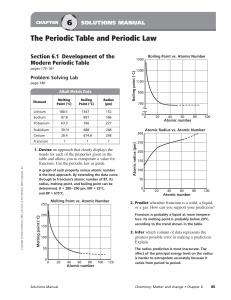
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... ordered differently than they are in the existing table? Argon and potassium would be switched. Cobalt and nickel would be switched. Tellurium and iodine would be switched. ...
... ordered differently than they are in the existing table? Argon and potassium would be switched. Cobalt and nickel would be switched. Tellurium and iodine would be switched. ...
11. Patterns in the Periodic Table
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
11. Patterns in the Periodic Table
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
File - eScience@Kings
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
Periodicity
... outermost s and nearby d sublevel contain electrons. The inner transition metals: In these metallic elements, the outermost s and nearby f sublevel generally contain electrons. ...
... outermost s and nearby d sublevel contain electrons. The inner transition metals: In these metallic elements, the outermost s and nearby f sublevel generally contain electrons. ...
Periodic Table Trends - Peoria Public Schools
... Periodic Table Trends Atomic Radii, Ionization Energy, & Electronegativity ...
... Periodic Table Trends Atomic Radii, Ionization Energy, & Electronegativity ...
Chapter 5 study guide - Peoria Public Schools
... At the completion of chapter 13 you should be able to... 1. Describe the contribution of each of the following to the development of the periodic table: a. Dobereiner b. Newlands c. Mendeleev d. Moseley 2. State Mendeleev's periodic law. 3. Describe how Mendeleev's periodic table is organized. 4. Ex ...
... At the completion of chapter 13 you should be able to... 1. Describe the contribution of each of the following to the development of the periodic table: a. Dobereiner b. Newlands c. Mendeleev d. Moseley 2. State Mendeleev's periodic law. 3. Describe how Mendeleev's periodic table is organized. 4. Ex ...
Week 1 (wk1) - Riverside Local Schools
... Cr2O3, into two of the dimples of a well plate. Add 20 drops of 6 M NaOH to one dimple and 20 drops of 6 M HCl to the other dimple. Stir the solution with a stirring rod and record your results in Data Table 2. ...
... Cr2O3, into two of the dimples of a well plate. Add 20 drops of 6 M NaOH to one dimple and 20 drops of 6 M HCl to the other dimple. Stir the solution with a stirring rod and record your results in Data Table 2. ...
Please answer the following using complete sentences on loose leaf
... As atomic number increases, the ionization energy decreases since the shielding effect is increases resulting in the outer electrons being held less tightly. 12. How does ionization energy vary within a period on the periodic table? Why? As atomic number increases, the ionization energy increases si ...
... As atomic number increases, the ionization energy decreases since the shielding effect is increases resulting in the outer electrons being held less tightly. 12. How does ionization energy vary within a period on the periodic table? Why? As atomic number increases, the ionization energy increases si ...
The Periodic Table - Crestwood Local Schools
... The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. The octet rule is useful for predicting what types of ions an element is likely to ...
... The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. The octet rule is useful for predicting what types of ions an element is likely to ...
Ch 4-1 Notes
... incompletely filled d sublevels are responsible for many characteristic properties of the d block elements. 1. Atomic Radii -Atomic Radius is one-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together. generally decrease across a period the decrease is less than that for m ...
... incompletely filled d sublevels are responsible for many characteristic properties of the d block elements. 1. Atomic Radii -Atomic Radius is one-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together. generally decrease across a period the decrease is less than that for m ...
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts & Connections 4th Edition
... Conclusions Continued • Valence electrons are the outermost electrons and are involved in chemical reactions. • We can write electron dot formulas for elements which indicate the number of valence electrons. • Ionization energy is the amount of energy that is required to remove an electron from an ...
... Conclusions Continued • Valence electrons are the outermost electrons and are involved in chemical reactions. • We can write electron dot formulas for elements which indicate the number of valence electrons. • Ionization energy is the amount of energy that is required to remove an electron from an ...
Periodic Trends C12-2-07
... 3. Lightium (L): This is the lightest of elements; aliens previously used it in their aircraft until their aircraft caught fire in a horrific accident. 4. Breathium(Br): When combined with Lightium (L), it makes the alien's most common liquid whose formula is L 2 Br. 5. Francium (F): A metal found i ...
... 3. Lightium (L): This is the lightest of elements; aliens previously used it in their aircraft until their aircraft caught fire in a horrific accident. 4. Breathium(Br): When combined with Lightium (L), it makes the alien's most common liquid whose formula is L 2 Br. 5. Francium (F): A metal found i ...
