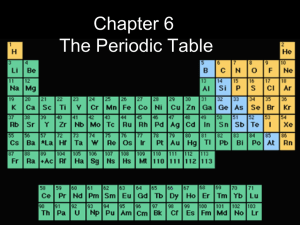
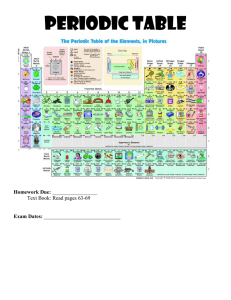
Worksheet 3.2 - contentextra
... radius is due to the increase in nuclear charge with atomic number across the period, which increases the attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons. ...
... radius is due to the increase in nuclear charge with atomic number across the period, which increases the attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons. ...
Ch 5: Periodiciy 2
... Metals are found to the left of the zig-zag line on the periodic table. Metal properties: ...
... Metals are found to the left of the zig-zag line on the periodic table. Metal properties: ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCE: CHEMISTRY REVIEW
... stable with their valence electrons or outer energy levels are full. The first energy level is full when it holds two electrons. The second energy level is full when it holds eight electrons. When two or more atoms bond covalently, they form a molecule. Covalent bonds are weaker bonds and have lower ...
... stable with their valence electrons or outer energy levels are full. The first energy level is full when it holds two electrons. The second energy level is full when it holds eight electrons. When two or more atoms bond covalently, they form a molecule. Covalent bonds are weaker bonds and have lower ...
Atomic Radius File - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... Atomic Radius = half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms ...
... Atomic Radius = half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms ...
Atomic structure and Periodic table revision guide File
... called the noble gases. They are unreactive and do not easily form molecules because their atoms have stable arrangements of electrons. The noble gases have eight electrons in their outer energy level, except for helium, which has only two electrons. The boiling points of the noble gases increase wi ...
... called the noble gases. They are unreactive and do not easily form molecules because their atoms have stable arrangements of electrons. The noble gases have eight electrons in their outer energy level, except for helium, which has only two electrons. The boiling points of the noble gases increase wi ...
14-15-Periodic Trends
... distance from the nucleus to a p electron is slightly larger than the average distance to an s electron in the same shell. There is a slight decrease from group 15 to group 16 due to electron-electron repulsion of electrons in the same orbital. ...
... distance from the nucleus to a p electron is slightly larger than the average distance to an s electron in the same shell. There is a slight decrease from group 15 to group 16 due to electron-electron repulsion of electrons in the same orbital. ...
Chemistry 1 Chapter 4, The Periodic Table
... •Metals Share Many Properties, continued • Other Properties of Metals – metals can be mixed with one or more other elements (usually metals) to form alloys • this mixing eliminates some of the disadvantages of the • independent elements and gives the new alloy properties that are different than the ...
... •Metals Share Many Properties, continued • Other Properties of Metals – metals can be mixed with one or more other elements (usually metals) to form alloys • this mixing eliminates some of the disadvantages of the • independent elements and gives the new alloy properties that are different than the ...
The Modern Periodic Table
... General Features of the Periodic Table • Metals are found on the left hand side of each period. Properties become more metallic as atomic number increases down a group. • Some elements, called metalloids, exhibit some metallic and non-metallic properties e.g. silicon. • Elements which are gases at ...
... General Features of the Periodic Table • Metals are found on the left hand side of each period. Properties become more metallic as atomic number increases down a group. • Some elements, called metalloids, exhibit some metallic and non-metallic properties e.g. silicon. • Elements which are gases at ...
Periodic Table Student Outline
... With a publisher’s deadline looming, Mendeleyev didn’t have time to describe all 63 then-known elements. So he turned to a data set of atomic weights meticulously gathered by others. To determine those weights, scientists had passed currents through various solutions to break them up into their cons ...
... With a publisher’s deadline looming, Mendeleyev didn’t have time to describe all 63 then-known elements. So he turned to a data set of atomic weights meticulously gathered by others. To determine those weights, scientists had passed currents through various solutions to break them up into their cons ...
Electron Affinity
... the Father of the Periodic Table. In 1869) Organized elements according to atomic weights BUT switched numerous elements around to “fit” characteristics of a different group! (Te & I) Left gaps where he hypothesized new elements would be found and Fit IN (gallium & the Nobel Gases) ...
... the Father of the Periodic Table. In 1869) Organized elements according to atomic weights BUT switched numerous elements around to “fit” characteristics of a different group! (Te & I) Left gaps where he hypothesized new elements would be found and Fit IN (gallium & the Nobel Gases) ...
Periodic Table Notes Ch. 6 ppt
... are some of the elemental properties that make the periodic table, well, periodic? Classification by metals, nonmetals and metalloids Metals - shiny ductile, malleable solids, good conductors of heat and electricity Nonmetals - dull, brittle solids; or gas, poor conductors of heat and electricit ...
... are some of the elemental properties that make the periodic table, well, periodic? Classification by metals, nonmetals and metalloids Metals - shiny ductile, malleable solids, good conductors of heat and electricity Nonmetals - dull, brittle solids; or gas, poor conductors of heat and electricit ...
Periodic Table Properties Notes s1
... • The electrons available for the formation of chemical compounds are referred to as valence electrons. • Valence electrons are located in the outermost energy levels in the s & p orbitals. • example: Na has 11 electrons: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 Sodium has 1 valence electron ...
