Ch 3 Matter & Change
... Each one has a unique name and symbol. In the symbol the first letter is always capitalized and the remaining letter(s) are lowercase. There are 91 naturally occurring elements Who was given credit for organizing them into a table? Dmitri Mendeleev ...
... Each one has a unique name and symbol. In the symbol the first letter is always capitalized and the remaining letter(s) are lowercase. There are 91 naturally occurring elements Who was given credit for organizing them into a table? Dmitri Mendeleev ...
Chapter 2 Matter and Change
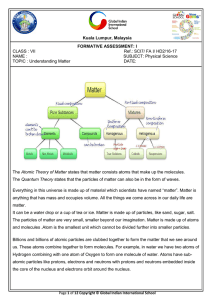
... simplest kind of matter cannot be broken down any simpler and still have properties of that element! all one kind of atom. _____________ are substances that can be broken down only by chemical methods when broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the original compoun ...
... simplest kind of matter cannot be broken down any simpler and still have properties of that element! all one kind of atom. _____________ are substances that can be broken down only by chemical methods when broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the original compoun ...
NSCC Chem 121 chapter6
... • No ideal gases actually exist. • If they did exist, they would behave exactly as predicted by the gas laws at all temperatures and pressures. • Real gases deviate from the behavior predicted by the gas laws, but under normally encountered temperatures and pressures, the deviations are small. • Con ...
... • No ideal gases actually exist. • If they did exist, they would behave exactly as predicted by the gas laws at all temperatures and pressures. • Real gases deviate from the behavior predicted by the gas laws, but under normally encountered temperatures and pressures, the deviations are small. • Con ...
Chem A Week 2 Matter Notes
... A.Solids– are ____________ matter They have a definite shape and volume matter B. Liquids – are ___________ They take the shape of their container, volume but still have a definite ________________. ...
... A.Solids– are ____________ matter They have a definite shape and volume matter B. Liquids – are ___________ They take the shape of their container, volume but still have a definite ________________. ...
1. A glucose molecule contains six carbons, twelve hydrogens and
... A. Potential energy is due to the motion of an object. B. Energy is destroyed in a chemical reaction. C. Chemical energy is associated with the motion of a molecule. D. Thermal energy is associated with temperature. ...
... A. Potential energy is due to the motion of an object. B. Energy is destroyed in a chemical reaction. C. Chemical energy is associated with the motion of a molecule. D. Thermal energy is associated with temperature. ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood (Pages 735
... *4. As the totally _________ water is heated by the surrounding ___ __ of the room, its temperature will _____ continue to ________, and as more ____________ is added the temperature of the water will rise _________ 0o C and continue rising until it reaches ___ __ causing __________________, a speci ...
... *4. As the totally _________ water is heated by the surrounding ___ __ of the room, its temperature will _____ continue to ________, and as more ____________ is added the temperature of the water will rise _________ 0o C and continue rising until it reaches ___ __ causing __________________, a speci ...
Photophoresis in action
... pc Tw Tw p = nk BT pw = pc nwvw < nc vc Thermal creep: net mass flow from cold to warm side (v: mean thermal velocity) ...
... pc Tw Tw p = nk BT pw = pc nwvw < nc vc Thermal creep: net mass flow from cold to warm side (v: mean thermal velocity) ...
3.2 Ideal gas- Boltzman constant
... • This represents the total internal energy of an ideal gas (only considering translational motion of molecules of monoatomic gases) This means; No intermolecular forces between molecules between collisions i.e. energy is completely kinetic • Gas consists of large number of identical tiny particles- ...
... • This represents the total internal energy of an ideal gas (only considering translational motion of molecules of monoatomic gases) This means; No intermolecular forces between molecules between collisions i.e. energy is completely kinetic • Gas consists of large number of identical tiny particles- ...
worksheer format 11-12
... A colloid is a mixture where very small particles of one substance are evenly distributed throughout another substance. They appear very similar to solutions, but the particles are suspended in the solution rather than fully dissolved. The difference between a colloid and a suspension is that the pa ...
... A colloid is a mixture where very small particles of one substance are evenly distributed throughout another substance. They appear very similar to solutions, but the particles are suspended in the solution rather than fully dissolved. The difference between a colloid and a suspension is that the pa ...
Star evolution - El Camino College
... • Big picture: carbon and stuff fuses until you get to a core made of … • Iron (Fe on the periodic table, #26, middle section, ...
... • Big picture: carbon and stuff fuses until you get to a core made of … • Iron (Fe on the periodic table, #26, middle section, ...
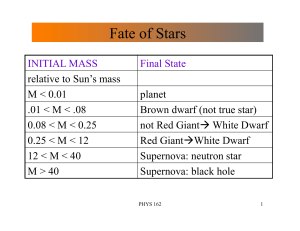
Fate of Stars
... • A heavier WD will have smaller radius • if Mass(WD) > 1.4 M(Sun) electrons can not resist gravity ! called Chandrasekhar limit and no WD has a mass greater than this • If WD can acquire mass from companion star and goes over this limit ! Supernova and (usually) a Neutron Star ...
... • A heavier WD will have smaller radius • if Mass(WD) > 1.4 M(Sun) electrons can not resist gravity ! called Chandrasekhar limit and no WD has a mass greater than this • If WD can acquire mass from companion star and goes over this limit ! Supernova and (usually) a Neutron Star ...
