BAT
... If a mixture of gases contains 3 gases - carbon dioxide with a partial pressure of 0.285 torr and nitrogen with a partial pressure of 593.525 torr and oxygen at partial pressure = ? find the partial pressure of ...
... If a mixture of gases contains 3 gases - carbon dioxide with a partial pressure of 0.285 torr and nitrogen with a partial pressure of 593.525 torr and oxygen at partial pressure = ? find the partial pressure of ...
FREEZING – is the change of a liquid to a solid. Freezing occurs
... At constant pressure… The volume of gas varies directly with the temperature. Volume UP… Temperature UP Volume DOWN… Temperature DOWN ...
... At constant pressure… The volume of gas varies directly with the temperature. Volume UP… Temperature UP Volume DOWN… Temperature DOWN ...
Recurring theme: conservation of energy
... d) Indicate where the cold red stars are [1pt] e) Indicate where on the diagram you would put a protostar [2pt] f) Indicate where on the diagram the Sun will move once it runs out of Hydrogen in its core. [2pt] ...
... d) Indicate where the cold red stars are [1pt] e) Indicate where on the diagram you would put a protostar [2pt] f) Indicate where on the diagram the Sun will move once it runs out of Hydrogen in its core. [2pt] ...
Chapter 5 Worksheet
... 1. Suppose you have one mole of an ideal gas. A) What is the effect on the volume if the pressure is tripled (T remains constant) ...
... 1. Suppose you have one mole of an ideal gas. A) What is the effect on the volume if the pressure is tripled (T remains constant) ...
Lecture 14
... Gravity causes gas cloud to shrink and fragment. Cores of shrinking cloud fragments heat up. Collapse only continues if the cloud cools by radiating away heat. If the initial cloud was spinning a protostellar disk is formed. Protostars approach the main sequence from the right hand side of the HR di ...
... Gravity causes gas cloud to shrink and fragment. Cores of shrinking cloud fragments heat up. Collapse only continues if the cloud cools by radiating away heat. If the initial cloud was spinning a protostellar disk is formed. Protostars approach the main sequence from the right hand side of the HR di ...
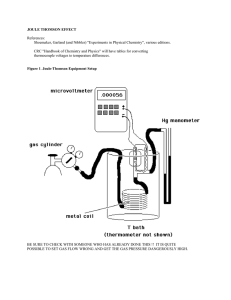
joule thomson effect
... µVvalues are proportional to ∆T, and therefore a plot of µV vs. kPa should be fairly linear. Before switching gases, make an Excel plot to see if the data is in fact reasonably linear. There may be a problem if there is significant curvature, and this should be ascertained before changing the gas. F ...
... µVvalues are proportional to ∆T, and therefore a plot of µV vs. kPa should be fairly linear. Before switching gases, make an Excel plot to see if the data is in fact reasonably linear. There may be a problem if there is significant curvature, and this should be ascertained before changing the gas. F ...
CYL110
... When a system is at equilibrium, its state is defined entirely by the state variables, and not by the history of the system. The properties of the system can be described by an equation of state which specifies the relationship between these variables. ...
... When a system is at equilibrium, its state is defined entirely by the state variables, and not by the history of the system. The properties of the system can be described by an equation of state which specifies the relationship between these variables. ...
Electron Configurations
... Aufbau Principle • Says each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available. • An Aufbau diagram shows the orbitals in order from lowest to highest energy required • Hints: – All orbitals within a sublevel have equal energy. (All 3 p sublevels are equal energy at any level.) – Energy subleve ...
... Aufbau Principle • Says each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available. • An Aufbau diagram shows the orbitals in order from lowest to highest energy required • Hints: – All orbitals within a sublevel have equal energy. (All 3 p sublevels are equal energy at any level.) – Energy subleve ...
final study guide answers - Ponce
... _________3. Suppose an atom has a mass number of 35. Which statement is true beyond any doubt? a. The atom has an odd number of neutrons. b. The atomic number is less than 17. c. The atom is not an isotope. d. The number of protons in the nucleus does not equal the number of neutrons. ________4. Whi ...