... • The electrons available for the formation of chemical compounds are referred to as valence electrons. • Valence electrons are located in the outermost energy levels in the s & p orbitals. • example: Na has 11 electrons: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 Sodium has 1 valence electron ...
Ch. 11.4 Notes (Periodicity) teacher 2012
... gases – ___________ are not listed in Figure 12.4 since they do not ________ form _____________ compounds ! ...
... gases – ___________ are not listed in Figure 12.4 since they do not ________ form _____________ compounds ! ...
Chapter 5 - Midway ISD
... configuration, but doesn’t share their properties Helium is grouped with 18 because it has similar properties since its outside energy level is full, even though it has the same electron configuration as group 2 ...
... configuration, but doesn’t share their properties Helium is grouped with 18 because it has similar properties since its outside energy level is full, even though it has the same electron configuration as group 2 ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table of Elements: The Secret
... trends or patterns found within the Periodic Table of Elements. The elements found within the Periodic Table are put in order in a very particular pattern, based on several common similarities or characteristics. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev produced a table of elements based on their atomic weights. P ...
... trends or patterns found within the Periodic Table of Elements. The elements found within the Periodic Table are put in order in a very particular pattern, based on several common similarities or characteristics. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev produced a table of elements based on their atomic weights. P ...
How Atoms Differ
... and slightly different amu. The greater the number of protons for an element, the greater the number of isotopes. ...
... and slightly different amu. The greater the number of protons for an element, the greater the number of isotopes. ...
Unit 1: Introduction to Chemistry
... 32. As we move from left to right metallic character of the elements _decreases_. As we move up a group, metallic character _decreases_. ...
... 32. As we move from left to right metallic character of the elements _decreases_. As we move up a group, metallic character _decreases_. ...
Periodic Law
... Squares in the Periodic Table The background colors in the squares are used to distinguish groups of elements. Group I elements are called alkali metals. Group 2 elements are called alkaline earth metals. The nonmetals of Group 17 are called halogens. Group 18 elements are called Noble Gases Groups ...
... Squares in the Periodic Table The background colors in the squares are used to distinguish groups of elements. Group I elements are called alkali metals. Group 2 elements are called alkaline earth metals. The nonmetals of Group 17 are called halogens. Group 18 elements are called Noble Gases Groups ...
Chapter 4
... In 1865, the English chemist John _____________ arranged the known elements according to their properties and in order of increasing _____________ ___________. He placed the elements in a table. Newlands noticed that all of the elements in a given row had similar chemical and physical properties. Be ...
... In 1865, the English chemist John _____________ arranged the known elements according to their properties and in order of increasing _____________ ___________. He placed the elements in a table. Newlands noticed that all of the elements in a given row had similar chemical and physical properties. Be ...
The Periodic Table
... described as alkaline, a term derived from the Arab word for ashes, al-qali. Alkaline mixtures found many uses, particularly in the preparation of soaps. This is why they are called alkali metals. We now know that alkaline ashes contain compounds of Group 1 elements, most notably potassium carbonate ...
... described as alkaline, a term derived from the Arab word for ashes, al-qali. Alkaline mixtures found many uses, particularly in the preparation of soaps. This is why they are called alkali metals. We now know that alkaline ashes contain compounds of Group 1 elements, most notably potassium carbonate ...
Periodic Table Packet
... b. Almost inert (not reactive) i. Krypton, xenon, and radon form compounds with oxygen and fluorine 7. Transition elements ...
... b. Almost inert (not reactive) i. Krypton, xenon, and radon form compounds with oxygen and fluorine 7. Transition elements ...
Atomic Radius - Atomic radius is simply the radius of
... Dmitri Mendeleev In 1869 Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer (Germany) published nearly identical classification schemes for elements known to date. The periodic table is base on the similarity of properties and reactivities exhibited by certain elements. Later, Henri Moseley ( England,1887-1915) establishe ...
... Dmitri Mendeleev In 1869 Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer (Germany) published nearly identical classification schemes for elements known to date. The periodic table is base on the similarity of properties and reactivities exhibited by certain elements. Later, Henri Moseley ( England,1887-1915) establishe ...
Name
... The graphs above provide the same information, but in two different ways. Look at the horizontal bar graph for the year 1999. Follow the end of the bar to the bottom axis and you will see that Company X made a profit of $30,000. The same data can be found on the vertical bar graph by following the e ...
... The graphs above provide the same information, but in two different ways. Look at the horizontal bar graph for the year 1999. Follow the end of the bar to the bottom axis and you will see that Company X made a profit of $30,000. The same data can be found on the vertical bar graph by following the e ...
Revising the Periodic Table
... 1. The Periodic Table is a way of arranging what we know about the chemical elements. 2. Each element in the Periodic Table is a different type of atom. 3. Each element has a different atomic number. 4. The Periodic Table is arranged in atomic number order. 5. Each atom has an atomic number. 6. An e ...
... 1. The Periodic Table is a way of arranging what we know about the chemical elements. 2. Each element in the Periodic Table is a different type of atom. 3. Each element has a different atomic number. 4. The Periodic Table is arranged in atomic number order. 5. Each atom has an atomic number. 6. An e ...