Chapter 5 - EZWebSite
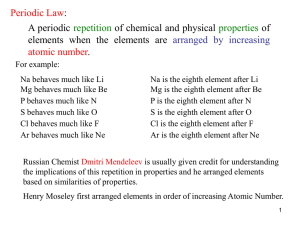
... Notice that Te, with an atomic mass of 128 comes before I with an atomic mass of 127. The scientific community disregarded Mendeleev’s work because he changed his rules to fit his table. ...
... Notice that Te, with an atomic mass of 128 comes before I with an atomic mass of 127. The scientific community disregarded Mendeleev’s work because he changed his rules to fit his table. ...
Increasing Radii
... These groups generally display a wide range of properties which are said to be representative of most elements. ...
... These groups generally display a wide range of properties which are said to be representative of most elements. ...
Chp4Sec1and2
... the pattern that led to the periodic table? Mendeleev noticed that a pattern of properties appeared when he arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass. ...
... the pattern that led to the periodic table? Mendeleev noticed that a pattern of properties appeared when he arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass. ...
Periodic Table
... you look at the modern periodic table, you will see several examples, such as cobalt and nickel, where the mass decreases from left to right. ...
... you look at the modern periodic table, you will see several examples, such as cobalt and nickel, where the mass decreases from left to right. ...
Period Trend
... Atomic radii decrease from left to right across a period Trend is caused by the increasing positive charge of the nucleus Group Trends In general, the atomic radii of the main-group elements increase down a group As electrons occupy the sublevels in successively higher main energy levels loc ...
... Atomic radii decrease from left to right across a period Trend is caused by the increasing positive charge of the nucleus Group Trends In general, the atomic radii of the main-group elements increase down a group As electrons occupy the sublevels in successively higher main energy levels loc ...
First Term Science Al-Karma Language School Prep 2 Question (1
... 14)-The positive ion carries a number of ---------- charges equals to the number -------- electrons. 15)-An element whose electronic configuration is (2,8) so, it exists in group ------- and period -------- in the modern periodic table. 16)-The new number of group (5A) is ---------, while that of ze ...
... 14)-The positive ion carries a number of ---------- charges equals to the number -------- electrons. 15)-An element whose electronic configuration is (2,8) so, it exists in group ------- and period -------- in the modern periodic table. 16)-The new number of group (5A) is ---------, while that of ze ...
Chemical Periodicity
... a) metals: relatively unreactive, shiny, good conductors of electricity and heat and, solid at room temperature (except for mercury), broad variety of melting points, malleable, ductile, similar to each other, 80% of elements are metals. b) Non-metals: opposite properties of metals, poor conductor o ...
... a) metals: relatively unreactive, shiny, good conductors of electricity and heat and, solid at room temperature (except for mercury), broad variety of melting points, malleable, ductile, similar to each other, 80% of elements are metals. b) Non-metals: opposite properties of metals, poor conductor o ...
Periodic Trends
... We will be studying four trends across the Periodic Table. Atomic radii: the distance from the nucleus to the farthest e-. Ionic radii: the distance from the nucleus to the farthest ein that element’s ion. Electronegativity: the propensity for an element to attract efrom another atom. It’s ability t ...
... We will be studying four trends across the Periodic Table. Atomic radii: the distance from the nucleus to the farthest e-. Ionic radii: the distance from the nucleus to the farthest ein that element’s ion. Electronegativity: the propensity for an element to attract efrom another atom. It’s ability t ...
Document
... The Periodic Table is arranged according to the Periodic Law. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. The properties that will be examined in this lesson are: atomic radius AND first ...
... The Periodic Table is arranged according to the Periodic Law. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. The properties that will be examined in this lesson are: atomic radius AND first ...
Graphing Periodic Trends
... Graphing the Periodic Trends Background The Periodic Table is arranged according to Periodic Law. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. These patterns can be discovered by examinin ...
... Graphing the Periodic Trends Background The Periodic Table is arranged according to Periodic Law. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. These patterns can be discovered by examinin ...
Chapter 6
... Match each item with the correct statement below. a. electronegativity f. b. ionization energy g. c. atomic radius h. d. metal i. e. transition metal j. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ...
... Match each item with the correct statement below. a. electronegativity f. b. ionization energy g. c. atomic radius h. d. metal i. e. transition metal j. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ...
The Periodic Table
... • Since the properties of the elements follow regular patterns, we can predict unknown properties of elements based on those around it. • For example, table 6.2 lists several properties of the alkali metals except francium, Fr. • We can predict the properties of francium based on the other alkali me ...
... • Since the properties of the elements follow regular patterns, we can predict unknown properties of elements based on those around it. • For example, table 6.2 lists several properties of the alkali metals except francium, Fr. • We can predict the properties of francium based on the other alkali me ...
Lecture 14-15 - U of L Class Index
... Most electrons do not ‘feel’ the full positive charge of the nucleus. Other electrons in the atom (particularly those in lower energy orbitals) ‘shield’ some of this charge. The amount of positive charge ‘felt’ by an electron in a given orbital is called the effective nuclear charge (Zeff). The foll ...
