Chapter 5 Notes
... The s-block elements consist of the elements in groups 1 and 2 of the periodic table. Electrons from these elements fill the s orbital of each period. Group 1 (ALKALI METALS) fill the s orbital with 1 electron. These elements are considered to be reactive metals because they are not readily found in ...
... The s-block elements consist of the elements in groups 1 and 2 of the periodic table. Electrons from these elements fill the s orbital of each period. Group 1 (ALKALI METALS) fill the s orbital with 1 electron. These elements are considered to be reactive metals because they are not readily found in ...
Periodic Trends - CK
... The concept of effective nuclear charge (Ze f f ) can be used in concert with electron shielding. In simplified form the effective nuclear charge is equal to the atomic number (Z) minus the number of inner or non-valence electrons. For example, lithium has 3 protons, 2 inner electrons, and 1 valence ...
... The concept of effective nuclear charge (Ze f f ) can be used in concert with electron shielding. In simplified form the effective nuclear charge is equal to the atomic number (Z) minus the number of inner or non-valence electrons. For example, lithium has 3 protons, 2 inner electrons, and 1 valence ...
Chapter 5: Electrons
... The s-Block Elements The elements of the s block are chemically reactive metals. The Group 1 metals are more reactive than the Group 2 metals. The outermost energy level in an atom of the Group 1 elements contain a single electron. The ease with which the single electron is lost make the Group 1 me ...
... The s-Block Elements The elements of the s block are chemically reactive metals. The Group 1 metals are more reactive than the Group 2 metals. The outermost energy level in an atom of the Group 1 elements contain a single electron. The ease with which the single electron is lost make the Group 1 me ...
Ch-6 - Stout Middle School
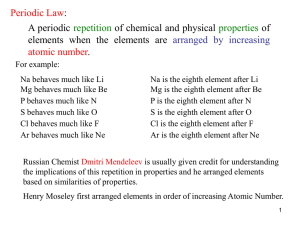
... repetition of chemical and physical properties of elements when arranged by increasing atomic number ...
... repetition of chemical and physical properties of elements when arranged by increasing atomic number ...
Chapter 1 - Study Guide Solutions
... 5) LOCATE THE GROUPS AND PERIODS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular method of displaying the chemical elements. A group (family) is a column (vertical line) in the periodic table of the elements. The groups are numbered in two ways: from 1-18 and with roma ...
... 5) LOCATE THE GROUPS AND PERIODS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular method of displaying the chemical elements. A group (family) is a column (vertical line) in the periodic table of the elements. The groups are numbered in two ways: from 1-18 and with roma ...
chemical periodicity
... • Good conductors of electricity and have a high luster • Less reactive than alkali and alkali-earth metal • Some (e.g. platinum and gold) are so unreactive that they do not form compounds easily. • Some are found as free element. ...
... • Good conductors of electricity and have a high luster • Less reactive than alkali and alkali-earth metal • Some (e.g. platinum and gold) are so unreactive that they do not form compounds easily. • Some are found as free element. ...
Final Review
... 14. Specific gravity = (density of substance)/ (density of water); 15. Kelvin = 273 + o C 16. Dalton’s atomic theory: 1] Elements are composed of indivisible particles called atoms. [2] Atoms of the same element are identical [3] Atoms of different elements can combine in whole-number ratios. [4] Ch ...
... 14. Specific gravity = (density of substance)/ (density of water); 15. Kelvin = 273 + o C 16. Dalton’s atomic theory: 1] Elements are composed of indivisible particles called atoms. [2] Atoms of the same element are identical [3] Atoms of different elements can combine in whole-number ratios. [4] Ch ...
Period Trend
... Ionization energy generally increases as you move across each period Trend caused by the increase nuclear charge a higher charge more strongly attracts electrons in the same energy level Group Trends Ionization energies generally decreases down the groups Trend caused by an increase in a ...
... Ionization energy generally increases as you move across each period Trend caused by the increase nuclear charge a higher charge more strongly attracts electrons in the same energy level Group Trends Ionization energies generally decreases down the groups Trend caused by an increase in a ...
Evidence Statements: HS-PS1-1
... HS-PS1-1 Students who demonstrate understanding can: HS-PS1-1. ...
... HS-PS1-1 Students who demonstrate understanding can: HS-PS1-1. ...
Increasing Radii
... poor conductors of heat and electricity brittle-break into pieces when hit or are gases dull looking solids if not a gas Non-metals are on the right side of the periodic table. Metalloids: elements that have properties of both metals and non-metals (these are also called semiconductors) B, Si, Ge, A ...
... poor conductors of heat and electricity brittle-break into pieces when hit or are gases dull looking solids if not a gas Non-metals are on the right side of the periodic table. Metalloids: elements that have properties of both metals and non-metals (these are also called semiconductors) B, Si, Ge, A ...
Atomic Radius reading assignment
... (from Chemistry: Connections to Our Changing World, pp. 174-175, Prentice-Hall, 1996) As you have learned, many of an element’s properties are determined by its electron configuration. In addition, the periodic table is organized so that elements with similar electron configurations are in the same ...
... (from Chemistry: Connections to Our Changing World, pp. 174-175, Prentice-Hall, 1996) As you have learned, many of an element’s properties are determined by its electron configuration. In addition, the periodic table is organized so that elements with similar electron configurations are in the same ...
Chapter 13
... Periodic Trend – There is a decrease in the size of cations as you move across a period from left to right – when you get to group 4A the anions (which are much larger) start to decrease in size Group Trend – Ionic size (both cations and anions) increases as you go down each group. ...
... Periodic Trend – There is a decrease in the size of cations as you move across a period from left to right – when you get to group 4A the anions (which are much larger) start to decrease in size Group Trend – Ionic size (both cations and anions) increases as you go down each group. ...
