chapter 7- periodic properties of the elements
... • Periodic Table Build! • You are given a set of element cards- all info on these cards should be used in order to organize the elements you are given into the first periodic table (correctly) ...
... • Periodic Table Build! • You are given a set of element cards- all info on these cards should be used in order to organize the elements you are given into the first periodic table (correctly) ...
CHEMISTRY SEPTEMBER 11, 2014
... • They are ductile (they can be drawn into thin wires). • They are malleable (they can be easily hammered into very thin sheets). • Tend to lose electrons easily • Reacts with oxygen ...
... • They are ductile (they can be drawn into thin wires). • They are malleable (they can be easily hammered into very thin sheets). • Tend to lose electrons easily • Reacts with oxygen ...
nucleic acids - Cloudfront.net
... 1. Chemical compound= a substance formed by the combination of 2 or more elements in definite proportions. Example: Sodium Chloride = Table salt Forms when sodium and chlorine combine in a 1:1 ratio 2. Chemical formula= a short hand that shows chemical composition Example: Sodium Chloride= NaCl Chem ...
... 1. Chemical compound= a substance formed by the combination of 2 or more elements in definite proportions. Example: Sodium Chloride = Table salt Forms when sodium and chlorine combine in a 1:1 ratio 2. Chemical formula= a short hand that shows chemical composition Example: Sodium Chloride= NaCl Chem ...
The electrons
... Copyright© 2013 J Smith - for text, atom pictures and atom diagrams. (Copyright is excluded for pictures/clip art in public domain - Public Domain Files). All rights reserved. Permission to copy for single classroom use only. The original purchaser may reproduce and use these materials for their own ...
... Copyright© 2013 J Smith - for text, atom pictures and atom diagrams. (Copyright is excluded for pictures/clip art in public domain - Public Domain Files). All rights reserved. Permission to copy for single classroom use only. The original purchaser may reproduce and use these materials for their own ...
The Periodic Table
... • Some are like metals • Some are like non-metals • Properties vary greatly within a group ...
... • Some are like metals • Some are like non-metals • Properties vary greatly within a group ...
The Periodic Table and Chemical Properties
... The designer of this table wanted to emphasize the periods, so it has two periods of 8 elements, then two of 18 elements, then two of 32, and so on. The “arms” that stick out from the spiral are the lanthanides and actinides. These are the elements that you will find in those two rows down below the ...
... The designer of this table wanted to emphasize the periods, so it has two periods of 8 elements, then two of 18 elements, then two of 32, and so on. The “arms” that stick out from the spiral are the lanthanides and actinides. These are the elements that you will find in those two rows down below the ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. The octet rule is useful for predicting what types of ions an element is likely ...
... The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. The octet rule is useful for predicting what types of ions an element is likely ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... Isotopes of Some Elements and Their Atomic Mass Most elements have two or more isotopes that contribute to the atomic mass of that element. ...
... Isotopes of Some Elements and Their Atomic Mass Most elements have two or more isotopes that contribute to the atomic mass of that element. ...
The Periodic Table
... 47. What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state called? a. nuclear energy c. shielding energy b. ionization energy d. electronegative energy 48. Which block in the periodic table contains the alkali metals? a. s b. p c. d d. f 49. Which of the foll ...
... 47. What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state called? a. nuclear energy c. shielding energy b. ionization energy d. electronegative energy 48. Which block in the periodic table contains the alkali metals? a. s b. p c. d d. f 49. Which of the foll ...
Metals
... Ch9.5 Naming Acids and Bases (Discuss these in more detail later) Acids: A compound that contains one or more hydrogen atoms and produces hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. (The names of compounds can change when acids are present). The name of an acidic compound depends on the type of a ...
... Ch9.5 Naming Acids and Bases (Discuss these in more detail later) Acids: A compound that contains one or more hydrogen atoms and produces hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. (The names of compounds can change when acids are present). The name of an acidic compound depends on the type of a ...
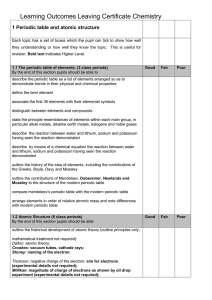
1 Periodic table and atomic structure
... Co for cancer treatment explain how 14C is used for age determination (calculations not required) 1.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (11 class periods) By the end of this section pupils should be able define and explain energy levels in atoms describe the organization of particles in atoms of element ...
... Co for cancer treatment explain how 14C is used for age determination (calculations not required) 1.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (11 class periods) By the end of this section pupils should be able define and explain energy levels in atoms describe the organization of particles in atoms of element ...
1 Periodic table and atomic structure
... Co for cancer treatment explain how 14C is used for age determination (calculations not required) 1.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (11 class periods) By the end of this section pupils should be able define and explain energy levels in atoms describe the organization of particles in atoms of element ...
... Co for cancer treatment explain how 14C is used for age determination (calculations not required) 1.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (11 class periods) By the end of this section pupils should be able define and explain energy levels in atoms describe the organization of particles in atoms of element ...
Chapter 5 The Periodic Table
... configuration for an element in that group. • Def.-an electron that is in the highest occupied energy level of an atom ...
... configuration for an element in that group. • Def.-an electron that is in the highest occupied energy level of an atom ...
