Chapter 5 study guide - Peoria Public Schools
... 1. Describe the contribution of each of the following to the development of the periodic table: a. Dobereiner b. Newlands c. Mendeleev d. Moseley 2. State Mendeleev's periodic law. 3. Describe how Mendeleev's periodic table is organized. 4. Explain was wrong with Mendeleev's periodic law? 5. State t ...
... 1. Describe the contribution of each of the following to the development of the periodic table: a. Dobereiner b. Newlands c. Mendeleev d. Moseley 2. State Mendeleev's periodic law. 3. Describe how Mendeleev's periodic table is organized. 4. Explain was wrong with Mendeleev's periodic law? 5. State t ...
Name:
... elements. Scientists during Dmitri’s time were trying to figure out an easy way in which they could organize the elements of matter so that it would be easy for them to communicate about their properties (i.e. scientists, even back then, were lazy and they didn’t want to have to memorize all the ele ...
... elements. Scientists during Dmitri’s time were trying to figure out an easy way in which they could organize the elements of matter so that it would be easy for them to communicate about their properties (i.e. scientists, even back then, were lazy and they didn’t want to have to memorize all the ele ...
ionic and covalent bonding - Atomic Theory and Periodic Table
... The formula of an ionic compound is actually the _______________ in which the ions are present. This can be easily determined because the overall charge on an ionic compound must neutral be _______________. As this formula gives a ratio rather than actual numbers of ions, it is empirical called an _ ...
... The formula of an ionic compound is actually the _______________ in which the ions are present. This can be easily determined because the overall charge on an ionic compound must neutral be _______________. As this formula gives a ratio rather than actual numbers of ions, it is empirical called an _ ...
"Part 1" Resource
... atoms of the same element are identical in all respects, particularly weight." - Dalton In the 1820's Jöns Jakob Berzelius developed a table of atomic weights, and introduced letters to symbolize elements, rather than the symbols originated by the early Greeks and following alchemists. Dobereiner no ...
... atoms of the same element are identical in all respects, particularly weight." - Dalton In the 1820's Jöns Jakob Berzelius developed a table of atomic weights, and introduced letters to symbolize elements, rather than the symbols originated by the early Greeks and following alchemists. Dobereiner no ...
03 Chapter 2 Atomic Structure Power point Periodic Table
... • Discuss the similarities and differences in the chemical properties of elements in the same group. • Discuss the changes in nature, from ionic to covalent and from basic to acidic, of the oxides across period 3. ...
... • Discuss the similarities and differences in the chemical properties of elements in the same group. • Discuss the changes in nature, from ionic to covalent and from basic to acidic, of the oxides across period 3. ...
Chapter 6 - The Periodic Table
... of an element to attract electrons in a chemical bond. Ionization energy reflects ability of atom to attract electrons in an isolated atom Generally, the higher the ionization energy of an atom, the more electronegative the atom will be in a molecule ...
... of an element to attract electrons in a chemical bond. Ionization energy reflects ability of atom to attract electrons in an isolated atom Generally, the higher the ionization energy of an atom, the more electronegative the atom will be in a molecule ...
Worksheet 8-1 Periodic Trends
... Period 1. Discuss the importance of Mendeleev’s periodic law. When elements are arranged by increasing number of protons (atomic number), there are repeating patterns of chemical and physical properties. 2. Identify each element as a metal, metalloid, or nonmetal. a) Fluorine Nonmetal b) Germanium ...
... Period 1. Discuss the importance of Mendeleev’s periodic law. When elements are arranged by increasing number of protons (atomic number), there are repeating patterns of chemical and physical properties. 2. Identify each element as a metal, metalloid, or nonmetal. a) Fluorine Nonmetal b) Germanium ...
New Title
... 4. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about valence electrons and chemical bonding. a. Most atoms are less stable when they have eight valence electrons. b. Atoms with eight valence electrons easily form compounds. c. Having eight valence electrons makes atoms very reactive. d. Atoms wi ...
