The History of the Periodic Table
... masses. Dalton published the first table of elements that included atomic masses.As more and more work was done in this area, it became obvious that there were experimental errors in many of the atomic masses that Dalton and other workers had reported. For the rest of the 19th century, atomic masses ...
... masses. Dalton published the first table of elements that included atomic masses.As more and more work was done in this area, it became obvious that there were experimental errors in many of the atomic masses that Dalton and other workers had reported. For the rest of the 19th century, atomic masses ...
Chapter 4:ааAtomic Structure Section 4.1анаDefining the Atom
... ● the mass of an atom can be determined using a mass spectrometer ○ the numbers are very small and impractical for working with ○ it is more useful to compare the relative masses of atoms using a reference isotope as a standard ■ the chosen isotope is carbon12 (assigned a mass of exactly 12 at ...
... ● the mass of an atom can be determined using a mass spectrometer ○ the numbers are very small and impractical for working with ○ it is more useful to compare the relative masses of atoms using a reference isotope as a standard ■ the chosen isotope is carbon12 (assigned a mass of exactly 12 at ...
Radioactivity
... • Unlike all previously discovered chemical reactions, radioactivity sometimes results in the formation of completely new atoms. Radioactivity results from having an unstable nucleus. When these nuclei lose energy and break apart, decay occurs. Radioactive decay releases energy from the nucleu ...
... • Unlike all previously discovered chemical reactions, radioactivity sometimes results in the formation of completely new atoms. Radioactivity results from having an unstable nucleus. When these nuclei lose energy and break apart, decay occurs. Radioactive decay releases energy from the nucleu ...
Modern Physics
... outside the belt of stability • All elements beyond number 83, Bismuth are unstable - WHY? ...
... outside the belt of stability • All elements beyond number 83, Bismuth are unstable - WHY? ...
Atomic Structure - Tumwater School District
... Dalton buys the Democritus hype. • John Dalton uses experiments to come up with 4 ideas about the atom 1. Elements are composed of indivisible atoms. 2. All atoms of the same elements are identical. Atoms of different elements must be different. 3. Atoms of different elements can be combined togeth ...
... Dalton buys the Democritus hype. • John Dalton uses experiments to come up with 4 ideas about the atom 1. Elements are composed of indivisible atoms. 2. All atoms of the same elements are identical. Atoms of different elements must be different. 3. Atoms of different elements can be combined togeth ...
Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table
... In the early 1800’s British scientist John Dalton proposed that each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Dalton stated that all of the atoms of a particular element are identical but are different from atoms of all other elements. Daltons theory also assumed that atoms could not be di ...
... In the early 1800’s British scientist John Dalton proposed that each element is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Dalton stated that all of the atoms of a particular element are identical but are different from atoms of all other elements. Daltons theory also assumed that atoms could not be di ...
atomic number
... Isotopes: are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Because isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons, they also have different mass numbers. Isotopes are chemically alike because they have identical numbers of protons and electrons, which are ...
... Isotopes: are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Because isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons, they also have different mass numbers. Isotopes are chemically alike because they have identical numbers of protons and electrons, which are ...
Elements, Compounds, Mixtures
... • 1803-1805: Dalton published his first table of relative atomic weights derived from analysis of water, ammonia, carbon dioxide, etc. Six elements appear in this table, namely hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, sulfur, and phosphorus, with the atom of hydrogen conventionally assumed to weigh 1. ...
... • 1803-1805: Dalton published his first table of relative atomic weights derived from analysis of water, ammonia, carbon dioxide, etc. Six elements appear in this table, namely hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, sulfur, and phosphorus, with the atom of hydrogen conventionally assumed to weigh 1. ...
Early Atomic Theory
... • Compounds are formed by combining two or more atoms of different elements. • Atoms combine to form compounds in simple whole number ratios. • Atoms of two elements may combine in different ratios, leading to formation of different compounds. ...
... • Compounds are formed by combining two or more atoms of different elements. • Atoms combine to form compounds in simple whole number ratios. • Atoms of two elements may combine in different ratios, leading to formation of different compounds. ...
Name Date Class DEFINING THE ATOM Section Review Objectives
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in an atom of that el ...
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in an atom of that el ...
PowerPoint
... What is a weighted average? • A weighted average accounts for the percent abundance and mass of each isotope in an element. • Percent abundance is a measure of how common or rare that isotope is. • The average atomic mass of an element can be calculated by multiplying the mass of each isotope by it ...
... What is a weighted average? • A weighted average accounts for the percent abundance and mass of each isotope in an element. • Percent abundance is a measure of how common or rare that isotope is. • The average atomic mass of an element can be calculated by multiplying the mass of each isotope by it ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... a) Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. b) Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons c) Electrons have so little mass th ...
... a) Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. b) Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons c) Electrons have so little mass th ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... His model of the atom is sometimes called the “Plum Pudding” model. Atoms were made from a positively charged substance with negatively charged electrons scattered about, like raisins in a pudding. ...
... His model of the atom is sometimes called the “Plum Pudding” model. Atoms were made from a positively charged substance with negatively charged electrons scattered about, like raisins in a pudding. ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... The periodic Table lists all of the elements and arranges them according to atomic number. The atomic number is ALWAYS equal to the number of _________________ in an element. The periodic table is arranged into horizontal rows, called __________________ and vertical columns, called _________________ ...
... The periodic Table lists all of the elements and arranges them according to atomic number. The atomic number is ALWAYS equal to the number of _________________ in an element. The periodic table is arranged into horizontal rows, called __________________ and vertical columns, called _________________ ...
Any substance that cannot be decomposed into
... is defined as a chemical element. Only 94 such substances are known to exist in nature. They are found either chemically free, such as the oxygen in air, or combined with other elements, such as the hydrogen and oxygen in water. About 20 additional elements have been produced in the laboratory throu ...
