ד"סב Chemistry Chapter 4 What is John Newland`s law of octaves
... Groups 2 and 6 are less reactive, then 3 and 5, then 4. Group 8 is nearly nonreactive. ...
... Groups 2 and 6 are less reactive, then 3 and 5, then 4. Group 8 is nearly nonreactive. ...
Periodicity - GEOCITIES.ws
... The first ionization energy, I1 is the energy required to remove one electron from an atom. Na(g) Na+(g) + e The 2nd ionization energy, I2, is the energy required to remove an electron from an ion. Na+(g) Na2+(g) + e Larger ionization energy, harder to remove ...
... The first ionization energy, I1 is the energy required to remove one electron from an atom. Na(g) Na+(g) + e The 2nd ionization energy, I2, is the energy required to remove an electron from an ion. Na+(g) Na2+(g) + e Larger ionization energy, harder to remove ...
physical science
... Unit Statement: Atomic Theory, the structure of atoms, and their arrangement in the periodic table according to their properties are established in this unit. Essential Outcomes: (Must be Assessed) 1. The Student Will summarize the main points of Dalton’s atomic theory and describe his evidence for ...
... Unit Statement: Atomic Theory, the structure of atoms, and their arrangement in the periodic table according to their properties are established in this unit. Essential Outcomes: (Must be Assessed) 1. The Student Will summarize the main points of Dalton’s atomic theory and describe his evidence for ...
orbital form the s block (groups 1 and 2). Elements in
... increasing atomic number. The vertical columns in the periodic table are referred to as groups and the horizontal rows are known as periods. The elements in groups 1 and 2 and those in groups 13 to 18 are called main-group elements. Elements in groups 3 to 12 are known as transition elements and the ...
... increasing atomic number. The vertical columns in the periodic table are referred to as groups and the horizontal rows are known as periods. The elements in groups 1 and 2 and those in groups 13 to 18 are called main-group elements. Elements in groups 3 to 12 are known as transition elements and the ...
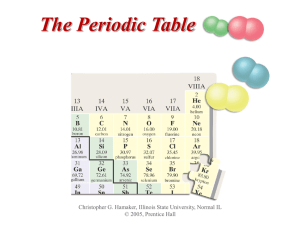
The Periodic Table
... go from the bottom to the top in a group. • In general, the ionization energy increases as you go from left to right across a period of elements. • The closer the electron to the nucleus, the more energy is required to remove the electron. ...
... go from the bottom to the top in a group. • In general, the ionization energy increases as you go from left to right across a period of elements. • The closer the electron to the nucleus, the more energy is required to remove the electron. ...
The Periodic Table
... Alkaline Earth Metals Second column on the periodic table. (Group 2) Reactive metals that are always combined with nonmetals in nature. Harder, denser, and stronger than alkali metals Several of these elements are important mineral nutrients (such as Mg in bones and Ca in teeth and bones. ...
... Alkaline Earth Metals Second column on the periodic table. (Group 2) Reactive metals that are always combined with nonmetals in nature. Harder, denser, and stronger than alkali metals Several of these elements are important mineral nutrients (such as Mg in bones and Ca in teeth and bones. ...
D. - Taylor County Schools
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
... • The elements were first organized by increasing atomic mass, which led to inconsistencies. Later, they were organized by increasing atomic number. • The periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physica ...
Document
... make a second line to represent Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Metals). Use a periodic table to determine which elements are members of Group 1 and which elements are members of Group 2. 4. What happens to the ionization energy as one goes down a group (use the term “ionization energy” in the response)? ...
... make a second line to represent Group 2 (Alkaline Earth Metals). Use a periodic table to determine which elements are members of Group 1 and which elements are members of Group 2. 4. What happens to the ionization energy as one goes down a group (use the term “ionization energy” in the response)? ...
Chapter 7 The Development of the Periodic Table
... • One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. • Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. • The family of noble gases includes helium, neon, argon, kr ...
... • One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. • Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. • The family of noble gases includes helium, neon, argon, kr ...
chem ch 5 - wbm
... Among the main-group elements, what is the relationship between group number and the number of valence electrons? In general, how do the periodic properties of the d-block elements compare with those of the maingroup elements? ...
... Among the main-group elements, what is the relationship between group number and the number of valence electrons? In general, how do the periodic properties of the d-block elements compare with those of the maingroup elements? ...
Periodic Properties of Elements
... reduced to effective nuclear charge (Zeff). Electrons that have a greater penetration shield others more effectively. For example, electrons in level n = 1 shield those in level n = 2 very effectively, and those in n = 1 and n = 2 shield electrons in level n = 3. Electrons at the same level, but in ...
... reduced to effective nuclear charge (Zeff). Electrons that have a greater penetration shield others more effectively. For example, electrons in level n = 1 shield those in level n = 2 very effectively, and those in n = 1 and n = 2 shield electrons in level n = 3. Electrons at the same level, but in ...
Graphing Periodic Trends
... Graphing the Periodic Trends Background The Periodic Table is arranged according to Periodic Law. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. These patterns can be discovered by examinin ...