... _________3. Suppose an atom has a mass number of 35. Which statement is true beyond any doubt? a. The atom has an odd number of neutrons. b. The atomic number is less than 17. c. The atom is not an isotope. d. The number of protons in the nucleus does not equal the number of neutrons. ________4. Whi ...
Atomic Structure and Quantum Theory Photon Energies
... If we consider electrons to have wave properties, how can we pinpoint the position of an electron? Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: ∆xy∆(mu) > h • It is impossible to fix both the position and energy of an electron with ...
... If we consider electrons to have wave properties, how can we pinpoint the position of an electron? Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle: ∆xy∆(mu) > h • It is impossible to fix both the position and energy of an electron with ...
QUANTUM NUMBERS
... This initial discussion of quantum numbers isn't going to go down very well. It's very foreign to think of things this way It will seem made-up and artificial. Rest assured that quantum numbers are a direct result of the kinds of solutions that come out of the Schrödinger equation. Work through it. ...
... This initial discussion of quantum numbers isn't going to go down very well. It's very foreign to think of things this way It will seem made-up and artificial. Rest assured that quantum numbers are a direct result of the kinds of solutions that come out of the Schrödinger equation. Work through it. ...
11 Stellar Remnants - Journigan-wiki
... point that their electrons and protons have been merged. In the most massive stars, the stars have collapsed so completely that their immense gravity warps space to the extent that no light escapes from them. ...
... point that their electrons and protons have been merged. In the most massive stars, the stars have collapsed so completely that their immense gravity warps space to the extent that no light escapes from them. ...
Pulsars - Chabot College
... “Two particles cannot occupy same space with same momentum (energy)” – Pauli exclusion principle ...
... “Two particles cannot occupy same space with same momentum (energy)” – Pauli exclusion principle ...
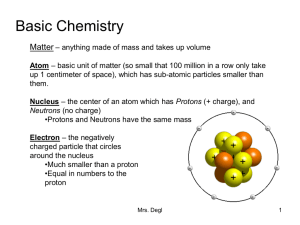
Basic Chemistry
... Basic Chemistry Matter – anything made of mass and takes up volume Atom – basic unit of matter (so small that 100 million in a row only take up 1 centimeter of space), which has sub-atomic particles smaller than them. Nucleus – the center of an atom which has Protons (+ charge), and Neutrons (no cha ...
... Basic Chemistry Matter – anything made of mass and takes up volume Atom – basic unit of matter (so small that 100 million in a row only take up 1 centimeter of space), which has sub-atomic particles smaller than them. Nucleus – the center of an atom which has Protons (+ charge), and Neutrons (no cha ...
Atomic Radii Answers File
... electron so the remaining ones are pulled in closer. When an atom gains an electron to form a negative ion, the nuclear charge has not changed. However, now the nucleus is attracting one more electron so they are not pulled as strongly as before. The negative ions will all be bigger than Ar and the ...
... electron so the remaining ones are pulled in closer. When an atom gains an electron to form a negative ion, the nuclear charge has not changed. However, now the nucleus is attracting one more electron so they are not pulled as strongly as before. The negative ions will all be bigger than Ar and the ...
nuc_alchemy_talk-fgs-dec07
... Nuclear Fusion creates energy up to A~56 (Z=26 = Iron) If the star is hot enough, nuclear fusion will fuel the star and create elements up to A~56 ...
... Nuclear Fusion creates energy up to A~56 (Z=26 = Iron) If the star is hot enough, nuclear fusion will fuel the star and create elements up to A~56 ...