... 4. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about valence electrons and chemical bonding. a. Most atoms are less stable when they have eight valence electrons. b. Atoms with eight valence electrons easily form compounds. c. Having eight valence electrons makes atoms very reactive. d. Atoms wi ...
October 11, 2007
... I am away next Monday thru Wednesday. Professor Martin will substitute for me in class and tutorial. ...
... I am away next Monday thru Wednesday. Professor Martin will substitute for me in class and tutorial. ...
Unit 10 Lecture Notes
... 1. Both the position of an element on the periodic table and the properties of that element arise from the electron configuration of the atoms a. The noble gases (group 18) all have an ending electron configuration of s2p6, they are all inert, unreactive gases 1) the most stability an atom can have ...
... 1. Both the position of an element on the periodic table and the properties of that element arise from the electron configuration of the atoms a. The noble gases (group 18) all have an ending electron configuration of s2p6, they are all inert, unreactive gases 1) the most stability an atom can have ...
Ch 4-1 Notes
... * Moving down the column the melting points decrease. Group 2 = alkaline earth metals * each element has two electrons in an s sublevel * tend to lose two electrons to form a +2 ion and achieve an octet. * harder, denser, and stronger than alkali metals * have higher melting points than alkali metal ...
... * Moving down the column the melting points decrease. Group 2 = alkaline earth metals * each element has two electrons in an s sublevel * tend to lose two electrons to form a +2 ion and achieve an octet. * harder, denser, and stronger than alkali metals * have higher melting points than alkali metal ...
Slide 1
... 4. There are seven rows or periods on the periodic table. 5. Each period corresponds to a principle energy level. 6. There are more elements in higher number periods because there are more orbitals in higher energy levels. 7. Elements are also arranged in groups or columns of elements with similar p ...
... 4. There are seven rows or periods on the periodic table. 5. Each period corresponds to a principle energy level. 6. There are more elements in higher number periods because there are more orbitals in higher energy levels. 7. Elements are also arranged in groups or columns of elements with similar p ...
III. Periodic Trends
... between the charge on the nucleus and the charge of the core electrons (inner electron shells). As atoms add more protons the nuclear charge increases Atoms are also adding more e- which are attracted to the p+ Results in the reduction of attractive force between the positive nucleus and the oute ...
... between the charge on the nucleus and the charge of the core electrons (inner electron shells). As atoms add more protons the nuclear charge increases Atoms are also adding more e- which are attracted to the p+ Results in the reduction of attractive force between the positive nucleus and the oute ...
Study guide for periodic table trends. A. By referring to electron
... a. Cl-, Ar, K+ b. K+, Ar, Clc. Cl-, K+, Ar d. Ar, Cl- K+ 17. What increases in equal steps of one from left to right in the periodic table for the elements lithium to neon? a. The number of occupied electron energy levels b. The number of neutrons in the most common isotope c. The number of electron ...
... a. Cl-, Ar, K+ b. K+, Ar, Clc. Cl-, K+, Ar d. Ar, Cl- K+ 17. What increases in equal steps of one from left to right in the periodic table for the elements lithium to neon? a. The number of occupied electron energy levels b. The number of neutrons in the most common isotope c. The number of electron ...
Document
... increased nuclear charge can change the energy of the orbital significantly compare to other orbitals (3d) which do not penetrate the nucleus as much. But, once the 4s orbital is filled, the 3d orbitals have a significant drop in energy (below that of 4s electrons) because they penetrate the 4s orbi ...
... increased nuclear charge can change the energy of the orbital significantly compare to other orbitals (3d) which do not penetrate the nucleus as much. But, once the 4s orbital is filled, the 3d orbitals have a significant drop in energy (below that of 4s electrons) because they penetrate the 4s orbi ...
III. Periodic Trends
... a. By what two metrics did he arrange the elements in his table? Increasing atomic mass & similar chemical and physical properties b. He predicted the discovery of several elements, and even described some of their physical and chemical properties. Gallium was one of those elements. The predictions ...
