
Classification of Fundamental Particles - Phy428-528
... The sum of masses of the individual components of a nucleus that contains Z protons and (A - Z) neutrons is larger than the mass of the nucleus M. This difference in masses is called the mass defect (deficit) and its energy ...
... The sum of masses of the individual components of a nucleus that contains Z protons and (A - Z) neutrons is larger than the mass of the nucleus M. This difference in masses is called the mass defect (deficit) and its energy ...
EPSc 446 STABLE ISOTOPE GEOCHEMISTRY Instructor: Bob Criss
... Primordial composition; stellar fuel! ...
... Primordial composition; stellar fuel! ...
Atomic Structure
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses, due to varying numbers of neutrons. ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses, due to varying numbers of neutrons. ...
Unit 3-The Atom Chapter Packet
... _____________________________3. proposed the first atomic model that accounted for the electrical nature of the atom _____________________________4. measured the size of the charge on an electron _____________________________5. suggested that alpha particles might be rebounding at an angle approachi ...
... _____________________________3. proposed the first atomic model that accounted for the electrical nature of the atom _____________________________4. measured the size of the charge on an electron _____________________________5. suggested that alpha particles might be rebounding at an angle approachi ...
CHH Review Unit 3
... Very few positively charged alpha particles deflected revealing a tiny, dense, positive region in atoms. 17. C 18. B 19. D 20. They are isotopes b/c they have different numbers of neutrons, but they are the same element b/c they have the same number of protons (same atomic number). 21. D 22. C 23. A ...
... Very few positively charged alpha particles deflected revealing a tiny, dense, positive region in atoms. 17. C 18. B 19. D 20. They are isotopes b/c they have different numbers of neutrons, but they are the same element b/c they have the same number of protons (same atomic number). 21. D 22. C 23. A ...
Chapter 4 power point notes
... What happens when an element emits radioactive particles? A. It gains energy. B. It gains neutrons. ...
... What happens when an element emits radioactive particles? A. It gains energy. B. It gains neutrons. ...
Lesson 1 & 2 Periodic table trends and formation
... - arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass - some elements were out of order therefore modern table is arranged in Atomic Number Meyer recognised Mendeleev’s work and both where awarded The Davy medal for Chemistry in 1882. ...
... - arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass - some elements were out of order therefore modern table is arranged in Atomic Number Meyer recognised Mendeleev’s work and both where awarded The Davy medal for Chemistry in 1882. ...
Chapter 4 PPT
... What happens when an element emits radioactive particles? A. It gains energy. B. It gains neutrons. ...
... What happens when an element emits radioactive particles? A. It gains energy. B. It gains neutrons. ...
ch 4 ppt - Madison County Schools
... What happens when an element emits radioactive particles? A. It gains energy. B. It gains neutrons. ...
... What happens when an element emits radioactive particles? A. It gains energy. B. It gains neutrons. ...
Document
... What happens when an element emits radioactive particles? A. It gains energy. B. It gains neutrons. ...
... What happens when an element emits radioactive particles? A. It gains energy. B. It gains neutrons. ...
CMC Chapter 04
... What happens when an element emits radioactive particles? A. It gains energy. B. It gains neutrons. ...
... What happens when an element emits radioactive particles? A. It gains energy. B. It gains neutrons. ...
ATOMS AND ELEMENTS Evolution of Atomic Theory
... ! Suppose the atom loses three electrons. ! We symbolize this ion as Al3+. ! Note that losing electrons is indicated with +, and gaining electrons is indicated with -. ...
... ! Suppose the atom loses three electrons. ! We symbolize this ion as Al3+. ! Note that losing electrons is indicated with +, and gaining electrons is indicated with -. ...
Name: Midterm Review (Part II) Fill in the blanks (Chapter 6.1 – 6.3
... How do you separate a mixture: physical methods chemical methods How do you separate a compound: physical methods chemical methods (p. 45) A solution is a mixture that has a uniform composition. The composition of a heterogeneous mixture is not uniform throughout. Classify the following solutions as ...
... How do you separate a mixture: physical methods chemical methods How do you separate a compound: physical methods chemical methods (p. 45) A solution is a mixture that has a uniform composition. The composition of a heterogeneous mixture is not uniform throughout. Classify the following solutions as ...
Masses of Atoms
... Atomic Mass Unit ~ 1/12th of the mass of one carbon-12 atom The periodic table shows the atomic mass of Nickel as 58.693. How can there be a decimal point, if the mass is whole numbers of protons and neutrons? ...
... Atomic Mass Unit ~ 1/12th of the mass of one carbon-12 atom The periodic table shows the atomic mass of Nickel as 58.693. How can there be a decimal point, if the mass is whole numbers of protons and neutrons? ...
atom atomic symbol atomic number # protons atomic mass
... (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
... (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, o ...
... particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, o ...
ATOM ATOMIC SYMBOL ATOMIC NUMBER
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
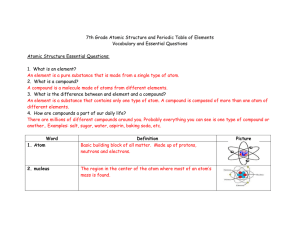
7th Grade Atomic Structure and Periodic Table of Elements
... A compound is a molecule made of atoms from different elements. 3. What is the difference between and element and a compound? An element is a substance that contains only one type of atom. A compound is composed of more than one atom of different elements. 4. How are compounds a part of our daily li ...
