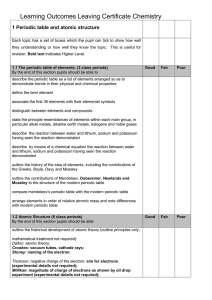
Families of elements
... Will gain one electron to become stable -1 ions Reaction of chlorine (a halogen) with sodium (an alkali metal) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1xT4OFS03jE ...
... Will gain one electron to become stable -1 ions Reaction of chlorine (a halogen) with sodium (an alkali metal) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1xT4OFS03jE ...
chemical-peiodicity
... which means that they can be hammered into very thin sheets without breaking. Ductile, which means that they can be drawn into wires. Fresh surface. Solids at room temperature. b. nonmetals Poor conductor of heat and electricity. Brittle— that they will shatter if struck with a hammer. Solids are no ...
... which means that they can be hammered into very thin sheets without breaking. Ductile, which means that they can be drawn into wires. Fresh surface. Solids at room temperature. b. nonmetals Poor conductor of heat and electricity. Brittle— that they will shatter if struck with a hammer. Solids are no ...
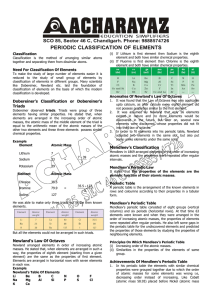
1 Periodic table and atomic structure
... they understanding or how well they know the topic. This is useful for revision. Bold text indicates Higher Level. ...
... they understanding or how well they know the topic. This is useful for revision. Bold text indicates Higher Level. ...
1 Periodic table and atomic structure
... they understanding or how well they know the topic. This is useful for revision. Bold text indicates Higher Level. ...
... they understanding or how well they know the topic. This is useful for revision. Bold text indicates Higher Level. ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... 14. Of the halogens, which are gases at room temperature and atmospheric pressure? (a). fluorine, bromine, and iodine (b). fluorine, chlorine, and bromine (c). fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine (d).fluorine and chlorine Explanation: Of the 4 common halogens, bromine is a liquid at room tempera ...
... 14. Of the halogens, which are gases at room temperature and atmospheric pressure? (a). fluorine, bromine, and iodine (b). fluorine, chlorine, and bromine (c). fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine (d).fluorine and chlorine Explanation: Of the 4 common halogens, bromine is a liquid at room tempera ...
periodic classification of elements
... a group. This is due to the fact that when an electron shell is added at each step while moving down in a group the size of the atom increases. The valence electrons become more and more away from the nucleus and the hold of the nucleus on the outermost electrons become less, so, the atom can easily ...
... a group. This is due to the fact that when an electron shell is added at each step while moving down in a group the size of the atom increases. The valence electrons become more and more away from the nucleus and the hold of the nucleus on the outermost electrons become less, so, the atom can easily ...
Unit 2 - Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding
... Periods and the Blocks of the Periodic Table A. Periods 1. Horizontal rows on the periodic table 2. Period number corresponds to the highest principal quantum number of the elements in the period B. Sublevel Blocks 1. Periodic table can be broken into blocks corresponding to s, p, d, f sublevels II. ...
... Periods and the Blocks of the Periodic Table A. Periods 1. Horizontal rows on the periodic table 2. Period number corresponds to the highest principal quantum number of the elements in the period B. Sublevel Blocks 1. Periodic table can be broken into blocks corresponding to s, p, d, f sublevels II. ...
ד"סב Chemistry Chapter 4 What is John Newland`s law of octaves
... ● Conduct electricity and heat ● Have a usually silver shine/luster ● Ductile ● Soft and malleable ● Act inconsistently with other elements- they react, often, to gain the stability of a half-filled shell even if it does not satisfy the octete What is an alloy? ...
... ● Conduct electricity and heat ● Have a usually silver shine/luster ● Ductile ● Soft and malleable ● Act inconsistently with other elements- they react, often, to gain the stability of a half-filled shell even if it does not satisfy the octete What is an alloy? ...
Chapter 8 Reading Guide Name: AP Chemistry 2016
... 37. Explain how to determine the number of electrons in an anion. Use O2- as an example. 38. Explain how to determine the number of electrons in a cation. Use Na+ as an example. ...
... 37. Explain how to determine the number of electrons in an anion. Use O2- as an example. 38. Explain how to determine the number of electrons in a cation. Use Na+ as an example. ...
Chapter #5 Notes
... • Main-group elements are the p-block and s-block elements. • Group 13- Boron's Family • Group 14- Carbon’s Family • Group 15- Nitrogen's Family • Group 16- Oxygen’s Family • Group 17- Halogens the most reactive nonmetals they form “salts” • Group 18- Noble Gases- Least reactive family. WHY???? ...
... • Main-group elements are the p-block and s-block elements. • Group 13- Boron's Family • Group 14- Carbon’s Family • Group 15- Nitrogen's Family • Group 16- Oxygen’s Family • Group 17- Halogens the most reactive nonmetals they form “salts” • Group 18- Noble Gases- Least reactive family. WHY???? ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... The Modern Periodic Table • Three main types of elements: – _________: shiny, solids at room temperature, good conductors, ductile, malleable. • Alkali Metals (group 1), Alkaline Earth Metals (group 2), transition metals (groups 3-12), and inner transition metals. ...