Periodic Trends
... attraction to the valence electrons (which are increasing as well). This pulls the valence electrons closer to the nucleus. Going down the periodic table, atomic radius tends get bigger within a group. Even though the number of protons is increasing, new energy levels are added as you move down whic ...
... attraction to the valence electrons (which are increasing as well). This pulls the valence electrons closer to the nucleus. Going down the periodic table, atomic radius tends get bigger within a group. Even though the number of protons is increasing, new energy levels are added as you move down whic ...
Periodic Table 2015
... • Discuss the similarities and differences in the chemical properties of elements in the same group. • Discuss the changes in nature, from ionic to covalent and from basic to acidic, of the oxides across period 3. ...
... • Discuss the similarities and differences in the chemical properties of elements in the same group. • Discuss the changes in nature, from ionic to covalent and from basic to acidic, of the oxides across period 3. ...
Topic 3 Periodic Trends Notes 14-15
... 3.1: The Periodic Table Understandings: 1. The Periodic Table is arranged into four blocks associated with the four sub-levels: s, p, d, and g 2. The Periodic Table consists of groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows) 3. The period number (n) is the outer energy level that is occupied ...
... 3.1: The Periodic Table Understandings: 1. The Periodic Table is arranged into four blocks associated with the four sub-levels: s, p, d, and g 2. The Periodic Table consists of groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows) 3. The period number (n) is the outer energy level that is occupied ...
The Periodic Table - Journigan-wiki
... If 1 mm= 1pm, how long would you cut a straw to represent fluorine’s atomic radius? If 1 mm= 1pm, how long would you cut a straw to represent germanium’s atomic radius? If 10 cm= 1 pauling, how long would you cut a straw to represent silver’s electronegativity? If 10 cm= 1 pauling, how long would yo ...
... If 1 mm= 1pm, how long would you cut a straw to represent fluorine’s atomic radius? If 1 mm= 1pm, how long would you cut a straw to represent germanium’s atomic radius? If 10 cm= 1 pauling, how long would you cut a straw to represent silver’s electronegativity? If 10 cm= 1 pauling, how long would yo ...
The Periodic Table
... Predicting that several new elements would appear. A few years passed and sure enough they came, Gallium, scandium, germanium were their names. Chemists everywhere were impressed with what they saw. There really must be something to this periodic law. ...
... Predicting that several new elements would appear. A few years passed and sure enough they came, Gallium, scandium, germanium were their names. Chemists everywhere were impressed with what they saw. There really must be something to this periodic law. ...
7-1 Notes: Arranging the Elements
... and metalloids. The number of ____________ in the outer energy level of an atom helps determine the category in which an element belongs. The __________ line on the periodic table can help you recognize metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Most elements are __________. Metals are found to the _______ ...
... and metalloids. The number of ____________ in the outer energy level of an atom helps determine the category in which an element belongs. The __________ line on the periodic table can help you recognize metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Most elements are __________. Metals are found to the _______ ...
Name Date ______ Period ______ Chapter 5: Periodic Table
... 1. Organized elements on the periodic table by increasing ___________________ ________________________. 2. Fixed problems in Mendeleev’s arrangement. C. Periodic Law 1. Properties of elements repeat in a predictable way when ___________________ _________________________ are used to arrange elements ...
... 1. Organized elements on the periodic table by increasing ___________________ ________________________. 2. Fixed problems in Mendeleev’s arrangement. C. Periodic Law 1. Properties of elements repeat in a predictable way when ___________________ _________________________ are used to arrange elements ...
PPT_Topic1d_Higher
... Today we will learn to Describe trends in different properties of elements. We will do this by Defining and analysing covalent radius, ionisation energy and electronegativity. We will have succeeded if We can show the pattern of increasing trends on a periodic table. ...
... Today we will learn to Describe trends in different properties of elements. We will do this by Defining and analysing covalent radius, ionisation energy and electronegativity. We will have succeeded if We can show the pattern of increasing trends on a periodic table. ...
The Periodic Law Notes (Chapter 5) – Part 2
... 3. Group trend – ionization energy increases as you move up a group (or decreases as you move down a group). In general, as you do down a group the ionization energy decreases because the size of the atom is increasing and the outermost electrons are further from the nucleus. 1. Which atom has the h ...
... 3. Group trend – ionization energy increases as you move up a group (or decreases as you move down a group). In general, as you do down a group the ionization energy decreases because the size of the atom is increasing and the outermost electrons are further from the nucleus. 1. Which atom has the h ...
The Periodic Table of Elements and Atom Types
... the nucleus and fill up one energy level after another. b. valence electron – an electron in the outermost energy level of an atom ...
... the nucleus and fill up one energy level after another. b. valence electron – an electron in the outermost energy level of an atom ...
Periodic Table
... John Newlands (1837 – 1898) proposed the law of octaves (~1865) It states; if the chemical elements are arranged according to increasing atomic weight, those with similar physical and chemical properties occur after each interval of seven elements. Meaning every eighth element shows similar properti ...
... John Newlands (1837 – 1898) proposed the law of octaves (~1865) It states; if the chemical elements are arranged according to increasing atomic weight, those with similar physical and chemical properties occur after each interval of seven elements. Meaning every eighth element shows similar properti ...