properties c. a halogen d. make good semiconductors e. alkali metals f. ...
the periodic law
... 7. Period trends – ionization energies of main group elements increase across each period a. Slight increase between IIA and IIIA due to p-sublevels having a higher energy so electrons are easier to remove b. Slight decrease between VA and VIA due to paired electrons in the p-sublevel. Paired e- ha ...
... 7. Period trends – ionization energies of main group elements increase across each period a. Slight increase between IIA and IIIA due to p-sublevels having a higher energy so electrons are easier to remove b. Slight decrease between VA and VIA due to paired electrons in the p-sublevel. Paired e- ha ...
Cations (positive ions) are smaller than their respective atoms.
... Properties of element types: 1) Metals- high luster, good conductors, ductile, malleable, most are solid at room temp (except Hg is liquid) 2)Nonmetals- low luster, poor conductors, very brittle, various states of matter at room temperature (ex: S is solid, O is gas, Br is liquid) 3) Semi-Conductor ...
... Properties of element types: 1) Metals- high luster, good conductors, ductile, malleable, most are solid at room temp (except Hg is liquid) 2)Nonmetals- low luster, poor conductors, very brittle, various states of matter at room temperature (ex: S is solid, O is gas, Br is liquid) 3) Semi-Conductor ...
CH04_Tro_LectureNotes_081 - Tutor
... rather than a metal. It is a colorless, diatomic gas, which means it occurs naturally in molecules consisting of two hydrogen atoms. It reacts with other nonmetals to form molecular compounds and reacts with metals to form hydrides. Ability to release hydrogen ions is an important characteristic of ...
... rather than a metal. It is a colorless, diatomic gas, which means it occurs naturally in molecules consisting of two hydrogen atoms. It reacts with other nonmetals to form molecular compounds and reacts with metals to form hydrides. Ability to release hydrogen ions is an important characteristic of ...
Period - scienceathylands
... • They are neutralised by acids to form salt and water. e.g. MgO(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l) or Ca(OH)2(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l) As the products of these reactions are soluble you will see the solid oxides or hydroxides dissolve ...
... • They are neutralised by acids to form salt and water. e.g. MgO(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l) or Ca(OH)2(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l) As the products of these reactions are soluble you will see the solid oxides or hydroxides dissolve ...
Chapter 4: The Periodic Table
... 8. What trends are evident in atomic size as you proceed down a group of elements? How do each of these trends progress as you move across a period? Atomic size increases, ionization energy decreases, and electron affinity decreases from top to bottom in a group. Atomic size decreases, ionization en ...
... 8. What trends are evident in atomic size as you proceed down a group of elements? How do each of these trends progress as you move across a period? Atomic size increases, ionization energy decreases, and electron affinity decreases from top to bottom in a group. Atomic size decreases, ionization en ...
Trends on the Periodic Table
... Periodic Trend: EA ______________ as we move left to right (# gets more negative) atom gets smaller with a larger (+) nuclear charge Group trend: EA __________________ as we move down the table (# gets more positive) shell is farther from nucleus ...
... Periodic Trend: EA ______________ as we move left to right (# gets more negative) atom gets smaller with a larger (+) nuclear charge Group trend: EA __________________ as we move down the table (# gets more positive) shell is farther from nucleus ...
Ch. 6 - The Periodic Table
... Relatively soft, but harder than alkali metals. Two valence electrons. Although not as reactive as alkali metals, still very reactive and not found in nature in the elemental state. ◦ Obtained in the pure form through electrolysis of their fused salts. ...
... Relatively soft, but harder than alkali metals. Two valence electrons. Although not as reactive as alkali metals, still very reactive and not found in nature in the elemental state. ◦ Obtained in the pure form through electrolysis of their fused salts. ...
Chapter TWO
... Elements are arranged in an increasing order according to their atomic numbers , where each element has one electron more than the element before it . This is based on Aufbau principle . ...
... Elements are arranged in an increasing order according to their atomic numbers , where each element has one electron more than the element before it . This is based on Aufbau principle . ...
Atomic Theory - Aurora City Schools
... called an isotope. • That’s why atomic mass is not a whole number, it averages all the isotopes • Write the mass number and atomic number to left of symbol ...
... called an isotope. • That’s why atomic mass is not a whole number, it averages all the isotopes • Write the mass number and atomic number to left of symbol ...
The Modern Periodic Table
... elements are called Lanthanides. Lanthanides are a part of sixth period. • The seventh period is incomplete. Some of the elements are not discovered yet. 14 elements (Atomic # 90103) of this period following the element Actinium (Ac) are placed separately from the body of the periodic table. These e ...
... elements are called Lanthanides. Lanthanides are a part of sixth period. • The seventh period is incomplete. Some of the elements are not discovered yet. 14 elements (Atomic # 90103) of this period following the element Actinium (Ac) are placed separately from the body of the periodic table. These e ...