... Most electrons do not ‘feel’ the full positive charge of the nucleus. Other electrons in the atom (particularly those in lower energy orbitals) ‘shield’ some of this charge. The amount of positive charge ‘felt’ by an electron in a given orbital is called the effective nuclear charge (Zeff). The foll ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. The octet rule is useful for predicting what types of ions an element is likely ...
... The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. The octet rule is useful for predicting what types of ions an element is likely ...
Introductory Chemistry
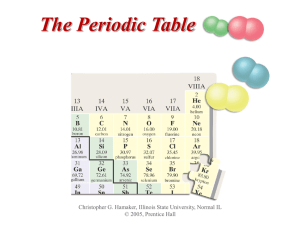
... Representative elements or main-group elements, are in the A groups. Transition elements are in the B groups. Inner transition elements or rare earth elements are found below the periodic table. ...
... Representative elements or main-group elements, are in the A groups. Transition elements are in the B groups. Inner transition elements or rare earth elements are found below the periodic table. ...
Chapter 5
... 14. Elements with atomic number 57 to 71 are called lanthanide series and elements with atomic number 89 to 103 are called actinide. 15. Elements having 1 valence electron are placed in group one. Elements having 2 valence electrons are placed in group 2. 16. Elements having 3 valence electrons are ...
... 14. Elements with atomic number 57 to 71 are called lanthanide series and elements with atomic number 89 to 103 are called actinide. 15. Elements having 1 valence electron are placed in group one. Elements having 2 valence electrons are placed in group 2. 16. Elements having 3 valence electrons are ...
Name: Date: Period: 1. Read the following and make annotations
... A positive ion is known as a cation. The formation of a cation by the loss of one or more electrons always leads to a decrease in atomic radius because the removal of the highest-energy-level electrons results in a smaller electron cloud. Also, the remaining electrons are drawn closer to the nucleus ...
... A positive ion is known as a cation. The formation of a cation by the loss of one or more electrons always leads to a decrease in atomic radius because the removal of the highest-energy-level electrons results in a smaller electron cloud. Also, the remaining electrons are drawn closer to the nucleus ...
Daily 40 no. – 15 John Newlands
... create an early periodic table. His organization led to the modern periodic table. He realized that every eighth element had similar characteristics. His incomplete table predicted other undiscovered elements. -Eric John Newlands was born in 1837 and died in 1898. He is known for creating the first ...
... create an early periodic table. His organization led to the modern periodic table. He realized that every eighth element had similar characteristics. His incomplete table predicted other undiscovered elements. -Eric John Newlands was born in 1837 and died in 1898. He is known for creating the first ...
The Periodic Law - Mona Shores Blogs
... periodic table and explains how the periodic law is used to predict elements’ physical and chemical properties. Mendeleev and Chemical Periodicity Dmitri Mendeleev noticed that when elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appear ...
... periodic table and explains how the periodic law is used to predict elements’ physical and chemical properties. Mendeleev and Chemical Periodicity Dmitri Mendeleev noticed that when elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appear ...
2 periodic table pd9
... a period, # of electrons do NOT protons increases necessarily have a larger atomic radius and outermost energy level stays the same, the attractive force between elecs. and pros. pulls the atom tighter (closer to nucleus) ...
... a period, # of electrons do NOT protons increases necessarily have a larger atomic radius and outermost energy level stays the same, the attractive force between elecs. and pros. pulls the atom tighter (closer to nucleus) ...
Lectures 14-15 - U of L Class Index
... Most electrons do not ‘feel’ the full positive charge of the nucleus. Other electrons in the atom (particularly those in lower energy orbitals) ‘shield’ some of this charge. The amount of positive charge ‘felt’ by an electron in a given orbital is called the effective nuclear charge (Zeff). The foll ...
... Most electrons do not ‘feel’ the full positive charge of the nucleus. Other electrons in the atom (particularly those in lower energy orbitals) ‘shield’ some of this charge. The amount of positive charge ‘felt’ by an electron in a given orbital is called the effective nuclear charge (Zeff). The foll ...
C:\docs\school\AP Chem\summer\SummerPacket02 key.wpd
... extremely reactive. It is a gas at room temperature. b. Xenon is a noble gas making it a very non-reactive substance. c. Sodium is an alkali metal. Like fluorine, extremely reactive. So reactive, in fact, that it’s not found in its pure form in nature. It is a silvery soft metal with a relatively lo ...
... extremely reactive. It is a gas at room temperature. b. Xenon is a noble gas making it a very non-reactive substance. c. Sodium is an alkali metal. Like fluorine, extremely reactive. So reactive, in fact, that it’s not found in its pure form in nature. It is a silvery soft metal with a relatively lo ...
Test Review
... Alkali Metals- Group 1, most reactive metals on the periodic table. Form +1 ions, losing 1 electron to look like a noble gas. Too reactive to exist in nature freely. Must be stored in mineral oil. Alkaline Earth Metals – Group 2, not as reactive as alkali metals. Form +2 ions, losing 2 electrons to ...
... Alkali Metals- Group 1, most reactive metals on the periodic table. Form +1 ions, losing 1 electron to look like a noble gas. Too reactive to exist in nature freely. Must be stored in mineral oil. Alkaline Earth Metals – Group 2, not as reactive as alkali metals. Form +2 ions, losing 2 electrons to ...