... a. By what two metrics did he arrange the elements in his table? Increasing atomic mass & similar chemical and physical properties b. He predicted the discovery of several elements, and even described some of their physical and chemical properties. Gallium was one of those elements. The predictions ...
STUDY GUIDE – CHAPTER 1 ATOMS AND ELEMENTS 1
... Because all elements situated in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, they display similar chemical properties. They are therefore, also called “families”. Some groups of the periodic table display very district characteristic and are given special names. Group 1 - ALKALI METALS ...
... Because all elements situated in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, they display similar chemical properties. They are therefore, also called “families”. Some groups of the periodic table display very district characteristic and are given special names. Group 1 - ALKALI METALS ...
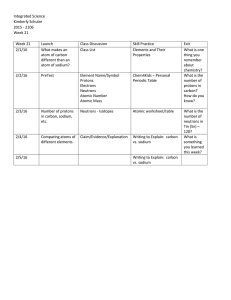
Week 21 Lessons - Highline Public Schools
... - # of protons = Atomic Number - # of electrons = # of protons (this is a neutral atom.) - Mass number = # of protons + # of neutrons - # of neutrons = mass number - # of protons (Mass number must be a whole number!!!! You can’t have half a neutron. Use atomic mass and round up.) Exit Ticket: The nu ...
... - # of protons = Atomic Number - # of electrons = # of protons (this is a neutral atom.) - Mass number = # of protons + # of neutrons - # of neutrons = mass number - # of protons (Mass number must be a whole number!!!! You can’t have half a neutron. Use atomic mass and round up.) Exit Ticket: The nu ...
Practice Questions
... 14) Most atoms prefer to fulfill the ______________ rule (having the valence shell comprise of 8 electrons). Elements on the left side of the Periodic Table have less than a half-full valence shell. Thus it is easier (takes less energy) to lose electrons to create a full valence shell, rather than g ...
... 14) Most atoms prefer to fulfill the ______________ rule (having the valence shell comprise of 8 electrons). Elements on the left side of the Periodic Table have less than a half-full valence shell. Thus it is easier (takes less energy) to lose electrons to create a full valence shell, rather than g ...
2 periodic table pd9
... Elements with the same Day 1 2-27 # of valence are in the same _______ on the periodic table. a. alkali metals = __ valence b. alkaline earth metals = __ valence ...
... Elements with the same Day 1 2-27 # of valence are in the same _______ on the periodic table. a. alkali metals = __ valence b. alkaline earth metals = __ valence ...
Teacher Background Information: The periodic table is arranged in
... A group is a vertical column of the periodic table. Elements with similar physical and chemical properties belong in a group. The group number gives the number of valence electrons in an element. For example, the Alkali Metals are in Group 1 (one valence electron), and the Halogens are in Group 7 (7 ...
... A group is a vertical column of the periodic table. Elements with similar physical and chemical properties belong in a group. The group number gives the number of valence electrons in an element. For example, the Alkali Metals are in Group 1 (one valence electron), and the Halogens are in Group 7 (7 ...
Appendices: Cluster 2 Atoms and Elements
... • Lavoisier defined the term “element” as a pure substance that cannot be chemically broken down into simpler substances. • He discovered and identified 23 elements. He based his investigations on careful measurement and observations. • He recognized mixtures exist and identified air as a mixture of ...
... • Lavoisier defined the term “element” as a pure substance that cannot be chemically broken down into simpler substances. • He discovered and identified 23 elements. He based his investigations on careful measurement and observations. • He recognized mixtures exist and identified air as a mixture of ...
Group 16: The Oxygen Family - Chemwiki
... Tellurium is the metalloid of the oxygen family, with a silvery white color and a metallic luster similar to that of tin at room temperature. Like selenium, it is also displays photoconductivity. Tellurium is an extremely rare element, and is most commonly found as a telluride of gold. It is often u ...
... Tellurium is the metalloid of the oxygen family, with a silvery white color and a metallic luster similar to that of tin at room temperature. Like selenium, it is also displays photoconductivity. Tellurium is an extremely rare element, and is most commonly found as a telluride of gold. It is often u ...