Name Date ______ Period ______ Chapter 5: Periodic Table
... 1. Organized elements on the periodic table by increasing ___________________ ________________________. 2. Fixed problems in Mendeleev’s arrangement. C. Periodic Law 1. Properties of elements repeat in a predictable way when ___________________ _________________________ are used to arrange elements ...
... 1. Organized elements on the periodic table by increasing ___________________ ________________________. 2. Fixed problems in Mendeleev’s arrangement. C. Periodic Law 1. Properties of elements repeat in a predictable way when ___________________ _________________________ are used to arrange elements ...
Ch 5 Notes
... • (excluding H), 1 valence e• Very reactive, especially with water • Soft, shiny white metals (can be cut with a knife!) ...
... • (excluding H), 1 valence e• Very reactive, especially with water • Soft, shiny white metals (can be cut with a knife!) ...
Regents Chemistry NOTE PACKET
... http://www.scienceclarified.com/everyday/Real-Life-Chemistry-Vol-1/Alkaline-Earth-Metals-Real-life-applications.html ...
... http://www.scienceclarified.com/everyday/Real-Life-Chemistry-Vol-1/Alkaline-Earth-Metals-Real-life-applications.html ...
Metals
... • Share properties of both metals and nonmetals • Can be shiny or dull, conduct ok, ductile and malleable or brittle • These elements have become really important because of the computer revolution • Computer chips are made out of semiconductors ...
... • Share properties of both metals and nonmetals • Can be shiny or dull, conduct ok, ductile and malleable or brittle • These elements have become really important because of the computer revolution • Computer chips are made out of semiconductors ...
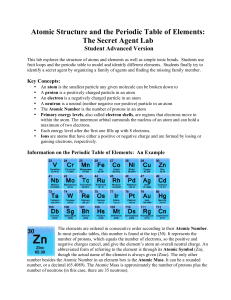
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table of Elements: The Secret
... Each energy level after the first one fills up with 8 electrons. Ions are atoms that have either a positive or negative charge and are formed by losing or gaining electrons, respectively. ...
... Each energy level after the first one fills up with 8 electrons. Ions are atoms that have either a positive or negative charge and are formed by losing or gaining electrons, respectively. ...
period
... Note that both hydrogen (H) and potassium (K) have just 1 electron in their outermost shell. Note also that these elements are both found in the 1st column of the periodic table. This is not a coincidence! ...
... Note that both hydrogen (H) and potassium (K) have just 1 electron in their outermost shell. Note also that these elements are both found in the 1st column of the periodic table. This is not a coincidence! ...
3 Periodic Trends
... Affinity”, and one rectangle “Ionization Energy”. Draw TWO arrows on each labeled indicating the trends. **Indicate if the arrow is increasing or decreasing. Example ...
... Affinity”, and one rectangle “Ionization Energy”. Draw TWO arrows on each labeled indicating the trends. **Indicate if the arrow is increasing or decreasing. Example ...
Chapter 6 notes
... Chemists used the properties of elements to sort them into groups Mendeleev's Periodic Table In ___________, a Russian chemist and teacher, Dmitri Mendeleev, published a table of the elements. Later that year, a German chemist, Lothar Meyer, published a nearly identical table. __________________ arr ...
... Chemists used the properties of elements to sort them into groups Mendeleev's Periodic Table In ___________, a Russian chemist and teacher, Dmitri Mendeleev, published a table of the elements. Later that year, a German chemist, Lothar Meyer, published a nearly identical table. __________________ arr ...
Notes for Standard 1 Objective 3 (Periodic Table)
... mass units). Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. For example, carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, but carbon-13 has 6 protons and 7 neutrons. Carbon-12 and carbon-13 are isotopes. On the periodic table, vertical columns are called groups a ...
... mass units). Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. For example, carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, but carbon-13 has 6 protons and 7 neutrons. Carbon-12 and carbon-13 are isotopes. On the periodic table, vertical columns are called groups a ...
Relationships in The PeriodicTable
... table by arranging elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses. Discrepancies in early versions of the periodic table were resolved by arranging the elements in order of their atomic numbers. 2.Electron configuration determines the properties of an element. The modern periodic table clas ...
... table by arranging elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses. Discrepancies in early versions of the periodic table were resolved by arranging the elements in order of their atomic numbers. 2.Electron configuration determines the properties of an element. The modern periodic table clas ...
graphingtrendschemistry
... b.) Fluorine would have the highest electronegativity in this set, and it’s actually the element with the highest electronegativity out of all the elements, and in general, elements in the halogen element group have high electronegative values. ...
... b.) Fluorine would have the highest electronegativity in this set, and it’s actually the element with the highest electronegativity out of all the elements, and in general, elements in the halogen element group have high electronegative values. ...
S8P1-study-guide
... the number of electrons each energy level can hold. The first energy level holds 2 electrons, the second holds 8, the third holds 18, the fourth holds 32, and the fifth holds 50. The number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom is referred to as the atoms valence electrons. The numbe ...
