Question (1): Explain `Dobereiner`s Triads and its drawback. Answer
... Question (35): In the third period, which is the most metallic and non-metallic element. Answer: 1) The most metallic element is - Na (Sodium) 2) The most non-metallic is - Cl (Chlorine). Question (36): How does the number of valence shell change on moving 1) Down a group? 2) Down a period? Answer: ...
... Question (35): In the third period, which is the most metallic and non-metallic element. Answer: 1) The most metallic element is - Na (Sodium) 2) The most non-metallic is - Cl (Chlorine). Question (36): How does the number of valence shell change on moving 1) Down a group? 2) Down a period? Answer: ...
Slide 1
... atomic number! Therefore, atomic number will increase as you move from left to right across a period and as you move from top to bottom down a group. We also know that the atomic number is exactly equal to the number of protons so the trend for protons will be the same In a neutral atom, the num ...
... atomic number! Therefore, atomic number will increase as you move from left to right across a period and as you move from top to bottom down a group. We also know that the atomic number is exactly equal to the number of protons so the trend for protons will be the same In a neutral atom, the num ...
Trends of the Periodic Table File
... properties of both metals and nonmetals. For example, a metalloid may conduct electricity like a metal, but also insulate against heat like a nonmetal. The metalloid groups hosts a diverse set of elements, such as silicon, boron, arsenic and antimony, and their diverse properties allow industries to ...
... properties of both metals and nonmetals. For example, a metalloid may conduct electricity like a metal, but also insulate against heat like a nonmetal. The metalloid groups hosts a diverse set of elements, such as silicon, boron, arsenic and antimony, and their diverse properties allow industries to ...
chapter8
... remove the electron. The amount of energy required to remove the first electron from the atom in its ground state. energy +X(g) ----> X (g) + e is called the first ionization energy. X represents an atom of any element, e is an electron, and g show the gaseous state, an atom in the gaseous phase is ...
... remove the electron. The amount of energy required to remove the first electron from the atom in its ground state. energy +X(g) ----> X (g) + e is called the first ionization energy. X represents an atom of any element, e is an electron, and g show the gaseous state, an atom in the gaseous phase is ...
III. Periodic Trends
... 46. How can electron configurations and position on the periodic table be used to predict the charges on ions (particularly for the representative elements)? Atoms gain or lose electrons to get 8 in the outermost energy level. Metals usually lose electrons and go down an energy level. Nonmetals usua ...
... 46. How can electron configurations and position on the periodic table be used to predict the charges on ions (particularly for the representative elements)? Atoms gain or lose electrons to get 8 in the outermost energy level. Metals usually lose electrons and go down an energy level. Nonmetals usua ...
8.4-8.6 Electron Configuration, The Explanatory Power of the
... accurately predict the electron configurations for most of the elements in the periodic table. However there are a few elements that have been proven, based on spectroscopy, to have a more stable electron configuration that is irregular. Memorization of the few exceptions is beyond the scope of the ...
... accurately predict the electron configurations for most of the elements in the periodic table. However there are a few elements that have been proven, based on spectroscopy, to have a more stable electron configuration that is irregular. Memorization of the few exceptions is beyond the scope of the ...
Activity 2 Elements and Their Properties
... or safe! However, chemists worldwide were sure that elements existed in families that had similar physical and chemical properties. To the Russian scientist, Dimitri Mendeleev (1843–1907), the development of a tool to organize the elements began the same way that so much of science inquiry begins. H ...
... or safe! However, chemists worldwide were sure that elements existed in families that had similar physical and chemical properties. To the Russian scientist, Dimitri Mendeleev (1843–1907), the development of a tool to organize the elements began the same way that so much of science inquiry begins. H ...
Coloring the Periodic Table - Families
... scientist born in Tobolsk, Siberia in 1834, is known as the father of the periodic table of the elements. The periodic table of the elements is an important tool used by students and chemists around the world to help them understand and simplify the often complex world of chemical reactions. ...
... scientist born in Tobolsk, Siberia in 1834, is known as the father of the periodic table of the elements. The periodic table of the elements is an important tool used by students and chemists around the world to help them understand and simplify the often complex world of chemical reactions. ...
Unit Two Test Review
... very low reactivity. good conductivity. very high reactivity. metallic character. ...
... very low reactivity. good conductivity. very high reactivity. metallic character. ...
chemical periodicity
... • Good conductors of electricity and have a high luster • Less reactive than alkali and alkali-earth metal • Some (e.g. platinum and gold) are so unreactive that they do not form compounds easily. • Some are found as free element. ...
... • Good conductors of electricity and have a high luster • Less reactive than alkali and alkali-earth metal • Some (e.g. platinum and gold) are so unreactive that they do not form compounds easily. • Some are found as free element. ...
Periodic Trends PDF - Warren County Schools
... • This group of metals is extremely reactive! This is due to the fact that they all have only 1 valence electron. • In their pure state, all members of this group are silvery in appearance and soft enough to be cut with a butter knife. • Because they are so reactive, they are not found in natur ...
... • This group of metals is extremely reactive! This is due to the fact that they all have only 1 valence electron. • In their pure state, all members of this group are silvery in appearance and soft enough to be cut with a butter knife. • Because they are so reactive, they are not found in natur ...
