* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introductory Chemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
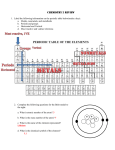
Chapter 10 Periodic Table and Its Trends 1 Groupings of Elements Representative elements or main-group elements, are in the A groups. Transition elements are in the B groups. Inner transition elements or rare earth elements are found below the periodic table. 2 Cont’d…Groupings of Elements The inner transition elements are called lanthanide series and the actinide series. 3 Common Names of Groups Several columns have common, trivial names. ¾Group IA/1 are the alkali metals ¾Group IIA/2 are the alkaline earth metals ¾Group VIIA/17 are the halogens ¾Group VIIIA/18 are the noble gases. 4 Cont’d…Common Names of Groups 5 Trends in Periodic Table Periodic table is based on the arrangement of the elements based on their physical properties. Trends for atomic radius (size of atom) for main group elements: Atomic radius decreases as you go up a group. Atomic radius decreases as you go left to right across a period. 6 Cont’d…Atomic Radius • Atoms get smaller as you go from bottom to top; this is because as you go up in a group, there are fewer energy levels on the atom. • Atomic radius decreases as you go from left to right; this is because of the increasing number of protons in the nucleus as you go from left to right. • As the number of protons increases, the nucleus pulls the electrons closer and reduces the size of the atom. 7 Metallic Character The degree of metal character of an element. Metallic character trends: decreases from left to right across a period and decreases from bottom to top in a group. 8 Cont’d…Metallic Character 9 Physical Properties of Elements Since elements follow regular patterns in periodic table, we can predict unknown properties of elements based on those around it. 10 Predicting Chemical Properties • Group members have similar chemical properties. • All alkali metals have oxides of the general formula M2O: – Li2O, Na2O, K2O, Rb2O, Cs2O, and Fr2O. Example: The formula for the chloride of calcium is CaCl2. What is the formula for the chloride of barium? – The general formula is MCl2, so the formula must be BaCl2. 11 Blocks of Elements • Filling of sublevels with electrons: 1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d < 4p < 5s … • Periodic table can be broken into blocks of elements where certain sublevels are being filled: ¾ s block of elements: Groups IA/1 and IIA/2 are filling s sublevels. ¾ d block of elements Groups IIIB/3 through IIB/12 are filling d sublevels. 12 Blocks and Sublevels We can predict which sublevel is being filled by a particular element. 13 Noble Gas Core Electron Configurations • The electron configuration for Na is: Na: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 • Abbreviate the electron configuration by indicating the innermost electrons with the symbol of the preceding noble gas. • The preceding noble gas with an atomic number less than sodium is neon, Ne. Rewrite the electron configuration: Na: [Ne] 3s1 14 Valence Electrons • Valence electrons: Electrons that have the highest energy and are furthest away from the nucleus. These are the electrons (outermost electrons) which are involved in the chemical reaction. • The valence electrons are the s and p electrons beyond the noble gas core. 15 Predicting Valence Electrons from Group Numbers Based on the American convention, Roman numeral indicates the number of valence electrons. – Group IA elements have: 1 valence electron – Group VA elements have: 5 valence electrons Based on the IUPAC designations for group numbers, the last digit indicates the number of valence electrons. – Group 14 elements have: 4 valence electrons – Group 2 elements have: 2 valence electrons 16 Electron Dot Formulas Electron dot formula of an element shows the symbol of the element surrounded by its valence electrons. Use one dot for each valence electron. Example: What is the electron dot formula of P? 17 Cont’d…Electron Dot Formulas 18 Ionization Energy (IE) IE is the amount of energy required to remove an electron in the gaseous state. The closer the electron to the nucleus, the more energy is required to remove the electron. General trend in ionization energy: ¾ In a group, ionization energy increases from bottom to the top. ¾ In a period of elements, ionization energy increases from left to right. 19 Ionic Charge The charge of an ion is related to the number of valence electrons on the atom. • Metals tend to lose electrons and nonmetals tend to gain electrons. • Group IA/1 metals lose their one valence electron to form 1+ ions. Losing valence electron metals form ions. Na → Na+ + e- 20 Cont’d…Ionic Charge Group IA/1 metals form 1+ ions, group IIA/2 metals form 2+ ions, group IIIA/13 metals form 3+ ions, and group IVA/14 metals from 4+ ions. By losing valence electrons, metals achieve a noble gas configuration. 21 Cont’d…Ionic Charge • Nonmetals can gain electrons to achieve a noble gas configuration. Group VA/15 elements form -3 ions, group VIA/16 elements form -2 ions, and group VIIA/17 elements form -1 ions. 22 Ion Electron Configurations ¾ To write the electron configuration of a positive ion, remove one electron for each positive charge: Na → Na+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 → 1s2 2s2 2p6 ¾ To write the electron configuration of a negative ion, add one electron for each negative charge: O 1s2 2s2 2p4 → → O21s2 2s2 2p6 23 Review ¾ The elements in the periodic table are arranged by increasing atomic number and they have repeating chemical and physical properties. ¾ Atomic radius and metallic character increase from bottom to top and from left to right across the periodic table. ¾ The periodic table can be broken down into blocks where a certain sublevel is being filled. 24 Cont’d…Review ¾ Valence electrons are the outermost electrons and are involved in chemical reactions. ¾ Electron dot formulas indicate the number of valence electrons. ¾ Ionization energy is the amount of energy that is required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state. 25 Cont’d…Review ¾ We can predict the charge on the ion of an element from its position on the periodic table. 26