Chemistry Lesson 10 Describing Matter
... volume or shape. Gases expand to fill any container they occupy. Their particles are free to move about. ...
... volume or shape. Gases expand to fill any container they occupy. Their particles are free to move about. ...
Structure of Atoms - Harrison County Schools
... •An atom is considered the building blocks of matter. ...
... •An atom is considered the building blocks of matter. ...
8.4 White Dwarfs
... Loose protons and electrons near the surface of the neutron star will be sweep up and stream along the magnetic field lines towards the north and south magnetic poles of the neutron star. The magnetic axis of the neutron star does not necessarily have to be aligned with the rotation axis (like the ...
... Loose protons and electrons near the surface of the neutron star will be sweep up and stream along the magnetic field lines towards the north and south magnetic poles of the neutron star. The magnetic axis of the neutron star does not necessarily have to be aligned with the rotation axis (like the ...
Module 8 - Brookville Local Schools
... By John T. Moore Part of the Chemistry For Dummies Cheat Sheet In bonding, atoms lose, gain, or share electrons in order to have the same number of electrons as the noble gas that's nearest on the periodic table. Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are formed by combinations of metals and nonmetals. ...
... By John T. Moore Part of the Chemistry For Dummies Cheat Sheet In bonding, atoms lose, gain, or share electrons in order to have the same number of electrons as the noble gas that's nearest on the periodic table. Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are formed by combinations of metals and nonmetals. ...
Final Exam Review Day 1
... Kinetic Molecular Theory assumes gases are made up of _________ ___________ moving in _____________ ___________, colliding into each other with ______________ collisions. As temperature increases, the particle movement also _____________________. Gases do not behave ideally when gases stop moving (o ...
... Kinetic Molecular Theory assumes gases are made up of _________ ___________ moving in _____________ ___________, colliding into each other with ______________ collisions. As temperature increases, the particle movement also _____________________. Gases do not behave ideally when gases stop moving (o ...
Chemistry 432: Final Exam Review Sheet
... c) alpha particle (24 or 24He ): a helium nucleus that has a charge of +2; common in very heavy nuclei. d) beta particle (-10 or -10e): an electron emitted from the nucleus and formed from the breakdown of one neutron into a proton and an electron. n p + -10 e) positron, anti-electron, (+10 or ...
... c) alpha particle (24 or 24He ): a helium nucleus that has a charge of +2; common in very heavy nuclei. d) beta particle (-10 or -10e): an electron emitted from the nucleus and formed from the breakdown of one neutron into a proton and an electron. n p + -10 e) positron, anti-electron, (+10 or ...
Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms and Ions
... Matter is composed of empty space through which atoms move Atoms are solid, homogeneous, indestructible, indivisible Atoms come in different sizes and shapes which creates different properties Changes in matter result from changes in groupings of atoms, not in the atoms themselves ...
... Matter is composed of empty space through which atoms move Atoms are solid, homogeneous, indestructible, indivisible Atoms come in different sizes and shapes which creates different properties Changes in matter result from changes in groupings of atoms, not in the atoms themselves ...
Word
... b. Water boils above 100 0C at higher pressures c. Water boils below 100 0C at lower pressures C. Condensation 1. The conversion of a gas to a liquid by the removal of energy IV. Freezing and Melting A. Freezing Point 1. The temperature at which the solid and liquid are in equilibrium at 1 atm 2. Fo ...
... b. Water boils above 100 0C at higher pressures c. Water boils below 100 0C at lower pressures C. Condensation 1. The conversion of a gas to a liquid by the removal of energy IV. Freezing and Melting A. Freezing Point 1. The temperature at which the solid and liquid are in equilibrium at 1 atm 2. Fo ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide_S2014
... c. CH3OH(l) CH3OH(g) h. C6H12O6(s)2C2H5OH(l) + 2CO2(g) d. NH3(l) NH3(g) i. H2SO4(l)H2O(l) + SO3(g) e. 2SO3(g) + CO2(g) CS2(g) +4O2(g) State whether the following processes are exothermic or endothermic: a. C2H5OH (l) C2H5OH(g) d. NaCl(s)NaCl(l) b. NH3(g) NH3(l) e. C5H12(g) + O2(g)CO2(g) ...
... c. CH3OH(l) CH3OH(g) h. C6H12O6(s)2C2H5OH(l) + 2CO2(g) d. NH3(l) NH3(g) i. H2SO4(l)H2O(l) + SO3(g) e. 2SO3(g) + CO2(g) CS2(g) +4O2(g) State whether the following processes are exothermic or endothermic: a. C2H5OH (l) C2H5OH(g) d. NaCl(s)NaCl(l) b. NH3(g) NH3(l) e. C5H12(g) + O2(g)CO2(g) ...
Review: How does a star*s mass determine its life story?
... the remaining cores of dead stars. • ________ degeneracy pressure supports them against gravity. ...
... the remaining cores of dead stars. • ________ degeneracy pressure supports them against gravity. ...
R= 8.31 J/mol K = 0.0821 L atm/mol K = 62.4 L torr/mol K PV = nRT
... magnetic field. The stream of atoms divided into two separate paths. This division would not be observed with atoms of A) Cu B) Cr C) Mg D) K E) Al ______26. The Pauli exclusion principle states that A) the velocity of all electromagnetic radiation equals the speed of light B) all particles with mas ...
... magnetic field. The stream of atoms divided into two separate paths. This division would not be observed with atoms of A) Cu B) Cr C) Mg D) K E) Al ______26. The Pauli exclusion principle states that A) the velocity of all electromagnetic radiation equals the speed of light B) all particles with mas ...