Power-point slides for Lecture 5
... than classical and an infinite central density is not allowed (there exists a critical for stability) ...
... than classical and an infinite central density is not allowed (there exists a critical for stability) ...
Lab # 28: Calculating the Value of the Ideal Gas Constant “R”
... this lab, you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the value of the ideal gas constant “R”. We will collect a sample of gas from a lighter by water displacement. See Figure 1 for the set up. Here are a few “nuts and bolts” of the lab to keep in mind: - The volume of gas, V, is simply the volume o ...
... this lab, you will use the ideal gas law to calculate the value of the ideal gas constant “R”. We will collect a sample of gas from a lighter by water displacement. See Figure 1 for the set up. Here are a few “nuts and bolts” of the lab to keep in mind: - The volume of gas, V, is simply the volume o ...
CHAPTER 7 READING GUIDE – IONIC COMPOUNDS AND METALS
... 28. __________________, which are small numbers to the lower right of a symbol, represent the number of ______________ of each element in an ionic compound. 29. Many ionic compounds contain ___________________ ions, which are ions made up of more than one atom. 30. Because a polyatomic ion exists a ...
... 28. __________________, which are small numbers to the lower right of a symbol, represent the number of ______________ of each element in an ionic compound. 29. Many ionic compounds contain ___________________ ions, which are ions made up of more than one atom. 30. Because a polyatomic ion exists a ...
Chemical Bonds
... cations two units lower in charge than the expected from their group number – the np-electrons have higher energy than the ns-electrons and are lost first – the two ns-electrons may or may not be lost ...
... cations two units lower in charge than the expected from their group number – the np-electrons have higher energy than the ns-electrons and are lost first – the two ns-electrons may or may not be lost ...
CHEMISTRY 1
... The Born- Haber cycle uses the law of Hess to determine the Lattice Energy. The lattice energy is the enthalphy change, ∆H, associated when gaseous cations and anions from a crystal: Na+(g) + Cl-(g) NaCl(s) ∆H = - 788KJ Since heat is always evolved in these processes, all lattice energies have a n ...
... The Born- Haber cycle uses the law of Hess to determine the Lattice Energy. The lattice energy is the enthalphy change, ∆H, associated when gaseous cations and anions from a crystal: Na+(g) + Cl-(g) NaCl(s) ∆H = - 788KJ Since heat is always evolved in these processes, all lattice energies have a n ...
Atoms and quantum phenomena
... we use the Electron Volt • Definition: The amount of kinetic energy gained by a single unbound electron when it accelerates through an electric potential difference of one volt. (Not SI, experimental) • 1eV = 1.602 x 10-19J ...
... we use the Electron Volt • Definition: The amount of kinetic energy gained by a single unbound electron when it accelerates through an electric potential difference of one volt. (Not SI, experimental) • 1eV = 1.602 x 10-19J ...
Exam 3 Answer Key
... Which of the following statements are true? A. In Bohr’s atomic theory, when an electron moves from one energy level to another energy level more distant from the nucleus, energy is emitted. B. The principal quantum number determines the size and the shape of the orbitals. C. Mendeleev assembled the ...
... Which of the following statements are true? A. In Bohr’s atomic theory, when an electron moves from one energy level to another energy level more distant from the nucleus, energy is emitted. B. The principal quantum number determines the size and the shape of the orbitals. C. Mendeleev assembled the ...
Notes - Ms. Dawkins
... A neutron has about the ______________ ___________ as a proton. They are grouped together in the ______________________. Atoms are extremely ________________. The electron cloud is about _______________ times the size of the __________________. Electrons are much smaller than _____________________ ...
... A neutron has about the ______________ ___________ as a proton. They are grouped together in the ______________________. Atoms are extremely ________________. The electron cloud is about _______________ times the size of the __________________. Electrons are much smaller than _____________________ ...
The Sun: Our Nearest Star
... This says that mH < mp + me = 1.00783. The difference is actually -13.6 eV. The Sun is fusing He from H. A He-4 nucleus has a mass of 4.0026 u. 4 Hydrogen atoms have a mass of 4.0313 u. Δm = 0.028697 u, or 0.7% of the total energy. This is an energy of E=Δmc2 = 26.731 MeV. This is the binding ...
... This says that mH < mp + me = 1.00783. The difference is actually -13.6 eV. The Sun is fusing He from H. A He-4 nucleus has a mass of 4.0026 u. 4 Hydrogen atoms have a mass of 4.0313 u. Δm = 0.028697 u, or 0.7% of the total energy. This is an energy of E=Δmc2 = 26.731 MeV. This is the binding ...
Chemistry EOC Review Name
... 24. How are frequency and wavelength related? 25. Calculate the wavelength of a yellow light by a sodium lamp if the frequency of the radiation is 3.34 x 10 14 Hz. 26. What is the energy associated with the photon in problem 37? 27. High energy electrons are found _________________ while low energy ...
... 24. How are frequency and wavelength related? 25. Calculate the wavelength of a yellow light by a sodium lamp if the frequency of the radiation is 3.34 x 10 14 Hz. 26. What is the energy associated with the photon in problem 37? 27. High energy electrons are found _________________ while low energy ...