CHM1 Exam 16 Name 2222222222222222222222222222 Multiple
... When the switch is closed, the electrons will flow from (1) the Pb (s) to the Cu (s) (2) the Cu (s) to the Pb (s) (3) the Pb2+ (aq) to the Pb (s) (4) the Cu2+ (aq) to the Cu (s) 24. Shown below are the reduction potentials for four half-reactions under standard ...
... When the switch is closed, the electrons will flow from (1) the Pb (s) to the Cu (s) (2) the Cu (s) to the Pb (s) (3) the Pb2+ (aq) to the Pb (s) (4) the Cu2+ (aq) to the Cu (s) 24. Shown below are the reduction potentials for four half-reactions under standard ...
PYP001-121 Major-I Solution. In all the questions, choice
... A) Carbon dioxide, water, and table salt are examples of compounds. B) Two or more atoms combine to form an isotope. C) The properties of compounds are the same as the properties of the elements from which they are made. D) The rocky soil in a garden is a compound. E) Matter is anything that has len ...
... A) Carbon dioxide, water, and table salt are examples of compounds. B) Two or more atoms combine to form an isotope. C) The properties of compounds are the same as the properties of the elements from which they are made. D) The rocky soil in a garden is a compound. E) Matter is anything that has len ...
World of matter - Kindle Education
... Matter is made up on small particles which are in constant motion. When you heat matter, the particles of matter absorb the heat energy and begin moving faster (in other words they gain kinetic energy). As more energy is provided the chemical bond between the particles become weaker and hence there ...
... Matter is made up on small particles which are in constant motion. When you heat matter, the particles of matter absorb the heat energy and begin moving faster (in other words they gain kinetic energy). As more energy is provided the chemical bond between the particles become weaker and hence there ...
Test Chap 5 gas laws
... 20 °C. If the total pressure is 400 kPa, what is the partial pressure of the hydrogen? (3 pts) 16. What is the pressure exerted by some nitrogen gas collected in a tube filled with water on a day when the room temperature is 18.0 °C and the room pressure is 750.0 mmHg? [The partial pressure of water ...
... 20 °C. If the total pressure is 400 kPa, what is the partial pressure of the hydrogen? (3 pts) 16. What is the pressure exerted by some nitrogen gas collected in a tube filled with water on a day when the room temperature is 18.0 °C and the room pressure is 750.0 mmHg? [The partial pressure of water ...
Gas Laws - myersparkphysics
... The container holds a very large number N of identical molecules. Each molecule has a mass m, and behaves as a point particle. The molecules move about the container in a random manner. They obey Newton’s laws of motion at all times. When the molecules hit the walls of the container or collide with ...
... The container holds a very large number N of identical molecules. Each molecule has a mass m, and behaves as a point particle. The molecules move about the container in a random manner. They obey Newton’s laws of motion at all times. When the molecules hit the walls of the container or collide with ...
QUATERLY 3 REVIEW CHAPTER 12- Stoichiometry Define the law
... 2. Calculate the mass of a product when given the mass / moles of reactant(s) 3. Define Limiting and excess reagent 4. Determine the limiting and excess reagents from given data 5. Define Percent Yield and calculate it from given data 6. a. What mass of iron must react with excess oxygen in order to ...
... 2. Calculate the mass of a product when given the mass / moles of reactant(s) 3. Define Limiting and excess reagent 4. Determine the limiting and excess reagents from given data 5. Define Percent Yield and calculate it from given data 6. a. What mass of iron must react with excess oxygen in order to ...
Lecture 11
... • How big and massive are white dwarfs? – A white dwarf with the mass of our sun is approximatley the size of the Earth. – The maximum mass of a white dwarf is 1.4 solar masses – higher mass white dwarfs are unstable. • What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? – Hot gas in acc ...
... • How big and massive are white dwarfs? – A white dwarf with the mass of our sun is approximatley the size of the Earth. – The maximum mass of a white dwarf is 1.4 solar masses – higher mass white dwarfs are unstable. • What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? – Hot gas in acc ...