Atomic Radius reading assignment
... Periodic Trends: Atomic Radius (from Chemistry: Connections to Our Changing World, pp. 174-175, Prentice-Hall, 1996) As you have learned, many of an element’s properties are determined by its electron configuration. In addition, the periodic table is organized so that elements with similar electron ...
... Periodic Trends: Atomic Radius (from Chemistry: Connections to Our Changing World, pp. 174-175, Prentice-Hall, 1996) As you have learned, many of an element’s properties are determined by its electron configuration. In addition, the periodic table is organized so that elements with similar electron ...
Metals - TeacherWeb
... they transmit heat and electricity easily. A metal that is attracted to a magnet or can be made into a magnet are described as magnetic. Iron, cobalt, and nickel are examples of magnetic metals. Most metals are solids at room temperatures. You would need to raise the temperature of some metals ...
... they transmit heat and electricity easily. A metal that is attracted to a magnet or can be made into a magnet are described as magnetic. Iron, cobalt, and nickel are examples of magnetic metals. Most metals are solids at room temperatures. You would need to raise the temperature of some metals ...
Periodic Classification of Elements
... always regular from one to its next. It was believed that a more fundamental property than atomic mass could explain periodic properties in a better manner. It was Henry Moseley who demonstrated that atomic number of an element could explain periodic properties in a better way than atomic mass of an ...
... always regular from one to its next. It was believed that a more fundamental property than atomic mass could explain periodic properties in a better manner. It was Henry Moseley who demonstrated that atomic number of an element could explain periodic properties in a better way than atomic mass of an ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... What does a group tell us about valence electrons and ion formation? ...
... What does a group tell us about valence electrons and ion formation? ...
Periodicity - ilc.edu.hk
... protons in an atom of the element. It is unique for each element. The mass of an atom of the element is mainly determined by the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Therefore, tellurium is heavier than iodine though the atomic number of tellurium is smaller than that of iodine. ...
... protons in an atom of the element. It is unique for each element. The mass of an atom of the element is mainly determined by the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Therefore, tellurium is heavier than iodine though the atomic number of tellurium is smaller than that of iodine. ...
Periodictable - Trupia
... electricity Metals are malleable Metals are ductile Metals have high tensile strength Metals have luster ...
... electricity Metals are malleable Metals are ductile Metals have high tensile strength Metals have luster ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Development of Periodic Table • Elements in the same group generally have similar chemical properties. • Properties are not identical, however. Periodic Properties of the Elements ...
... Development of Periodic Table • Elements in the same group generally have similar chemical properties. • Properties are not identical, however. Periodic Properties of the Elements ...
Periodic Table Ch4 Honors
... • They have “typical metallic properties” • Luster, ductile, malleable, good conductors of heat and electricity • Less reactive than Group 1 and 2 • Many are unreactive (for example, palladium, platinum and gold are found as pure elements in nature) • These elements begin in Period 4 and include Gro ...
... • They have “typical metallic properties” • Luster, ductile, malleable, good conductors of heat and electricity • Less reactive than Group 1 and 2 • Many are unreactive (for example, palladium, platinum and gold are found as pure elements in nature) • These elements begin in Period 4 and include Gro ...
Unit 4 Notes
... • They have typical metallic properties such as conduction of electricity and high luster. • Less reactive than group 1 and 2 elements. • Some (i.e. platinum & gold) are so unreactive they usually don’t form compounds. ...
... • They have typical metallic properties such as conduction of electricity and high luster. • Less reactive than group 1 and 2 elements. • Some (i.e. platinum & gold) are so unreactive they usually don’t form compounds. ...
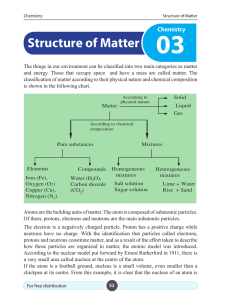
Structure of Matter - e
... number of electrons in the energy levels of potassium and calcium are not 9 and 10. ...
... number of electrons in the energy levels of potassium and calcium are not 9 and 10. ...