... Graphing the Periodic Trends Background The Periodic Table is arranged according to Periodic Law. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. These patterns can be discovered by examinin ...
Periodic trends - Cloudfront.net
... Atomic and ionic radius The size of an atom or ion (we’ll talk about ions later) Trend Increases right to left of a row Increases top to bottom of a column. Ex: Which of the following elements has the largest ...
... Atomic and ionic radius The size of an atom or ion (we’ll talk about ions later) Trend Increases right to left of a row Increases top to bottom of a column. Ex: Which of the following elements has the largest ...
to chapter:3
... electrons; small negatively charged particles in an atom. John Townsend and Robert Millikan determined their exact charge and mass. In 1900 Bequerel discovered that electrons and beta particles as identified by the Curies are the same thing. In 1903 Rutherford announced that radioactivity is caused ...
... electrons; small negatively charged particles in an atom. John Townsend and Robert Millikan determined their exact charge and mass. In 1900 Bequerel discovered that electrons and beta particles as identified by the Curies are the same thing. In 1903 Rutherford announced that radioactivity is caused ...
Chapter 5 - EZWebSite
... Hydrogen ends in s1, but is not an alkali metal. It is a unique element that is considered to be in its own family, and its properties do not resemble those of any known group. ...
... Hydrogen ends in s1, but is not an alkali metal. It is a unique element that is considered to be in its own family, and its properties do not resemble those of any known group. ...
History of the Periodic Table Chapter 6.1 Who developed the first
... atomic mass of Sr was closely related to the atomic mass of Ca and Ba. • He called this grouping a triad. • Several other triads were created based on his system but eventually there were not enough triads to make the system useful. ...
... atomic mass of Sr was closely related to the atomic mass of Ca and Ba. • He called this grouping a triad. • Several other triads were created based on his system but eventually there were not enough triads to make the system useful. ...
Key
... (E) Cr, Mn, Fe, Co Answer E. Atomic radius decreases across a row and increases down a group. This is primarily due to the increase in effective nuclear charge and the shielding affect. Atomic d orbitals are not as penetrating as s or p orbitals and therefore do not shield as much. The atomic radii ...
... (E) Cr, Mn, Fe, Co Answer E. Atomic radius decreases across a row and increases down a group. This is primarily due to the increase in effective nuclear charge and the shielding affect. Atomic d orbitals are not as penetrating as s or p orbitals and therefore do not shield as much. The atomic radii ...
(Periodic Trends) - stroh
... Monday Mystery Element Discovered by boiling urine There are 2 forms: white and red The white forms combusts in air ...
... Monday Mystery Element Discovered by boiling urine There are 2 forms: white and red The white forms combusts in air ...
- Williamsburg High School for
... • In the ground state, each atom of an element has two valence ...
... • In the ground state, each atom of an element has two valence ...
Chemical Periodicity
... 7. Trends in the periodic table. a) How does the size of the atom vary as you move left to right across the periodic table? Why? The atomic radius of atoms typically decreases from left to right across a period. This is because the force of attraction between nuclei and electrons lessens as you move ...
... 7. Trends in the periodic table. a) How does the size of the atom vary as you move left to right across the periodic table? Why? The atomic radius of atoms typically decreases from left to right across a period. This is because the force of attraction between nuclei and electrons lessens as you move ...
UNIT 4 NOTES: THE PERIODIC TABLE
... 1. These are known as the ___________________________ metals. 2. They are __________ at reactive as other metals. 3. They form _______________ solutions when dissolved in water. For example Cu+2 is ___________, while Fe3+ is ___________. In other words transition elements have _______________ ions. ...
... 1. These are known as the ___________________________ metals. 2. They are __________ at reactive as other metals. 3. They form _______________ solutions when dissolved in water. For example Cu+2 is ___________, while Fe3+ is ___________. In other words transition elements have _______________ ions. ...
THE GASEOUS STATE
... configurations of atoms lead to periodicity of elements and form the basis for chemical and physical properties of elements. • PERIODIC LAW: When the elements are arranged according to Z, their physical and ...
... configurations of atoms lead to periodicity of elements and form the basis for chemical and physical properties of elements. • PERIODIC LAW: When the elements are arranged according to Z, their physical and ...
Document
... elements. Scientists during Dmitri’s time were trying to figure out an easy way in which they could organize the elements of matter so that it would be easy for them to communicate about their properties (i.e. scientists, even back then, were lazy and they didn’t want to have to memorize all the ele ...
... elements. Scientists during Dmitri’s time were trying to figure out an easy way in which they could organize the elements of matter so that it would be easy for them to communicate about their properties (i.e. scientists, even back then, were lazy and they didn’t want to have to memorize all the ele ...
Introductory Chemistry
... this is because of the increasing number of protons in the nucleus as you go from left to right. • As the number of protons increases, the nucleus pulls the electrons closer and reduces the size of the atom. ...
... this is because of the increasing number of protons in the nucleus as you go from left to right. • As the number of protons increases, the nucleus pulls the electrons closer and reduces the size of the atom. ...