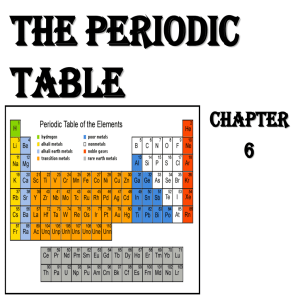
The Periodic Table
... Warm up: why are tables useful to us? In the early 1800s, scientists began to classify elements. German chemist Dobereiner grouped them into triads of similar properties. English chemist Newlands, arranged them based on mass. ...
... Warm up: why are tables useful to us? In the early 1800s, scientists began to classify elements. German chemist Dobereiner grouped them into triads of similar properties. English chemist Newlands, arranged them based on mass. ...
number of protons - Waterford Public Schools
... Metals lose electrons, so they form cations Non-metals gain electrons, so they form anions Can be determined by looking at the Periodic Table Since ions are formed by losing or gaining valence electrons, the group number also represents the charge the elements in that group like to form! ...
... Metals lose electrons, so they form cations Non-metals gain electrons, so they form anions Can be determined by looking at the Periodic Table Since ions are formed by losing or gaining valence electrons, the group number also represents the charge the elements in that group like to form! ...
Writing and Naming Chemical Formulas
... Metals lose electrons, so they form cations Non-metals gain electrons, so they form anions Can be determined by looking at the Periodic Table Since ions are formed by losing or gaining valence electrons, the group number also represents the charge the elements in that group like to form! ...
... Metals lose electrons, so they form cations Non-metals gain electrons, so they form anions Can be determined by looking at the Periodic Table Since ions are formed by losing or gaining valence electrons, the group number also represents the charge the elements in that group like to form! ...
Atomic Structure Test – Study Guide
... 2. Proton – positive charge; located in the center or nucleus of the atom 3. Neutron - no charge; located in the center or nucleus of the atom What subatomic particles are in the nucleus of the atom and what is the charge of the nucleus? Answer: Protons and neutrons so the charge of the nucleus is p ...
... 2. Proton – positive charge; located in the center or nucleus of the atom 3. Neutron - no charge; located in the center or nucleus of the atom What subatomic particles are in the nucleus of the atom and what is the charge of the nucleus? Answer: Protons and neutrons so the charge of the nucleus is p ...
Water Metal Hydroxide + Hydrogen
... The atomic radius of an atom is defined as the distance of closest approach to another atom and is the distance at which the mutual repulsion of the electron clouds and the mutual attraction of the nuclear charge of each for the electrons of the other are in equilibrium. The size of an atom in a mol ...
... The atomic radius of an atom is defined as the distance of closest approach to another atom and is the distance at which the mutual repulsion of the electron clouds and the mutual attraction of the nuclear charge of each for the electrons of the other are in equilibrium. The size of an atom in a mol ...
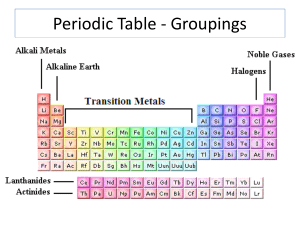
Groups in a Periodic Table
... Ions: An atom or a group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge resulting from a loss or gain of electrons, respectively. Cation: An ion with a positive charge Anion: An ion with a negative charge ...
... Ions: An atom or a group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge resulting from a loss or gain of electrons, respectively. Cation: An ion with a positive charge Anion: An ion with a negative charge ...
Unit 9: Periodicity
... The nitrogen family is named after the element that makes up 78% of our atmosphere. This family includes nonmetals, metalloids, and metals. Atoms in the nitrogen family have 5 valence electrons. They tend to share electrons when they bond. Other elements in this family are phosphorus, arseni ...
... The nitrogen family is named after the element that makes up 78% of our atmosphere. This family includes nonmetals, metalloids, and metals. Atoms in the nitrogen family have 5 valence electrons. They tend to share electrons when they bond. Other elements in this family are phosphorus, arseni ...
Atomic radii decrease from left to right across a period
... Explanation of the General Trends The way atomic radius varies with increasing atomic numbercan be explained by the arrangement of electrons in shells of fixed capacity. Shells closer to the nucleus—those with a smaller radius—are generally filled first, since the negatively charged electrons are at ...
... Explanation of the General Trends The way atomic radius varies with increasing atomic numbercan be explained by the arrangement of electrons in shells of fixed capacity. Shells closer to the nucleus—those with a smaller radius—are generally filled first, since the negatively charged electrons are at ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE - IGCSE STUDY BANK
... indicator is green. The salt is a typical ionic compound ie a brittle solid with a high melting point. Similarly potassium and bromine form potassium bromide KBr, or lithium and iodine form lithium iodide LiI. Again note the group formula pattern. If aluminium or iron is heated strongly in a stream ...
... indicator is green. The salt is a typical ionic compound ie a brittle solid with a high melting point. Similarly potassium and bromine form potassium bromide KBr, or lithium and iodine form lithium iodide LiI. Again note the group formula pattern. If aluminium or iron is heated strongly in a stream ...
Chapter 3 Physical Science - St. Pius X Classical Academy
... Introduction to Atoms Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment Rutherford was surprised that a few particles were deflected strongly. Which are the paths of the particles that were not predicted by Thomson’s atomic model? ...
... Introduction to Atoms Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment Rutherford was surprised that a few particles were deflected strongly. Which are the paths of the particles that were not predicted by Thomson’s atomic model? ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table of Elements: The Secret
... o The group number—usually depicted by a Roman numeral above the group—refers to the number of valence electrons in the outermost electron shell. Ex: Group IA elements (Alkali Metals) have one valence electron in their outermost shells. o The period number refers to the number of electron shells or ...