Chemistry_Review_Packet - AP-Biology
... 2. Name the six most abundant elements found in the human body. The universe is composed of about 92 naturally occurring elements. In nature, most of these elements are found in combination with one or more other elements. These combinations of elements are called compounds. Twenty-five of the known ...
... 2. Name the six most abundant elements found in the human body. The universe is composed of about 92 naturally occurring elements. In nature, most of these elements are found in combination with one or more other elements. These combinations of elements are called compounds. Twenty-five of the known ...
This activity will make use of the following website
... 4. Define second ionization energy. 5. Why is there a huge jump between the first and second ionization energies for Sodium, but only a small jump for Calcium? ...
... 4. Define second ionization energy. 5. Why is there a huge jump between the first and second ionization energies for Sodium, but only a small jump for Calcium? ...
C11 Periodic Table Trends Powerpoint
... shell is now (n-1). (Why do you think there is such a large jump in the ionization energies when the n-1 shell is now valence?) ...
... shell is now (n-1). (Why do you think there is such a large jump in the ionization energies when the n-1 shell is now valence?) ...
History of the Periodic Table Chapter 6.1 Who developed the first
... • After discovering U, Th, Pa, Seaborg was advised to revise the periodic table. • After examining the properties of the elements, Seaborg was convinced that the elements were part of the inner transition elements because they behaved similarly to ...
... • After discovering U, Th, Pa, Seaborg was advised to revise the periodic table. • After examining the properties of the elements, Seaborg was convinced that the elements were part of the inner transition elements because they behaved similarly to ...
Periodic properties
... group from Li to Cs, therefore, the reactivity of alkali metal increases from Li to Cs. All the elements are highly electropositive giving +1 ions. Because of the very high second ionisation energies of these elements, their oxidation state in compounds never exceeds +1. On the other hand , alkaline ...
... group from Li to Cs, therefore, the reactivity of alkali metal increases from Li to Cs. All the elements are highly electropositive giving +1 ions. Because of the very high second ionisation energies of these elements, their oxidation state in compounds never exceeds +1. On the other hand , alkaline ...
6.1 Development of the Modern Periodic Table Objectives: 1
... He also predicted the properties of those elements. Henry Moseley – English Chemist (1887-1915) Working in Rutherford’s lab he correlates the positive charges from the nucleus with an integer resulting in the atomic number. Determines that the order of the elements should be based on this fund ...
... He also predicted the properties of those elements. Henry Moseley – English Chemist (1887-1915) Working in Rutherford’s lab he correlates the positive charges from the nucleus with an integer resulting in the atomic number. Determines that the order of the elements should be based on this fund ...
This activity will make use of the following website
... Be sure to include vocabulary such as shielding, energy levels, and effective nuclear charge in your explanations to the following questions. 1. Which property of a nucleus, is most responsible for producing a high electronegativity value? ...
... Be sure to include vocabulary such as shielding, energy levels, and effective nuclear charge in your explanations to the following questions. 1. Which property of a nucleus, is most responsible for producing a high electronegativity value? ...
The Modern Periodic Table (cont.)
... • Non-metals are elements that are generally gases or brittle, dull-looking solids, and poor conductors of heat and electricity. • Group 17 is composed of highly reactive elements called halogens. • Group 18 gases are extremely unreactive and commonly called noble gases. ...
... • Non-metals are elements that are generally gases or brittle, dull-looking solids, and poor conductors of heat and electricity. • Group 17 is composed of highly reactive elements called halogens. • Group 18 gases are extremely unreactive and commonly called noble gases. ...
ch 6 ppt - Madison County Schools
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
Chapter 6 PP
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
Document
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
D. - Telluride Middle/High School
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
Worksheet 3.2 - contentextra
... radius is due to the increase in nuclear charge with atomic number across the period, which increases the attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons. ...
... radius is due to the increase in nuclear charge with atomic number across the period, which increases the attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons. ...
periodic law
... • The arrangement of the periodic table means that the physical properties of the elements follow a regular pattern. ...
... • The arrangement of the periodic table means that the physical properties of the elements follow a regular pattern. ...