Document
... end result also yields energy. • This energy causes pressure which counters gravity. • But Iron doesn’t fuse. ...
... end result also yields energy. • This energy causes pressure which counters gravity. • But Iron doesn’t fuse. ...
Chemistry 2202 Background Information – Chapter 1 (pg
... Mass number (A) – The total number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom; each proton or neutron is counted as one unit of mass number. Atomic symbol – The symbol for the element – Fig. 1.8 pg. 13 Number of neutrons = Mass number – Atomic number =A–Z In any neutral atom of an element, ...
... Mass number (A) – The total number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom; each proton or neutron is counted as one unit of mass number. Atomic symbol – The symbol for the element – Fig. 1.8 pg. 13 Number of neutrons = Mass number – Atomic number =A–Z In any neutral atom of an element, ...
Document
... Only in high mass stars is pressure great enough for carbon to be made by nuclear fusion. Only in high mass stars do we find the C-N-O cycle of nuclear fusion. In low mass stars the pressure due to gravity isn’t as high as the pressure in the core of a high mass star. Only a high mass star ends in a ...
... Only in high mass stars is pressure great enough for carbon to be made by nuclear fusion. Only in high mass stars do we find the C-N-O cycle of nuclear fusion. In low mass stars the pressure due to gravity isn’t as high as the pressure in the core of a high mass star. Only a high mass star ends in a ...
20.1 A Solar System is Born
... The Solar Nebula Nebula – a large cloud of gas and dust in interstellar space • Where stars are born or explode at the end of their lives • Hydrogen, helium, carbon, iron • Two forces that interact with nebulas to create planets and stars – Gravity & Pressure ...
... The Solar Nebula Nebula – a large cloud of gas and dust in interstellar space • Where stars are born or explode at the end of their lives • Hydrogen, helium, carbon, iron • Two forces that interact with nebulas to create planets and stars – Gravity & Pressure ...
The Chemical Earth (8.2.3)
... Electron Shells (contd.) • The lowest energy level is the “K” shell, it is the nearest to the nucleus. Electrostatic attraction at this level is greatest for the electrons. • As we move away from the nucleus into higher energy levels, nuclear attraction becomes less. (See “Atomic Size” power point ...
... Electron Shells (contd.) • The lowest energy level is the “K” shell, it is the nearest to the nucleus. Electrostatic attraction at this level is greatest for the electrons. • As we move away from the nucleus into higher energy levels, nuclear attraction becomes less. (See “Atomic Size” power point ...
Ch 10 equations - mvhs
... Equal volumes of gases at the same T & P contain equal numbers of molecules. Molar Volume= Volume occupied by 1 mol of any gas at S.T.P.= 22.4 L Combined gas law: the pressure (P) of a fixed quantity (n) of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature (T) and inversely proportional to the volum ...
... Equal volumes of gases at the same T & P contain equal numbers of molecules. Molar Volume= Volume occupied by 1 mol of any gas at S.T.P.= 22.4 L Combined gas law: the pressure (P) of a fixed quantity (n) of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature (T) and inversely proportional to the volum ...
Key - Sardis Secondary
... 18. Helium is an inert gas that does not react with other substances to form compounds. Would it be correct to say that helium has no chemical properties? Explain your answer. ...
... 18. Helium is an inert gas that does not react with other substances to form compounds. Would it be correct to say that helium has no chemical properties? Explain your answer. ...
Chapter 13 Gases handout
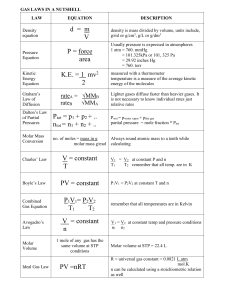
... density is mass divided by volume, units include, g/ml or g/cm3, g/L or g/dm3 Usually pressure is expressed in atmospheres 1 atm = 760. mmHg = 101.325kPa or 101, 325 Pa = 29.92 inches Hg = 760. torr ...
... density is mass divided by volume, units include, g/ml or g/cm3, g/L or g/dm3 Usually pressure is expressed in atmospheres 1 atm = 760. mmHg = 101.325kPa or 101, 325 Pa = 29.92 inches Hg = 760. torr ...
File
... Periodic Trends (Chapter 5) Atomic Radius – distance from nucleus to outer electrons (PreIB only) Shielding – inner electrons “blocking” or “shielding” the valence electrons from the pull of the nucleus. Ionization Energy – energy needed to remove an electron Electronegativity – ability of an ...
... Periodic Trends (Chapter 5) Atomic Radius – distance from nucleus to outer electrons (PreIB only) Shielding – inner electrons “blocking” or “shielding” the valence electrons from the pull of the nucleus. Ionization Energy – energy needed to remove an electron Electronegativity – ability of an ...