... the number of electrons each energy level can hold. The first energy level holds 2 electrons, the second holds 8, the third holds 18, the fourth holds 32, and the fifth holds 50. The number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom is referred to as the atoms valence electrons. The numbe ...
California Standards Practice
... A. Its density and weight both decrease slightly. B. Its density decreases significantly, and its weight decreases slightly. C. Its density and weight both decrease significantly. D. Its density increases significantly, and its weight decreases slightly. ...
... A. Its density and weight both decrease slightly. B. Its density decreases significantly, and its weight decreases slightly. C. Its density and weight both decrease significantly. D. Its density increases significantly, and its weight decreases slightly. ...
2 periodic table pd9
... The elements in the middle of the periodic table (or the d-block are transition metals called the _________________. ...
... The elements in the middle of the periodic table (or the d-block are transition metals called the _________________. ...
Study Guide
... the number of electrons each energy level can hold. The first energy level holds 2 electrons, the second holds 8, the third holds 18, the fourth holds 32, and the fifth holds 50. The number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom is referred to as the atoms valence electrons. The numbe ...
... the number of electrons each energy level can hold. The first energy level holds 2 electrons, the second holds 8, the third holds 18, the fourth holds 32, and the fifth holds 50. The number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom is referred to as the atoms valence electrons. The numbe ...
Diff Chemistry
... or higher) first ionization energies. What do you think? Metals are more likely to (lose or gain) electrons to form (cations or anions). ...
... or higher) first ionization energies. What do you think? Metals are more likely to (lose or gain) electrons to form (cations or anions). ...
the periodic table
... due to increase in nuclear charge iii) Decrease in size becomes smaller with increasing atomic number due to increased repulsion between electrons ...
... due to increase in nuclear charge iii) Decrease in size becomes smaller with increasing atomic number due to increased repulsion between electrons ...
Unit Bohr Model and Electromagnetic Radiation - Jones
... 1. Gaining energy results in the electron moving from its ground state to a higher energy level. 2. When the electron moves to a lower energy level, it releases the energy difference in the two levels as electromagnetic radiation (emissions spectrum). Chm.1.3 Understand the physical and chemical pro ...
... 1. Gaining energy results in the electron moving from its ground state to a higher energy level. 2. When the electron moves to a lower energy level, it releases the energy difference in the two levels as electromagnetic radiation (emissions spectrum). Chm.1.3 Understand the physical and chemical pro ...
Section 6.1 Development of the Modern Periodic Table
... Development of the Periodic Table (cont.) • Meyer and Mendeleev both demonstrated a connection between atomic mass and elemental properties. • Moseley rearranged the table by increasing atomic number, and resulted in a clear periodic pattern. • Periodic repetition of chemical and physical propertie ...
... Development of the Periodic Table (cont.) • Meyer and Mendeleev both demonstrated a connection between atomic mass and elemental properties. • Moseley rearranged the table by increasing atomic number, and resulted in a clear periodic pattern. • Periodic repetition of chemical and physical propertie ...
Untitled
... The Modern Periodic Table (cont.) • Elements are classified as metals, non-metals, and metalloids. • Metals are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. • Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hyd ...
... The Modern Periodic Table (cont.) • Elements are classified as metals, non-metals, and metalloids. • Metals are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. • Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hyd ...
Adv Chem Multiple Choice Practice: The Periodic Table
... as you move from top to bottom within a group. c. Electronegativity generally is higher for metals than for nonmetals. d. Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a period. ____ 37. Compared with the electronegativities of the elements on the left side of a period, the electro ...
... as you move from top to bottom within a group. c. Electronegativity generally is higher for metals than for nonmetals. d. Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a period. ____ 37. Compared with the electronegativities of the elements on the left side of a period, the electro ...
The Periodic Table
... Trends in Atomic Size Atomic size is an atom’s atomic radius, or one-half the distance between two like atoms when they are joined together. Atomic size generally increases from top to bottom within a group because the number of energy levels increases. Atomic size decreases from left to right acros ...
... Trends in Atomic Size Atomic size is an atom’s atomic radius, or one-half the distance between two like atoms when they are joined together. Atomic size generally increases from top to bottom within a group because the number of energy levels increases. Atomic size decreases from left to right acros ...
Section 6.1 Development of the Modern Periodic Table
... The Modern Periodic Table (cont.) • Vertical columns of elements are called ___________ • Rows of elements are called _________ • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements (or the main group elements). ...
... The Modern Periodic Table (cont.) • Vertical columns of elements are called ___________ • Rows of elements are called _________ • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements (or the main group elements). ...
Changes in matter
... Elements a) Elements have atoms of only one kind, having the same number of protons. There are a little more than 100 different elements. b)The periodic table organizes elements with common properties. c)Atomic symbol and atomic number d)Well known elements and their symbols ...
... Elements a) Elements have atoms of only one kind, having the same number of protons. There are a little more than 100 different elements. b)The periodic table organizes elements with common properties. c)Atomic symbol and atomic number d)Well known elements and their symbols ...