Equations of State for White Dwarfs Elena Heikkilä Kandidaatin
... formulated Fermi–Dirac statistics on the foundations established by E. Fermi, and R.H. Fowler applied Fermi–Dirac statistics to identify the pressure holding up the stars from gravitational collapse with electron degeneracy pressure. [1] S. Chandrasekhar constructed the actual white dwarf models, ta ...
... formulated Fermi–Dirac statistics on the foundations established by E. Fermi, and R.H. Fowler applied Fermi–Dirac statistics to identify the pressure holding up the stars from gravitational collapse with electron degeneracy pressure. [1] S. Chandrasekhar constructed the actual white dwarf models, ta ...
WS on obj. 1-11
... 14. _____ (T/F) Calcium will need to lose two electrons to get the electron configuration of argon. 15. _____ (T/F) All the alkaline earth elements (Group 2A) will need to lose two electrons to obtain a noble gas electron configuration. 16. _____ (T/F) All the elements of the oxygen group (Group 6A ...
... 14. _____ (T/F) Calcium will need to lose two electrons to get the electron configuration of argon. 15. _____ (T/F) All the alkaline earth elements (Group 2A) will need to lose two electrons to obtain a noble gas electron configuration. 16. _____ (T/F) All the elements of the oxygen group (Group 6A ...
Answers - Shelton State
... Melting point and freezing point are the same temperature. What is vapor pressure? The pressure of vapor in equilibrium with its liquid state. The pressure of a vapor evaporating from the liquid state. What is boiling? The especially rapid evaporation that occurs when the vapor pressure of a liquid ...
... Melting point and freezing point are the same temperature. What is vapor pressure? The pressure of vapor in equilibrium with its liquid state. The pressure of a vapor evaporating from the liquid state. What is boiling? The especially rapid evaporation that occurs when the vapor pressure of a liquid ...
42.89 KB
... 17. "The volume of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of the gas at constant temperature and pressure" is a statement of _____________ Law. A) B) C) D) E) ...
... 17. "The volume of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of the gas at constant temperature and pressure" is a statement of _____________ Law. A) B) C) D) E) ...
Chemical Bonds
... Remember when I said atoms like to have equal numbers of protons and electrons. Well… that’s not always the case… An ion is an atom or molecule with a net electric charge (either positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons. ...
... Remember when I said atoms like to have equal numbers of protons and electrons. Well… that’s not always the case… An ion is an atom or molecule with a net electric charge (either positive or negative) due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons. ...
Matter Quiz 2 With Answers
... 3. This state of matter has no defined shape of volume. No bonds exist between the atoms of the substance. a. Plasma b. Liquid c. Gas d. Solid 4. This state of matter has a definitive volume, but no specific shape. Consists of loose bonds between atoms. a. Plasma b. Liquid c. Gas d. Solid 5. The ___ ...
... 3. This state of matter has no defined shape of volume. No bonds exist between the atoms of the substance. a. Plasma b. Liquid c. Gas d. Solid 4. This state of matter has a definitive volume, but no specific shape. Consists of loose bonds between atoms. a. Plasma b. Liquid c. Gas d. Solid 5. The ___ ...
Chapter 9: Chemical Quantities
... - Emission and Absorption of Light by atoms and possible transitions of electrons ...
... - Emission and Absorption of Light by atoms and possible transitions of electrons ...
Chemistry 111 Study Sheet - Answers
... Melting point and freezing point are the same temperature. What is vapor pressure? The pressure of vapor in equilibrium with its liquid state. The pressure of a vapor evaporating from the liquid state. What is boiling? The especially rapid evaporation that occurs when the vapor pressure of a liquid ...
... Melting point and freezing point are the same temperature. What is vapor pressure? The pressure of vapor in equilibrium with its liquid state. The pressure of a vapor evaporating from the liquid state. What is boiling? The especially rapid evaporation that occurs when the vapor pressure of a liquid ...
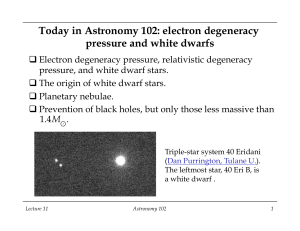
Today in Astronomy 102: electron degeneracy pressure and white
... q Important result of the theory: maximum mass for white dwarfs, which turns out to be 1.4 M⊙. Electron degeneracy pressure cannot hold up a heavier mass. q Implication: for stars with core mass less than 1.4 M⊙, core collapse is stopped by electron degeneracy pressure before the horizon size is rea ...