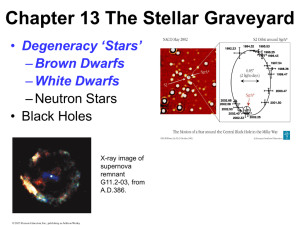
Chapter 13 The Stellar Graveyard
... don’t know for sure yet). • The mass of the white dwarf may gradually increase, • At about 1 M⊙, the gravitation force overcomes the electron degenerate pressure, and the white dwarf collapses, increasing temperature and density until it reaches carbon fusion temperature. • The carbon inside the whi ...
... don’t know for sure yet). • The mass of the white dwarf may gradually increase, • At about 1 M⊙, the gravitation force overcomes the electron degenerate pressure, and the white dwarf collapses, increasing temperature and density until it reaches carbon fusion temperature. • The carbon inside the whi ...
Gas Sampler
... P1V1 ‗ P2V2 T1 T2 P = pressure, and calculations can be done when P is in millimeters of Hg (mm), kilopascals (kPa), or atmospheres (atm) as long as both pressures are in the same units. Standard pressure is 760 mm, 101.32 kPa, or 1 atm. T = temperature, and calculations can be done only when T is i ...
... P1V1 ‗ P2V2 T1 T2 P = pressure, and calculations can be done when P is in millimeters of Hg (mm), kilopascals (kPa), or atmospheres (atm) as long as both pressures are in the same units. Standard pressure is 760 mm, 101.32 kPa, or 1 atm. T = temperature, and calculations can be done only when T is i ...
SNC 1D1 Exam Review 2016 Chemistry: Define the following terms
... Name the postulates for the Particle Theory of Matter. 1. All matter is made up of particles 2. All particles in a pure substance are identical (no two different pure substances have the same particles) 3. All particles have space between them 4. All particles are always moving – more energy (heat) ...
... Name the postulates for the Particle Theory of Matter. 1. All matter is made up of particles 2. All particles in a pure substance are identical (no two different pure substances have the same particles) 3. All particles have space between them 4. All particles are always moving – more energy (heat) ...
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW PACKET – GAS LAWS
... 12. Hydrogen gas is produced when zinc reacts with sulfuric acid: Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g) If 159 mL of wet H2 is collected over water at 24.00C and a barometric pressure of 738 torr, how many grams of Zn have been consumed? Look up the water vapor pressure in the tables in the text ...
... 12. Hydrogen gas is produced when zinc reacts with sulfuric acid: Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + H2 (g) If 159 mL of wet H2 is collected over water at 24.00C and a barometric pressure of 738 torr, how many grams of Zn have been consumed? Look up the water vapor pressure in the tables in the text ...
File
... The stream of atoms divided into two separate paths. This division would not be observed with atoms of A) Cu B) Cr C) Mg D) K E) Al ______26. The Pauli exclusion principle states that A) the velocity of all electromagnetic radiation equals the speed of light B) all particles with mass also have a wa ...
... The stream of atoms divided into two separate paths. This division would not be observed with atoms of A) Cu B) Cr C) Mg D) K E) Al ______26. The Pauli exclusion principle states that A) the velocity of all electromagnetic radiation equals the speed of light B) all particles with mass also have a wa ...
Chapter 3 Make up Test 2004
... ______26. Which of the following statements explains why chemists do not count atoms and molecules directly? A. Atoms and molecules are extremely small B. All of the relationships in a chemical reaction can be expressed as mass ratios C. Matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction ...
... ______26. Which of the following statements explains why chemists do not count atoms and molecules directly? A. Atoms and molecules are extremely small B. All of the relationships in a chemical reaction can be expressed as mass ratios C. Matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction ...
Chapter 14 Stellar Corpses Stellar Corpses White Dwarfs White
... • White dwarfs are compact stars with a mass similar to the Sun’s and a diameter about that of the Earth • Despite their high surface temperature of about 25,000 K, they are very dim due to ...
... • White dwarfs are compact stars with a mass similar to the Sun’s and a diameter about that of the Earth • Despite their high surface temperature of about 25,000 K, they are very dim due to ...
Kinetic-Molecular theory of Matter/Ch10, Gases/Ch11 –Column
... be kept constant for this relationship to work? 39) What does R represent in the Ideal Gas Law? How were the number and its units derived from the other 4 quantities? 40) Why are there 4 different numbers for the gas constant R? How do you decide which one to use for a particular problem? Which unit ...
... be kept constant for this relationship to work? 39) What does R represent in the Ideal Gas Law? How were the number and its units derived from the other 4 quantities? 40) Why are there 4 different numbers for the gas constant R? How do you decide which one to use for a particular problem? Which unit ...
Properties of Gases
... 1. A gas is composed of very minute particles called molecules. 2. The molecules are in a state of constant motion in random directions. During their movement they collide with each other and also with the walls of the container. 3. The molecules are perfectly elastic and the collisions do not resul ...
... 1. A gas is composed of very minute particles called molecules. 2. The molecules are in a state of constant motion in random directions. During their movement they collide with each other and also with the walls of the container. 3. The molecules are perfectly elastic and the collisions do not resul ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... no longer undergo fusion • Most white dwarfs are composed of carbon and oxygen • Very dense – Some have densities of 3 million grams per cubic centimeter – A teaspoon of a white dwarf would weigh as much as an elephant ...
... no longer undergo fusion • Most white dwarfs are composed of carbon and oxygen • Very dense – Some have densities of 3 million grams per cubic centimeter – A teaspoon of a white dwarf would weigh as much as an elephant ...