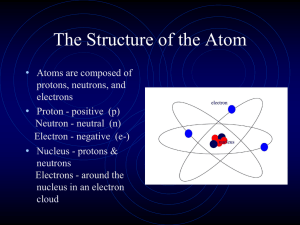
Subatomic Particles
... • This is the number of protons in an atom • Hydrogen has 1 proton and thus is atomic number 1 • Oxygen has 8 protons and thus atomic number 8 • Every element is different due to its different numbers of protons • So changing the number of protons changes the element! – Some elements may have the sa ...
... • This is the number of protons in an atom • Hydrogen has 1 proton and thus is atomic number 1 • Oxygen has 8 protons and thus atomic number 8 • Every element is different due to its different numbers of protons • So changing the number of protons changes the element! – Some elements may have the sa ...
Atomic Structure File
... other out, so the charge of an atom is the difference between how many positive charges (protons) it has, and how many negative charges (electrons) it has. For example, a chlorine atom with 17 protons (+17) and 18 electrons (−18) would have a charge of −1. (The difference is 1, and it’s negative bec ...
... other out, so the charge of an atom is the difference between how many positive charges (protons) it has, and how many negative charges (electrons) it has. For example, a chlorine atom with 17 protons (+17) and 18 electrons (−18) would have a charge of −1. (The difference is 1, and it’s negative bec ...
atomic mass and symb..
... electrons All the elements can be represented as symbols that are organized in the periodic table. Carbon is represented by ...
... electrons All the elements can be represented as symbols that are organized in the periodic table. Carbon is represented by ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... Nuclear Chemistry The strong force, also known as strong nuclear force, is stronger than the electrostatic repulsion. It holds the nucleus together. ...
... Nuclear Chemistry The strong force, also known as strong nuclear force, is stronger than the electrostatic repulsion. It holds the nucleus together. ...
Atom - WCHS Physical Science
... • proton, electron, and neutron locations. • atomic mass and atomic number. • atoms with different numbers of neutrons (isotopes). • explain the relationship of the proton number to the element's identity. ...
... • proton, electron, and neutron locations. • atomic mass and atomic number. • atoms with different numbers of neutrons (isotopes). • explain the relationship of the proton number to the element's identity. ...
Topic 2 Microscopic World I
... (3) They are poor conductors of heat. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) ...
... (3) They are poor conductors of heat. (1) and (2) only (1) and (3) only (2) and (3) only (1), (2) and (3) ...
Unit 2 Lesson 1 - Mrs. Tainter`s Physical Science Class
... neutrons in a single atom. the number of protons in every atom of an element. atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons but same number of protons. states that the properties of elements are periodic or recurring as the elements increase in atomic number. occurs when chemical bond ...
... neutrons in a single atom. the number of protons in every atom of an element. atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons but same number of protons. states that the properties of elements are periodic or recurring as the elements increase in atomic number. occurs when chemical bond ...
Unit 2 Spiraling
... 2. Calculate the atomic mass of bromine. The two istopes of bromine have atomic masses and relative abundance of 78.92 amu (50.69%) and 80.92 amu (49.31%) Show your work and calculate to the correct number of significant figures: 4. How can there be more than 1000 different atoms when there are only ...
... 2. Calculate the atomic mass of bromine. The two istopes of bromine have atomic masses and relative abundance of 78.92 amu (50.69%) and 80.92 amu (49.31%) Show your work and calculate to the correct number of significant figures: 4. How can there be more than 1000 different atoms when there are only ...
Name Honors Chemistry ___/___/___ Subatomic Particles Atomic
... Isotopes are two or more atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. The existence of isotopes proves that another part of Dalton's atomic theory is incorrect. Dalton wrote that atoms of the same element have the same physical and chemical properties ...
... Isotopes are two or more atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. The existence of isotopes proves that another part of Dalton's atomic theory is incorrect. Dalton wrote that atoms of the same element have the same physical and chemical properties ...
Year 9 Science revison _15-16_ end of year CHEM
... it has 1 electron in the outer shell. It loses that electron (in a chemical reaction) to have a full outer shell and become “stable” like the noble gases. You know that it loses 1 electron…..because it’s in group 1. ii) what is the charge on a rubidium ion ? ...
... it has 1 electron in the outer shell. It loses that electron (in a chemical reaction) to have a full outer shell and become “stable” like the noble gases. You know that it loses 1 electron…..because it’s in group 1. ii) what is the charge on a rubidium ion ? ...
Chapter 3 - WordPress.com
... • In 1911, Rutherford and his coworkers at the University of Manchester, England, directed a narrow beam of alpha particles at a very thin sheet of gold foil. • Based on Thomson’s model of the atom he expected the alpha particles to pass through the foil but not all did! ...