File
... reactivity of the alkaline earth metals increases as we go down the family! • However, these metals are not as reactive as the alkali metals in the same period! • So Mg is less reactive than Na, but more reactive than Be!!! • Location allows prediction of reactivity! ...
... reactivity of the alkaline earth metals increases as we go down the family! • However, these metals are not as reactive as the alkali metals in the same period! • So Mg is less reactive than Na, but more reactive than Be!!! • Location allows prediction of reactivity! ...
Chapter 4
... produce the first orderly arrangement, or ___________ table, of all 63 elements known at the time. Mendeleev wrote the symbol for each element, along with the physical and chemical properties and the relative atomic mass of the element, on a card. Mendeleev started a new row each time he noticed tha ...
... produce the first orderly arrangement, or ___________ table, of all 63 elements known at the time. Mendeleev wrote the symbol for each element, along with the physical and chemical properties and the relative atomic mass of the element, on a card. Mendeleev started a new row each time he noticed tha ...
Periodic Table Properties Notes s1
... An ion is an atom that has lost or gained electrons and has a negative or positive charge. • Atoms that lose electrons have a positive charge. Atoms that gain electrons have a negative charge. • What ion an atom will form can be determined by its group on the periodic table. ...
... An ion is an atom that has lost or gained electrons and has a negative or positive charge. • Atoms that lose electrons have a positive charge. Atoms that gain electrons have a negative charge. • What ion an atom will form can be determined by its group on the periodic table. ...
chem 1411 – chapter 8
... Some elements of the second and third periods which are diagonally positioned, show similarities in their properties. Ex. Li and Mg, Be and Al, B and Si Diagonal relationship is due to the closeness of the charge densities (magnitude of charge / volume) of their cations. Variation in Chemical Proper ...
... Some elements of the second and third periods which are diagonally positioned, show similarities in their properties. Ex. Li and Mg, Be and Al, B and Si Diagonal relationship is due to the closeness of the charge densities (magnitude of charge / volume) of their cations. Variation in Chemical Proper ...
Chapter 5 - The Periodic Law
... Periods and the Blocks of the Periodic Table A. Periods 1. Horizontal rows on the periodic table 2. Period number corresponds to the highest principal quantum number of the elements in the period B. Sublevel Blocks 1. Periodic table can be broken into blocks corresponding to s, p, d, f sublevels II. ...
... Periods and the Blocks of the Periodic Table A. Periods 1. Horizontal rows on the periodic table 2. Period number corresponds to the highest principal quantum number of the elements in the period B. Sublevel Blocks 1. Periodic table can be broken into blocks corresponding to s, p, d, f sublevels II. ...
Periodic trends - poynette.k12.wi.us
... Prepare a graph of first, second, and third ionization energy vs. atomic number. 1. What is a kJ/mol? ...
... Prepare a graph of first, second, and third ionization energy vs. atomic number. 1. What is a kJ/mol? ...
The Periodic Table - Anderson High School
... (like in salt). • Soft enough to cut with a butter knife ...
... (like in salt). • Soft enough to cut with a butter knife ...
Periodic Trends Student
... – Moseley • Revised Mendeleev’s table and gave us the one we use today • Elements arranged by increasing ATOMIC NUMBERS! ...
... – Moseley • Revised Mendeleev’s table and gave us the one we use today • Elements arranged by increasing ATOMIC NUMBERS! ...
II. Ch. 5.2: Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
... Name two other elements that would have similar chemical properties as chlorine. Explain your ...
... Name two other elements that would have similar chemical properties as chlorine. Explain your ...
Periodic Table
... layer of electrons at a specific energy level • Each period begins with a new outer electron orbital • Each period ends with a completely filled outer orbital that has the maximum number of electrons for that orbital. ...
... layer of electrons at a specific energy level • Each period begins with a new outer electron orbital • Each period ends with a completely filled outer orbital that has the maximum number of electrons for that orbital. ...
Chapter 3: Atoms and the periodic table
... an isotope has, given its symbol, atomic number, and mass number; Describe how the abundance of isotopes affects an element’s average atomic mass. ...
... an isotope has, given its symbol, atomic number, and mass number; Describe how the abundance of isotopes affects an element’s average atomic mass. ...
17.3 The periodic table
... Use the periodic table to find the name, atomic number, symbols, the average atomic mass , group, and the period for the first 20 elements Define the periodic law Compare and contrast the ways in which Mendeleev and Moseley classify the elements in the periodic table ...
... Use the periodic table to find the name, atomic number, symbols, the average atomic mass , group, and the period for the first 20 elements Define the periodic law Compare and contrast the ways in which Mendeleev and Moseley classify the elements in the periodic table ...