Semester 2 review questions
... 1. A packet of light energy that carries a quantum of energy. 2. The state when all electrons of an atom are in the lowest possible energy levels. 3. When an electron jumps up to a higher energy level, the atom is in its ___. 4. The scientist who applied Einstein’s particle-wave theory to electrons. ...
... 1. A packet of light energy that carries a quantum of energy. 2. The state when all electrons of an atom are in the lowest possible energy levels. 3. When an electron jumps up to a higher energy level, the atom is in its ___. 4. The scientist who applied Einstein’s particle-wave theory to electrons. ...
STATES OF MATTER - Science Education at Jefferson Lab
... ionized gas. A plasma is a very good conductor of electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. Plasmas, like gases • Plasma is the have an indefinite common state shape and an of matter indefinite volume. ...
... ionized gas. A plasma is a very good conductor of electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. Plasmas, like gases • Plasma is the have an indefinite common state shape and an of matter indefinite volume. ...
states of matter - lf008.k12.sd.us
... ionized gas. A plasma is a very good conductor of electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. Plasmas, like gases • Plasma is the have an indefinite common state shape and an of matter indefinite volume. ...
... ionized gas. A plasma is a very good conductor of electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. Plasmas, like gases • Plasma is the have an indefinite common state shape and an of matter indefinite volume. ...
Stellar Physics 2
... A. They are supported by electron degeneracy pressure. B. They are very small but very bright. Y C. They have much leftover gravitational energy from collapse so they are very hot. D. They have a very high density: ~109 kg m-3. ...
... A. They are supported by electron degeneracy pressure. B. They are very small but very bright. Y C. They have much leftover gravitational energy from collapse so they are very hot. D. They have a very high density: ~109 kg m-3. ...
Scale, structure and behaviour
... (atoms of the blackbody) that emit radiation. It was Einstein who later proposed that it is the electromagnetic radiation itself that is quantized, and not the energy of radiating atoms. In 1905, Albert Einstein provided an explanation of the photoelectric effect, a hitherto troubling experiment tha ...
... (atoms of the blackbody) that emit radiation. It was Einstein who later proposed that it is the electromagnetic radiation itself that is quantized, and not the energy of radiating atoms. In 1905, Albert Einstein provided an explanation of the photoelectric effect, a hitherto troubling experiment tha ...
Review_WB_1
... 1. What volume will a sample of hydrogen occupy at 28.0 oC at 2.23 dm3 . What will the volume be at temperature of 0.0 oC? Assume that the pressure remains constant. (Remember Kelvin). P ...
... 1. What volume will a sample of hydrogen occupy at 28.0 oC at 2.23 dm3 . What will the volume be at temperature of 0.0 oC? Assume that the pressure remains constant. (Remember Kelvin). P ...
Open Houses at the Campus Observatory Astronomical Horizons Lecture
... • What is pressure? • Think of gas particles in a balloon as baseballs in the balloon. • Baseballs move and hit walls of balloon • Baseballs push on the balloon ...
... • What is pressure? • Think of gas particles in a balloon as baseballs in the balloon. • Baseballs move and hit walls of balloon • Baseballs push on the balloon ...
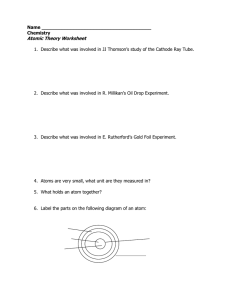
Atomic Theory Worksheet
... a. number of protons = b. number of electrons = c. number of neutrons = d. mass number = e. the charge on an ion = 9. What does it mean for an atom to be a. neutral – b. an ion – c. an isotope 10. How do you represent an isotope (how is it to be written)? 11. What does amu stand for? 12. What is a n ...
... a. number of protons = b. number of electrons = c. number of neutrons = d. mass number = e. the charge on an ion = 9. What does it mean for an atom to be a. neutral – b. an ion – c. an isotope 10. How do you represent an isotope (how is it to be written)? 11. What does amu stand for? 12. What is a n ...
E5 stellar processes and stellar evolution (HL only)
... • The resultant White dwarf has no energy source so is doomed to cool down to become a Black dwarf. ...
... • The resultant White dwarf has no energy source so is doomed to cool down to become a Black dwarf. ...
Biology Class Notes 3-1
... Atom: basic unit of matter Made up of subatomic particles i. Protons: positive charge ii. Neutrons: no charge iii. Electrons: negative charge Atoms have the same number of protons and electrons—makes them neutral Protons and neutrons are found inside the called in what is called the nucleus ...
... Atom: basic unit of matter Made up of subatomic particles i. Protons: positive charge ii. Neutrons: no charge iii. Electrons: negative charge Atoms have the same number of protons and electrons—makes them neutral Protons and neutrons are found inside the called in what is called the nucleus ...