Periodic Table
... Conclusions Continued • Valence electrons are the outermost electrons and are involved in chemical reactions. • We can write electron dot formulas for elements which indicate the number of valence electrons. • Ionization energy is the amount of energy that is required to remove an electron from an ...
... Conclusions Continued • Valence electrons are the outermost electrons and are involved in chemical reactions. • We can write electron dot formulas for elements which indicate the number of valence electrons. • Ionization energy is the amount of energy that is required to remove an electron from an ...
What is the PERIODIC TABLE?
... Success Criteria: Can I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? (SPI0807.9.1) Can I use the Periodic Table to determine the properties of an element? (SPI0807.9.9) ...
... Success Criteria: Can I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? (SPI0807.9.1) Can I use the Periodic Table to determine the properties of an element? (SPI0807.9.9) ...
Organic Functional Groups: Halocarbons
... • The halogens are in the second column from the right. • Astatine (At) is not included: it is unstable and extremely rare. • Halogens each have seven valence electrons – three more than carbon. • Halogens are very hungry to gain an 8th electron. When they do, the eight electrons collectively drop i ...
... • The halogens are in the second column from the right. • Astatine (At) is not included: it is unstable and extremely rare. • Halogens each have seven valence electrons – three more than carbon. • Halogens are very hungry to gain an 8th electron. When they do, the eight electrons collectively drop i ...
Mendeleev`s Periodic Table of the Elements The periodic table is
... Isotopes and Radioactivity The periodic table comprises elements. Type of elemental is determined by number of protons, termed the atomic number (Z). It is possible for atoms of the same element to have different numbers of neutrons and hence different mass numbers. Such species are called isotopes. ...
... Isotopes and Radioactivity The periodic table comprises elements. Type of elemental is determined by number of protons, termed the atomic number (Z). It is possible for atoms of the same element to have different numbers of neutrons and hence different mass numbers. Such species are called isotopes. ...
Chapter 6 Periodic Table Lecture Notes
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
Study guide for periodic table trends. A. By referring to electron
... A. I ONLY B. I AND II ONLY C. I AND III ONLY D. I, II AND III 12. Element X is in group 2 and element Y is in group 7, of the periodic table. Which ions will be present in the compound formed when X and Y react together? a. X+ and Yb. X2+ and Y – c. X + and Y 2d. X2- and Y + 13. For which element ar ...
... A. I ONLY B. I AND II ONLY C. I AND III ONLY D. I, II AND III 12. Element X is in group 2 and element Y is in group 7, of the periodic table. Which ions will be present in the compound formed when X and Y react together? a. X+ and Yb. X2+ and Y – c. X + and Y 2d. X2- and Y + 13. For which element ar ...
periods - Madeira City Schools
... good conductors of heat and electricity. ¥ Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. ¥ Alkaline earth metals are in group 2, and are also highly reactive. ...
... good conductors of heat and electricity. ¥ Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. ¥ Alkaline earth metals are in group 2, and are also highly reactive. ...
Chapter 12 The Periodic Table
... • Found some inconsistencies - felt that the properties were more important than the mass, so switched order. ...
... • Found some inconsistencies - felt that the properties were more important than the mass, so switched order. ...
Chapter 6 Notes
... • This ties all the previous trends together in one package. • However, we must treat metals and nonmetals separately, as one will gain electrons and one will lose electrons. • The most reactive metals are the largest since they are the best electron givers. • The most reactive nonmetals are the sma ...
... • This ties all the previous trends together in one package. • However, we must treat metals and nonmetals separately, as one will gain electrons and one will lose electrons. • The most reactive metals are the largest since they are the best electron givers. • The most reactive nonmetals are the sma ...
Electronegativity Periodic Trend
... In the Graph window to the right, click on “X” or “Y” to choose the values you want to graph on each axes. Choose atomic number (under atomic properties) for the X-axis and for the Y-axis choose electronegativity (under atomic properties). 6. Do you notice a general trend (don’t worry about the few ...
... In the Graph window to the right, click on “X” or “Y” to choose the values you want to graph on each axes. Choose atomic number (under atomic properties) for the X-axis and for the Y-axis choose electronegativity (under atomic properties). 6. Do you notice a general trend (don’t worry about the few ...
03 Chapter 2 Atomic Structure Power point Periodic Table
... • 3.1.1 Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number. • 3.1.2 Distinguish between the terms group and period. • 3.1.3 Apply the relationship between the electron arrangement of elements and their position in the periodic table up to Z = 20. • 3.1.4 ...
... • 3.1.1 Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number. • 3.1.2 Distinguish between the terms group and period. • 3.1.3 Apply the relationship between the electron arrangement of elements and their position in the periodic table up to Z = 20. • 3.1.4 ...