... A compound is a molecule made of atoms from different elements. 3. What is the difference between and element and a compound? An element is a substance that contains only one type of atom. A compound is composed of more than one atom of different elements. 4. How are compounds a part of our daily li ...
Hydrogen (/ˈhaɪdrɵdʒən/ HY-drə-jən)[7] is a chemical element
... whereas the far more common hydrogen isotope, protium, has no neutron in the nucleus. The deuterium isotope's name is formed from the Greek deuteros meaning "second", to denote the two particles composing the nucleus. Deuterium was discovered and named in 1931 by Harold Urey, earning him a Nobel Pri ...
... whereas the far more common hydrogen isotope, protium, has no neutron in the nucleus. The deuterium isotope's name is formed from the Greek deuteros meaning "second", to denote the two particles composing the nucleus. Deuterium was discovered and named in 1931 by Harold Urey, earning him a Nobel Pri ...
The Atom
... First, remember and discuss briefly what a model is. Then read the last paragraph on page 271 aloud. Democratis (about 2000 years ago) Matter can be divided into atoms The word Atom from the Greek word Atomos meaning not to be cut. Dalton (1800's) Elements are composed of atoms. Atoms are indivisibl ...
... First, remember and discuss briefly what a model is. Then read the last paragraph on page 271 aloud. Democratis (about 2000 years ago) Matter can be divided into atoms The word Atom from the Greek word Atomos meaning not to be cut. Dalton (1800's) Elements are composed of atoms. Atoms are indivisibl ...
C. - Taylor County Schools
... radioactive decay. • Atoms that contain too many or too few neutrons are unstable and lose energy through radioactive decay to form a stable nucleus. ...
... radioactive decay. • Atoms that contain too many or too few neutrons are unstable and lose energy through radioactive decay to form a stable nucleus. ...
GHW - Louisiana Tech University
... The gram mole is the grams of any chemical substance using the value atomic mass obtained from the periodic table. E.g. for carbon gram mole is 12.01 grams of carbon since its atomic mass is 12.01 amu in the periodic table. if you take atomic mass in grams the number of atoms is simply 6.022 x 10 23 ...
... The gram mole is the grams of any chemical substance using the value atomic mass obtained from the periodic table. E.g. for carbon gram mole is 12.01 grams of carbon since its atomic mass is 12.01 amu in the periodic table. if you take atomic mass in grams the number of atoms is simply 6.022 x 10 23 ...
final exam review packet
... C-Atomic Structure -1801. I can identify the location, charge, and relative mass of each subatomic particle: (electron, neutron, and proton). C-Atomic Structure -1802. I can recognize that electrons exist in energy levels outside the nucleus. C-Atomic Structure -1803. I can identify the element base ...
... C-Atomic Structure -1801. I can identify the location, charge, and relative mass of each subatomic particle: (electron, neutron, and proton). C-Atomic Structure -1802. I can recognize that electrons exist in energy levels outside the nucleus. C-Atomic Structure -1803. I can identify the element base ...
Parts of the Atom - Dalton Local Schools
... 14. What is true about the number of electrons and protons in an element? a. There is always twice the number of electrons than protons in the nucleus. b. The numbers of protons and electrons are always changing. c. The number of electrons in an atom always equals the number of protons in the nucle ...
... 14. What is true about the number of electrons and protons in an element? a. There is always twice the number of electrons than protons in the nucleus. b. The numbers of protons and electrons are always changing. c. The number of electrons in an atom always equals the number of protons in the nucle ...
Promethium

Promethium, originally prometheum, is a chemical element with symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is one of only two such elements that are followed in the periodic table by elements with stable forms, a distinction shared with technetium. Chemically, promethium is a lanthanide, which forms salts when combined with other elements. Promethium shows only one stable oxidation state of +3; however, a few +2 compounds may exist.In 1902, Bohuslav Brauner suggested there was an element with properties intermediate between those of the known elements neodymium (60) and samarium (62); this was confirmed in 1914 by Henry Moseley who, having measured the atomic numbers of all the elements then known, found there was an element with atomic number 61. In 1926, an Italian and an American group claimed to have isolated a sample of element 61; both ""discoveries"" were soon proven to be false. In 1938, during a nuclear experiment conducted at Ohio State University, a few radioactive nuclides were produced that certainly were not radioisotopes of neodymium or samarium, but there was a lack of chemical proof that element 61 was produced, and the discovery was not generally recognized. Promethium was first produced and characterized at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in 1945 by the separation and analysis of the fission products of uranium fuel irradiated in a graphite reactor. The discoverers proposed the name ""prometheum"" (the spelling was subsequently changed), derived from Prometheus, the Titan in Greek mythology who stole fire from Mount Olympus and brought it down to humans, to symbolize ""both the daring and the possible misuse of mankind's intellect"". However, a sample of the metal was made only in 1963.There are two possible sources for natural promethium: rare decays of natural europium-151 (producing promethium-147), and uranium (various isotopes). Practical applications exist only for chemical compounds of promethium-147, which are used in luminous paint, atomic batteries, and thickness measurement devices, even though promethium-145 is the most stable promethium isotope. Because natural promethium is exceedingly scarce, it is typically synthesized by bombarding uranium-235 (enriched uranium) with thermal neutrons to produce promethium-147.
















![Hydrogen (/ˈhaɪdrɵdʒən/ HY-drə-jən)[7] is a chemical element](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001197267_1-624cb7c7c4dbdb26b0769567aa77b6ad-300x300.png)