The Periodic Table!
... Elements 90-103 Most are synthetic (man-made) Almost all are radio active Very dense Can be found in smoke detectors, nuclear weapons, and radio active minerals ...
... Elements 90-103 Most are synthetic (man-made) Almost all are radio active Very dense Can be found in smoke detectors, nuclear weapons, and radio active minerals ...
Chapter 13 Homework
... the historical development of atomic theory, especially the contributions of Rutherford, Bohr and Schrodinger Bohr’s planetary model of the atom and how this explains the bright line (emission) spectrum of hydrogen the electron energy levels in an atom are quantized electrons absorb energy m ...
... the historical development of atomic theory, especially the contributions of Rutherford, Bohr and Schrodinger Bohr’s planetary model of the atom and how this explains the bright line (emission) spectrum of hydrogen the electron energy levels in an atom are quantized electrons absorb energy m ...
Element Project - Dover Bay
... Hydrogen is also a really cool and friendly guy because he’s extremely reactive. He has only one valence electron, so he always wants to bond with other students like Nitrogen, Chlorine, and Oxygen. For that reason, he can form many different types of compounds. Most importantly, he and his friend O ...
... Hydrogen is also a really cool and friendly guy because he’s extremely reactive. He has only one valence electron, so he always wants to bond with other students like Nitrogen, Chlorine, and Oxygen. For that reason, he can form many different types of compounds. Most importantly, he and his friend O ...
Families of elements
... valence electrons and form positive ions Elements on the right (nonmetals) tend to gain electrons to become negative ions ...
... valence electrons and form positive ions Elements on the right (nonmetals) tend to gain electrons to become negative ions ...
Periodic Trends Reading
... (electronegativity) because it is the transfer/interaction of electrons that is the basis of chemical reactions. Metals and nonmetals each have their own trends. When we look at the metals, we see that the reactivity increases as you move down the group. However, as we move across a period, the reac ...
... (electronegativity) because it is the transfer/interaction of electrons that is the basis of chemical reactions. Metals and nonmetals each have their own trends. When we look at the metals, we see that the reactivity increases as you move down the group. However, as we move across a period, the reac ...
The Periodic Table
... The Atom and the Periodic Table • Elements sorted according to properties • Groups – vertical columns; similar properties – Same group = electrons in same energy level – Electrons in same energy level = similar chemical properties and behavior ...
... The Atom and the Periodic Table • Elements sorted according to properties • Groups – vertical columns; similar properties – Same group = electrons in same energy level – Electrons in same energy level = similar chemical properties and behavior ...
Periodic Table Ch4 Honors
... • They have “typical metallic properties” • Luster, ductile, malleable, good conductors of heat and electricity • Less reactive than Group 1 and 2 • Many are unreactive (for example, palladium, platinum and gold are found as pure elements in nature) • These elements begin in Period 4 and include Gro ...
... • They have “typical metallic properties” • Luster, ductile, malleable, good conductors of heat and electricity • Less reactive than Group 1 and 2 • Many are unreactive (for example, palladium, platinum and gold are found as pure elements in nature) • These elements begin in Period 4 and include Gro ...
The Periodic Law Notes (Chapter 5) – Part 2
... 3. Group trend - atomic radii decrease as you move up a group (or increase as you move down a group). Shielding effect - an invisible barrier made of core electrons serve to decrease the pull of the nucleus on the outer (valence) electrons. Shielding increases as you go down a group because there a ...
... 3. Group trend - atomic radii decrease as you move up a group (or increase as you move down a group). Shielding effect - an invisible barrier made of core electrons serve to decrease the pull of the nucleus on the outer (valence) electrons. Shielding increases as you go down a group because there a ...
This activity will make use of the following website
... 4. Define second ionization energy. 5. Why is there a huge jump between the first and second ionization energies for Sodium, but only a small jump for Calcium? ...
... 4. Define second ionization energy. 5. Why is there a huge jump between the first and second ionization energies for Sodium, but only a small jump for Calcium? ...
Nov 9 Agenda
... 2) Atoms with a larger period number have lower ionization energies because it’s easier to remove an electron that far away from the nucleus. ...
... 2) Atoms with a larger period number have lower ionization energies because it’s easier to remove an electron that far away from the nucleus. ...
Ionic Compounds and Their Names
... 1. Metals are to left of stair line (includes Al) 2. Lanthanides and Actinides are Transition Metals (Period 6 and 7) D. Nonmetals – to right of stair line (Halogens and Noble Gases) E. Metalloids – have side along stair line (Excludes Al and most times, B) Group I A. Alkali Metals (Group 1) - form ...
... 1. Metals are to left of stair line (includes Al) 2. Lanthanides and Actinides are Transition Metals (Period 6 and 7) D. Nonmetals – to right of stair line (Halogens and Noble Gases) E. Metalloids – have side along stair line (Excludes Al and most times, B) Group I A. Alkali Metals (Group 1) - form ...
This activity will make use of the following website
... Be sure to include vocabulary such as shielding, energy levels, and effective nuclear charge in your explanations to the following questions. 1. Which property of a nucleus, is most responsible for producing a high electronegativity value? ...
... Be sure to include vocabulary such as shielding, energy levels, and effective nuclear charge in your explanations to the following questions. 1. Which property of a nucleus, is most responsible for producing a high electronegativity value? ...
Elements, Periodic Trends and Lewis Dot Diagrams
... – Bronze (copper-‐Jn alloy), Iron 2000 BC (Bronze Age) – Steel (iron-‐carbon alloy) 1200 BC (Iron Age) ...
... – Bronze (copper-‐Jn alloy), Iron 2000 BC (Bronze Age) – Steel (iron-‐carbon alloy) 1200 BC (Iron Age) ...