... q Important result of the theory: maximum mass for white dwarfs, which turns out to be 1.4 M⊙. Electron degeneracy pressure cannot hold up a heavier mass. q Implication: for stars with core mass less than 1.4 M⊙, core collapse is stopped by electron degeneracy pressure before the horizon size is rea ...
atoms
... small compared to entire size of atom) - Most of the mass of the atom is in the center - The positive charged particle (proton) must be in the center of the atom ...
... small compared to entire size of atom) - Most of the mass of the atom is in the center - The positive charged particle (proton) must be in the center of the atom ...
12.1 Introduction
... gas. It is therefore inevitable that stars evolve with time. In the next few lectures we shall look in some detail at the process of stellar evolution. Stellar evolution, as opposed to equilibrium, can be reproduced in our computers by solving a series of equilibrium stellar models—normally referre ...
... gas. It is therefore inevitable that stars evolve with time. In the next few lectures we shall look in some detail at the process of stellar evolution. Stellar evolution, as opposed to equilibrium, can be reproduced in our computers by solving a series of equilibrium stellar models—normally referre ...
SupernovaExplosionPhysics_8pages
... Consider an “evolved” star, one which has evolved off the main sequence and has an evolved mass M which may be significantly smaller than its zero-age main-sequence (ZAMS) mass. As discussed in previous lectures, at some point the pressure due to electron degeneracy becomes important. This is the pr ...
... Consider an “evolved” star, one which has evolved off the main sequence and has an evolved mass M which may be significantly smaller than its zero-age main-sequence (ZAMS) mass. As discussed in previous lectures, at some point the pressure due to electron degeneracy becomes important. This is the pr ...
R= 8.31 J/mol K = 0.0821 L atm/mol K = 62.4 L torr/mol K PV = nRT
... The stream of atoms divided into two separate paths. This division would not be observed with atoms of A) Cu B) Cr C) Mg D) K E) Al ...
... The stream of atoms divided into two separate paths. This division would not be observed with atoms of A) Cu B) Cr C) Mg D) K E) Al ...
File
... Law of definite proportions- When two or more elements combine to form a compound, their masses in that compound are in a fixed and definite ratio, (e.g. NaCl is always 60.66% of Na and 39.34% of Cl by mass regardless of the size or the source of the compound). Law of multiple proportions-When two e ...
... Law of definite proportions- When two or more elements combine to form a compound, their masses in that compound are in a fixed and definite ratio, (e.g. NaCl is always 60.66% of Na and 39.34% of Cl by mass regardless of the size or the source of the compound). Law of multiple proportions-When two e ...
–1– 3. Equation of State In the stellar interior, as we shall see, the
... in other words, u = 3P , for all ultra-relativistic particles, such as photons. Note these two relations are very general, independent of the momentum distribution! Eqs. (16) and (31) in principle allow us to calculate the pressure as a function of the number density for any gas made of identical pa ...
... in other words, u = 3P , for all ultra-relativistic particles, such as photons. Note these two relations are very general, independent of the momentum distribution! Eqs. (16) and (31) in principle allow us to calculate the pressure as a function of the number density for any gas made of identical pa ...
9.1 Heat and Temperature
... liquid, or gas). 1. As Kinetic Energy of molecules increases, so does the temperature of that sample of matter. B. Temperature can be measured in Fahrenheit, Celsius, or in Kelvin. 1. K = 273 + OC 2. OC = (OF -32) x 5/9 3. OF = (9/5 x OC) +32 IV. Specific Heat (CP) A value of energy associated with ...
... liquid, or gas). 1. As Kinetic Energy of molecules increases, so does the temperature of that sample of matter. B. Temperature can be measured in Fahrenheit, Celsius, or in Kelvin. 1. K = 273 + OC 2. OC = (OF -32) x 5/9 3. OF = (9/5 x OC) +32 IV. Specific Heat (CP) A value of energy associated with ...
What is Chemistry
... • Results in the formation of a new substances – A chemical reaction takes place • Evidence that a chemical reaction has taken place – Change in energy • Temperature increase or decrease – Production of a gas • Formation of bubbles or detection of odor – Formation of a precipitate • Presence of a so ...
... • Results in the formation of a new substances – A chemical reaction takes place • Evidence that a chemical reaction has taken place – Change in energy • Temperature increase or decrease – Production of a gas • Formation of bubbles or detection of odor – Formation of a precipitate • Presence of a so ...