... is defined as a chemical element. Only 94 such substances are known to exist in nature. They are found either chemically free, such as the oxygen in air, or combined with other elements, such as the hydrogen and oxygen in water. About 20 additional elements have been produced in the laboratory throu ...
chemistry chapter 5 notes
... Rutherford’s model of the atom stated that the atom is mostly empty space with all the positive charge and almost all of the mass concentrated in a small region, which he called the nucleus. ...
... Rutherford’s model of the atom stated that the atom is mostly empty space with all the positive charge and almost all of the mass concentrated in a small region, which he called the nucleus. ...
Science 9 Unit B 2.0 - Vegreville Composite High
... • There were holes in his pattern created by undiscovered elements • These holes were filled over time – showing that Mendeleev’s table was accurate ...
... • There were holes in his pattern created by undiscovered elements • These holes were filled over time – showing that Mendeleev’s table was accurate ...
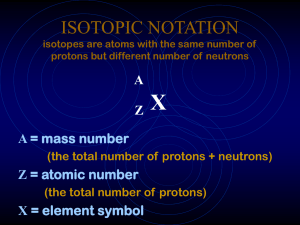
ISOTOPIC NOTATION isotopes are atoms with the same number
... • The atomic mass of an element represents the average mass of all the isotopes found in nature. No element exists with only one possible isotope. Hydrogen has the smallest number of isotopes: 1H protium, 2H deuterium, 3H tritium. Its atomic mass is 1.0079 amu (atomic mass units). The atomic mass is ...
... • The atomic mass of an element represents the average mass of all the isotopes found in nature. No element exists with only one possible isotope. Hydrogen has the smallest number of isotopes: 1H protium, 2H deuterium, 3H tritium. Its atomic mass is 1.0079 amu (atomic mass units). The atomic mass is ...
Standard Atomic Notation Standard Atomic Notation
... • Although they exist, we will not draw elements with more than three orbits. Extra Rules: • You have to put electrons into the lowest orbits first. • Put electrons in the second and third orbits one at a time until you get 4 electrons in the orbit, and then start to pair them up. Draw the Bohr-Ruth ...
... • Although they exist, we will not draw elements with more than three orbits. Extra Rules: • You have to put electrons into the lowest orbits first. • Put electrons in the second and third orbits one at a time until you get 4 electrons in the orbit, and then start to pair them up. Draw the Bohr-Ruth ...
Name
... 16. Most of the alpha particles traveled through the gold atoms showing atoms are mostly empty space. Very few positively charged alpha particles deflected revealing a tiny, dense, positive region in atoms. 17. C 18. B 19. D 20. They are isotopes b/c they have different numbers of neutrons, but they ...
... 16. Most of the alpha particles traveled through the gold atoms showing atoms are mostly empty space. Very few positively charged alpha particles deflected revealing a tiny, dense, positive region in atoms. 17. C 18. B 19. D 20. They are isotopes b/c they have different numbers of neutrons, but they ...
Atom - Perry Local Schools
... people who have taken radioactive iodine will emit beta particles. Radioactive iodine may enter the environment during a nuclear reactor accident and find its way into the food chain. ...
... people who have taken radioactive iodine will emit beta particles. Radioactive iodine may enter the environment during a nuclear reactor accident and find its way into the food chain. ...
atom
... their nuclei are unstable and break down at a constant rate over time. Although the radiation these isotopes give off can be dangerous, they have important scientific and practical uses. ...
... their nuclei are unstable and break down at a constant rate over time. Although the radiation these isotopes give off can be dangerous, they have important scientific and practical uses. ...
Structures of Matter
... mass number is equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons The number of neutrons is equal to the difference between the mass number and the atomic number ...
... mass number is equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons The number of neutrons is equal to the difference between the mass number and the atomic number ...
Promethium

Promethium, originally prometheum, is a chemical element with symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is one of only two such elements that are followed in the periodic table by elements with stable forms, a distinction shared with technetium. Chemically, promethium is a lanthanide, which forms salts when combined with other elements. Promethium shows only one stable oxidation state of +3; however, a few +2 compounds may exist.In 1902, Bohuslav Brauner suggested there was an element with properties intermediate between those of the known elements neodymium (60) and samarium (62); this was confirmed in 1914 by Henry Moseley who, having measured the atomic numbers of all the elements then known, found there was an element with atomic number 61. In 1926, an Italian and an American group claimed to have isolated a sample of element 61; both ""discoveries"" were soon proven to be false. In 1938, during a nuclear experiment conducted at Ohio State University, a few radioactive nuclides were produced that certainly were not radioisotopes of neodymium or samarium, but there was a lack of chemical proof that element 61 was produced, and the discovery was not generally recognized. Promethium was first produced and characterized at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in 1945 by the separation and analysis of the fission products of uranium fuel irradiated in a graphite reactor. The discoverers proposed the name ""prometheum"" (the spelling was subsequently changed), derived from Prometheus, the Titan in Greek mythology who stole fire from Mount Olympus and brought it down to humans, to symbolize ""both the daring and the possible misuse of mankind's intellect"". However, a sample of the metal was made only in 1963.There are two possible sources for natural promethium: rare decays of natural europium-151 (producing promethium-147), and uranium (various isotopes). Practical applications exist only for chemical compounds of promethium-147, which are used in luminous paint, atomic batteries, and thickness measurement devices, even though promethium-145 is the most stable promethium isotope. Because natural promethium is exceedingly scarce, it is typically synthesized by bombarding uranium-235 (enriched uranium) with thermal neutrons to produce promethium-147.