The Periodic Table - Warren County Public Schools
... • This group of metals is extremely reactive! This is due to the fact that they all have only 1 valence electron. • In their pure state, all members of this group are silvery in appearance and soft enough to be cut with a butter knife. • Because they are so reactive, they are not found in nature as ...
... • This group of metals is extremely reactive! This is due to the fact that they all have only 1 valence electron. • In their pure state, all members of this group are silvery in appearance and soft enough to be cut with a butter knife. • Because they are so reactive, they are not found in nature as ...
Periodic Table
... ii) Compare the periodic trends of atomic radii, ionization energy, and electronegativity, and state the reasons for these variations. iii) Define valence electrons, and state how many are present in atoms of each main-group element. ...
... ii) Compare the periodic trends of atomic radii, ionization energy, and electronegativity, and state the reasons for these variations. iii) Define valence electrons, and state how many are present in atoms of each main-group element. ...
POGIL: Periodic Table Trends
... b. Why does Hydrogen fit into this group? c. Why does Hydrogen NOT fit into this group? (Hint: Why does it make sense that European Periodic Tables show H in both Group 1 and 17?) ...
... b. Why does Hydrogen fit into this group? c. Why does Hydrogen NOT fit into this group? (Hint: Why does it make sense that European Periodic Tables show H in both Group 1 and 17?) ...
Page 8: Review 1
... Explain the variations in ionization energies of elements as their atomic numbers increase in a period or family of the P.T. Define electron affinity and electronegativity. Predict trends in electron affinities and electronegativities for elements, based on their location in the P.T. Define family, ...
... Explain the variations in ionization energies of elements as their atomic numbers increase in a period or family of the P.T. Define electron affinity and electronegativity. Predict trends in electron affinities and electronegativities for elements, based on their location in the P.T. Define family, ...
periodic table trends assignment 2013 billo
... electron from another atom. If an atom is really good at ‘stealing’ electrons from another atom, then it has a high electronegativity value. The Noble Gas elements do not have electronegativity values since they are stable with full outer energy levels. Procedure: For each set of data... 1. Turn the ...
... electron from another atom. If an atom is really good at ‘stealing’ electrons from another atom, then it has a high electronegativity value. The Noble Gas elements do not have electronegativity values since they are stable with full outer energy levels. Procedure: For each set of data... 1. Turn the ...
The Modern Periodic Table
... • These elements form part of the actinide series in which the 5f orbitals are being filled. • The transuranium elements do not occur in nature. They are classified as artificial elments because they can only be generated in a laboratory by using sophisticated equipment. • Today, elements with atomi ...
... • These elements form part of the actinide series in which the 5f orbitals are being filled. • The transuranium elements do not occur in nature. They are classified as artificial elments because they can only be generated in a laboratory by using sophisticated equipment. • Today, elements with atomi ...
11-chemistry-exemplar-chapter-3
... electron repulsion outweighs the stability gained by achieving noble gas configuration. ...
... electron repulsion outweighs the stability gained by achieving noble gas configuration. ...
Document
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
CHAPTER-3 CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
... The carbonates of alkaline earth metals are relatively less stable. On heating, they decompose to give corresponding oxide and CO 2 gas. The decomposition temperature for alkaline earth metal carbonates increases as we go down the group. Anomalous Properties of Second Period Elements Their anomalous ...
... The carbonates of alkaline earth metals are relatively less stable. On heating, they decompose to give corresponding oxide and CO 2 gas. The decomposition temperature for alkaline earth metal carbonates increases as we go down the group. Anomalous Properties of Second Period Elements Their anomalous ...
Mendeleev`s Periodic Table - Scotch Plains
... 8. Is the following statement true or false? The periodic law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of physical and chemical properties. ...
... 8. Is the following statement true or false? The periodic law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of physical and chemical properties. ...
Periodicity
... Different kinds of periodic tables may present different kinds of information or present information in different ways. • The shape of the periodic table comes from the periodic law. • Elements with similar properties are aligned in vertical columns called groups or families. • The horizontal rows ...
... Different kinds of periodic tables may present different kinds of information or present information in different ways. • The shape of the periodic table comes from the periodic law. • Elements with similar properties are aligned in vertical columns called groups or families. • The horizontal rows ...
Periodic trends
... VERY reactive because one valence e• Found as compounds in nature • Not including H! ...
... VERY reactive because one valence e• Found as compounds in nature • Not including H! ...
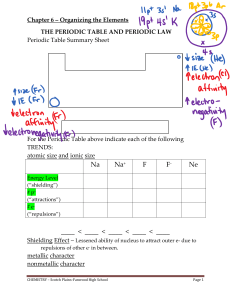
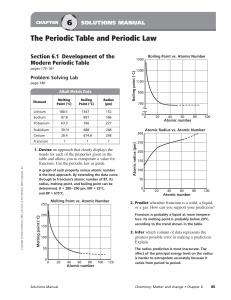
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... ordered differently than they are in the existing table? Argon and potassium would be switched. Cobalt and nickel would be switched. Tellurium and iodine would be switched. ...
... ordered differently than they are in the existing table? Argon and potassium would be switched. Cobalt and nickel would be switched. Tellurium and iodine would be switched. ...