... • In 1911, Rutherford and his coworkers at the University of Manchester, England, directed a narrow beam of alpha particles at a very thin sheet of gold foil. • Based on Thomson’s model of the atom he expected the alpha particles to pass through the foil but not all did! ...
atomic number
... Sometimes, when they tried to react substances together, nothing happened! Substances that DO NOT react are Inert They found that most materials will react to form new substances. These elements are said to be chemically active (reactive) Oxygen is very reactive, so is hydrogen which we will look a ...
... Sometimes, when they tried to react substances together, nothing happened! Substances that DO NOT react are Inert They found that most materials will react to form new substances. These elements are said to be chemically active (reactive) Oxygen is very reactive, so is hydrogen which we will look a ...
Ch. 3 - My CCSD
... Sometimes, when they tried to react substances together, nothing happened! Substances that DO NOT react are Inert They found that most materials will react to form new substances. These elements are said to be chemically active (reactive) Oxygen is very reactive, so is hydrogen which we will look a ...
... Sometimes, when they tried to react substances together, nothing happened! Substances that DO NOT react are Inert They found that most materials will react to form new substances. These elements are said to be chemically active (reactive) Oxygen is very reactive, so is hydrogen which we will look a ...
ISOTOPIC NOTATION isotopes are atoms with the same number of
... 2. Give the complete chemical notation for the nuclide with 23 protons, 26 neutrons and 20 electrons. ...
... 2. Give the complete chemical notation for the nuclide with 23 protons, 26 neutrons and 20 electrons. ...
Review for Chapter 2
... Review for Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1. Dalton’s Atomic Theory says: • Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called “atoms”. • All atoms of the same element are identical. • Compounds contain atoms of different elements combined in whole-number ratios. • Atoms are combined or ...
... Review for Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1. Dalton’s Atomic Theory says: • Matter is composed of tiny, indivisible particles called “atoms”. • All atoms of the same element are identical. • Compounds contain atoms of different elements combined in whole-number ratios. • Atoms are combined or ...
Multiple Choice - EDU360ScienceMethods
... The vertical rows are called periods. The elements that share a period have the same number of atomic orbitals. The elements that are within the same group have the same number of electrons in their outer atomic orbitals. All the elements within a same family have the same properties. It is organize ...
... The vertical rows are called periods. The elements that share a period have the same number of atomic orbitals. The elements that are within the same group have the same number of electrons in their outer atomic orbitals. All the elements within a same family have the same properties. It is organize ...
AP Chemistry Name: Ch.2 – The Nuclear Atom Date: Period:
... _______________ discovered radioactivity ...
... _______________ discovered radioactivity ...
SECTION REVIEW
... that are introduced in this section. Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. Dalton theorized that atoms are indivisible, but the discovery ...
... that are introduced in this section. Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. Dalton theorized that atoms are indivisible, but the discovery ...
Unit 2 Notes unit_2_atomic-nuclear-electronic
... 1a. Atoms are divisible into protons, neutrons & electrons (& even smaller!). 1b. In nuclear decay they actually fall apart! 2. All atoms of a single element have the same number of protons, but not neutrons. (isotopes) 4. Compounds may be very complex! ...
... 1a. Atoms are divisible into protons, neutrons & electrons (& even smaller!). 1b. In nuclear decay they actually fall apart! 2. All atoms of a single element have the same number of protons, but not neutrons. (isotopes) 4. Compounds may be very complex! ...
Promethium

Promethium, originally prometheum, is a chemical element with symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is one of only two such elements that are followed in the periodic table by elements with stable forms, a distinction shared with technetium. Chemically, promethium is a lanthanide, which forms salts when combined with other elements. Promethium shows only one stable oxidation state of +3; however, a few +2 compounds may exist.In 1902, Bohuslav Brauner suggested there was an element with properties intermediate between those of the known elements neodymium (60) and samarium (62); this was confirmed in 1914 by Henry Moseley who, having measured the atomic numbers of all the elements then known, found there was an element with atomic number 61. In 1926, an Italian and an American group claimed to have isolated a sample of element 61; both ""discoveries"" were soon proven to be false. In 1938, during a nuclear experiment conducted at Ohio State University, a few radioactive nuclides were produced that certainly were not radioisotopes of neodymium or samarium, but there was a lack of chemical proof that element 61 was produced, and the discovery was not generally recognized. Promethium was first produced and characterized at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in 1945 by the separation and analysis of the fission products of uranium fuel irradiated in a graphite reactor. The discoverers proposed the name ""prometheum"" (the spelling was subsequently changed), derived from Prometheus, the Titan in Greek mythology who stole fire from Mount Olympus and brought it down to humans, to symbolize ""both the daring and the possible misuse of mankind's intellect"". However, a sample of the metal was made only in 1963.There are two possible sources for natural promethium: rare decays of natural europium-151 (producing promethium-147), and uranium (various isotopes). Practical applications exist only for chemical compounds of promethium-147, which are used in luminous paint, atomic batteries, and thickness measurement devices, even though promethium-145 is the most stable promethium isotope. Because natural promethium is exceedingly scarce, it is typically synthesized by bombarding uranium-235 (enriched uranium) with thermal neutrons to produce promethium-147.