Characteristics of Gases Pressure Gas Laws The Ideal
... Some nitrogen gas is in a 2.00-L tank at a pressure of 3.00 atm. The tank is connected to a 5.00-L tank that is completely empty (evacuated), and a valve connects the two tanks., If the valve is opened, determine the total pressure in this two-tank system after the nitrogen stops flowing. No tempera ...
... Some nitrogen gas is in a 2.00-L tank at a pressure of 3.00 atm. The tank is connected to a 5.00-L tank that is completely empty (evacuated), and a valve connects the two tanks., If the valve is opened, determine the total pressure in this two-tank system after the nitrogen stops flowing. No tempera ...
Chapter 10 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
... • As a white dwarf’s mass approaches 1.4MSun, its electrons must move at nearly the speed of light. • Because nothing can move faster than light, a white dwarf cannot be more massive than 1.4MSun, the white dwarf limit (or Chandrasekhar limit). ...
... • As a white dwarf’s mass approaches 1.4MSun, its electrons must move at nearly the speed of light. • Because nothing can move faster than light, a white dwarf cannot be more massive than 1.4MSun, the white dwarf limit (or Chandrasekhar limit). ...
Chem 1a Midterm Review
... Look at pictures of the hydrogen orbitals at http://www.shef.ac.uk/chemistry/orbitron/ . Note particularly the shape, nodes and sign of the orbitals. Note that the s and d orbitals are symmetric to inversion through the origin while the p is anti-symmetric toward inversions. Orbital energy: one ele ...
... Look at pictures of the hydrogen orbitals at http://www.shef.ac.uk/chemistry/orbitron/ . Note particularly the shape, nodes and sign of the orbitals. Note that the s and d orbitals are symmetric to inversion through the origin while the p is anti-symmetric toward inversions. Orbital energy: one ele ...
WEEK 8: CSI UCSC: ASTRO EDITION SOLUTIONS This week you
... (1) Compare Types I and II supernovae. What kinds of objects explode and what are their explosion mechanisms? There are two main types. The first one is Type Ia supernova, which comes from a white dwarf in a binary system with another star. A white dwarf may steal material from the companion star, a ...
... (1) Compare Types I and II supernovae. What kinds of objects explode and what are their explosion mechanisms? There are two main types. The first one is Type Ia supernova, which comes from a white dwarf in a binary system with another star. A white dwarf may steal material from the companion star, a ...
Document
... 10. Compared to the charge of a proton, the charge of an electron has a. A greater magnitude and the same sign b. A greater magnitude and the opposite sign c. The same magnitude and the same sign d. The same magnitude and the opposite sign 11. Which phrase describes an atom? a. A negatively charged ...
... 10. Compared to the charge of a proton, the charge of an electron has a. A greater magnitude and the same sign b. A greater magnitude and the opposite sign c. The same magnitude and the same sign d. The same magnitude and the opposite sign 11. Which phrase describes an atom? a. A negatively charged ...
THE GASEOUS STATE
... molecules. • These forces are much weaker than chemical bonds that hold atoms together. • And they are nearly nonexistent between gas molecules at room temp. and pressure. • However, they are important in liquids and solids. ...
... molecules. • These forces are much weaker than chemical bonds that hold atoms together. • And they are nearly nonexistent between gas molecules at room temp. and pressure. • However, they are important in liquids and solids. ...
Lecture 7
... • What prevents stars from collapsing under the weight of their own gravity? Text • Why is the center of the Sun hot? • What is the source of the Sun’s energy? • What are neutrinos & why do we care • How does energy get from the inside to the outside of a star? ...
... • What prevents stars from collapsing under the weight of their own gravity? Text • Why is the center of the Sun hot? • What is the source of the Sun’s energy? • What are neutrinos & why do we care • How does energy get from the inside to the outside of a star? ...
Wednesday, Oct. 22
... white dwarf. How does the pressure inside a white dwarf differ from normal gas pressure? How does nuclear fusion inside of very massive stars differ from the fusion that will occur inside of the Sun? How do the processes that occur inside of massive stars lead to supernova explosions? ...
... white dwarf. How does the pressure inside a white dwarf differ from normal gas pressure? How does nuclear fusion inside of very massive stars differ from the fusion that will occur inside of the Sun? How do the processes that occur inside of massive stars lead to supernova explosions? ...