... The Modern Periodic Table • Three main types of elements: – _________: shiny, solids at room temperature, good conductors, ductile, malleable. • Alkali Metals (group 1), Alkaline Earth Metals (group 2), transition metals (groups 3-12), and inner transition metals. ...
version
... All elements possess from very low to very high metallic character. The scale is from Fr to F. Fr has the most metallic character and F has the least. In groups, metallic character increases with atomic number because each successive element gets closest to Fr. In periods, metallic charact ...
... All elements possess from very low to very high metallic character. The scale is from Fr to F. Fr has the most metallic character and F has the least. In groups, metallic character increases with atomic number because each successive element gets closest to Fr. In periods, metallic charact ...
Introduction to Atoms
... 13. Each horizontal row in the periodic table is called a(n)________________________. 14. Is the following sentence true or false? Across a period from left to right, the properties of elements change according to a pattern.________________________. 15. Circle the letter of each term that refers to ...
... 13. Each horizontal row in the periodic table is called a(n)________________________. 14. Is the following sentence true or false? Across a period from left to right, the properties of elements change according to a pattern.________________________. 15. Circle the letter of each term that refers to ...
PeriodicTrends
... • SC4a. Use the Periodic Table to predict periodic trends including atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization energy, and electronegativity of various elements. ...
... • SC4a. Use the Periodic Table to predict periodic trends including atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization energy, and electronegativity of various elements. ...
Study Guide - Rochester Century High School
... • Alkaline earth metal • Group • Halogen • Inner transition metal • Lanthanide series • Metal • Metalloid • Noble gas • Nonmetal • Period • Periodic law • Representative element • Transition element • Transition metal ...
... • Alkaline earth metal • Group • Halogen • Inner transition metal • Lanthanide series • Metal • Metalloid • Noble gas • Nonmetal • Period • Periodic law • Representative element • Transition element • Transition metal ...
Chemical Periodicity
... 2. Who is Dmitri Mendeleev, and what was his contribution to chemistry? 3. How is the modern periodic table different from the first periodic table? 4. What is the modern periodic law? 5. Organization of the periodic table. Indicate where the following are located on the periodic table. h. Transitio ...
... 2. Who is Dmitri Mendeleev, and what was his contribution to chemistry? 3. How is the modern periodic table different from the first periodic table? 4. What is the modern periodic law? 5. Organization of the periodic table. Indicate where the following are located on the periodic table. h. Transitio ...
Periodic Table
... gave off x-rays with distinct wavelengths. Essentially what was happening was that the cathode rays (high energy electrons) were knocking out the inner-most electrons of the metal targets. X-rays were emitted when an outer electron "fell" down into this inner shell. Since the inner-most electrons ar ...
... gave off x-rays with distinct wavelengths. Essentially what was happening was that the cathode rays (high energy electrons) were knocking out the inner-most electrons of the metal targets. X-rays were emitted when an outer electron "fell" down into this inner shell. Since the inner-most electrons ar ...
Teacher Background Information: The periodic table is arranged in
... The periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number. A group is a vertical column of the periodic table. Elements with similar physical and chemical properties belong in a group. The group number gives the number of valence electrons in an element. For example, the Alkali Metals are ...
... The periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number. A group is a vertical column of the periodic table. Elements with similar physical and chemical properties belong in a group. The group number gives the number of valence electrons in an element. For example, the Alkali Metals are ...
groups - Northside Middle School
... Luster, ductile, malleable, good conductors of heat and electricity Less reactive than Group 1 and 2 Many are unreactive (for example, palladium, platinum and gold are found as pure elements in nature) • As ions, the transition elements form colorful solutions. • These elements begin in Period 4 and ...
... Luster, ductile, malleable, good conductors of heat and electricity Less reactive than Group 1 and 2 Many are unreactive (for example, palladium, platinum and gold are found as pure elements in nature) • As ions, the transition elements form colorful solutions. • These elements begin in Period 4 and ...
Periodic Table Notes Ch. 6 ppt
... Law states that chemical and physical properties repeat in regular cyclic patterns when they are arranged by increasing atomic number. Starts ...
... Law states that chemical and physical properties repeat in regular cyclic patterns when they are arranged by increasing atomic number. Starts ...
Chapter 5.3 Periodic Properties
... Consider two main-group elements, A and B. Element A has a first ionization energy of 419 kJ/mol. Element B has a first ionization energy of 1000 kJ/mol. Decide if each element is more likely to be in the s block or p block. Which element is more likely to form a positive ion ...
... Consider two main-group elements, A and B. Element A has a first ionization energy of 419 kJ/mol. Element B has a first ionization energy of 1000 kJ/mol. Decide if each element is more likely to be in the s block or p block. Which element is more likely to form a positive ion ...