... o The group number—usually depicted by a Roman numeral above the group—refers to the number of valence electrons in the outermost electron shell. Ex: Group IA elements (Alkali Metals) have one valence electron in their outermost shells. o The period number refers to the number of electron shells or ...
Writing and Naming Chemical Formulas
... Metals lose electrons, so they form cations Non-metals gain electrons, so they form anions Can be determined by looking at the Periodic Table Since ions are formed by losing or gaining valence electrons, the group number also represents the charge the elements in that group like to form! ...
... Metals lose electrons, so they form cations Non-metals gain electrons, so they form anions Can be determined by looking at the Periodic Table Since ions are formed by losing or gaining valence electrons, the group number also represents the charge the elements in that group like to form! ...
The Periodic Law
... Do not occur in nature as free elements Good conductors with low melting points Ductile and malleable (can be cut with a knife) Very reactive (with water to make hydrogen gas) Usually held in kerosene due to the high reacting level • Used in lights, electricity technology ...
... Do not occur in nature as free elements Good conductors with low melting points Ductile and malleable (can be cut with a knife) Very reactive (with water to make hydrogen gas) Usually held in kerosene due to the high reacting level • Used in lights, electricity technology ...
CHAPTER-3 CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY
... The carbonates of alkaline earth metals are relatively less stable. On heating, they decompose to give corresponding oxide and CO 2 gas. The decomposition temperature for alkaline earth metal carbonates increases as we go down the group. Anomalous Properties of Second Period Elements Their anomalous ...
... The carbonates of alkaline earth metals are relatively less stable. On heating, they decompose to give corresponding oxide and CO 2 gas. The decomposition temperature for alkaline earth metal carbonates increases as we go down the group. Anomalous Properties of Second Period Elements Their anomalous ...
The Periodic Table
... periodic table (cont) • Dimitri Mendeleev, in 1869, used this information and produced the first orderly arrangement of all 63 known elements. • He arranged them in a similar way to Newlands and created the first periodic table. • Mendeleev started a new row each time he noticed that the chemical pr ...
... periodic table (cont) • Dimitri Mendeleev, in 1869, used this information and produced the first orderly arrangement of all 63 known elements. • He arranged them in a similar way to Newlands and created the first periodic table. • Mendeleev started a new row each time he noticed that the chemical pr ...
for the quiz on 6 mar
... 19.98 In order to have a stronger acid, you want to make the O-H bond weaker. (There is a figure on p.646 in Ch. 15 which may help with this…) If you increase the number of oxygens in the molecule, you are drawing more electron density away from the Cl by bonding it to more (greater number of) elect ...
... 19.98 In order to have a stronger acid, you want to make the O-H bond weaker. (There is a figure on p.646 in Ch. 15 which may help with this…) If you increase the number of oxygens in the molecule, you are drawing more electron density away from the Cl by bonding it to more (greater number of) elect ...
PERIODIC TABLE
... 6. The actinides have an unstable arrangement of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. They are usually radioactive. ...
... 6. The actinides have an unstable arrangement of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. They are usually radioactive. ...
File
... table in Part 1 and the diagram above to answer the following questions. Record the symbols of the elements in Period 2 so they are stretched out horizontally across a page. Place the symbols of the elements in Period 3 directly beneath them, as they appear in the table. Most of the elements are sol ...
... table in Part 1 and the diagram above to answer the following questions. Record the symbols of the elements in Period 2 so they are stretched out horizontally across a page. Place the symbols of the elements in Period 3 directly beneath them, as they appear in the table. Most of the elements are sol ...
Topic 5 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... table in Part 1 and the diagram above to answer the following questions. Record the symbols of the elements in Period 2 so they are stretched out horizontally across a page. Place the symbols of the elements in Period 3 directly beneath them, as they appear in the table. Most of the elements are sol ...
... table in Part 1 and the diagram above to answer the following questions. Record the symbols of the elements in Period 2 so they are stretched out horizontally across a page. Place the symbols of the elements in Period 3 directly beneath them, as they appear in the table. Most of the elements are sol ...
File
... 6. Which of the following statements are true for the atomic radius within the same period? I) Moving from left to right across a given period, there is an increase in the number of electrons, protons and neutrons, and thus the atomic radius increases. II) The atomic radius decreases with the increa ...
... 6. Which of the following statements are true for the atomic radius within the same period? I) Moving from left to right across a given period, there is an increase in the number of electrons, protons and neutrons, and thus the atomic radius increases. II) The atomic radius decreases with the increa ...
Periodic Table
... • All atoms what to have a balanced charge but they also want to have a full valance shell. Atoms will often take, loose or share electrons on order to fill the valance. All atoms that have the same # of electrons behave in a similar fashion. The atoms with fewer electrons on the valance and/or the ...
... • All atoms what to have a balanced charge but they also want to have a full valance shell. Atoms will often take, loose or share electrons on order to fill the valance. All atoms that have the same # of electrons behave in a similar fashion. The atoms with fewer electrons on the valance and/or the ...
atoms - sciencegeek
... maximum of two electrons. The electrons must have opposite spins. Hund’s Rule: When electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron ...
... maximum of two electrons. The electrons must have opposite spins. Hund’s Rule: When electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron ...
Matter ppt NOTES
... bonds with one or more atoms to fill their outermost energy level (valence!) Compounds form when atoms are more stable in a combined form Most stable elements = Noble gases ...
... bonds with one or more atoms to fill their outermost energy level (valence!) Compounds form when atoms are more stable in a combined form Most stable elements = Noble gases ...