Document
... The latest low-temperature of Colorado in Boulder when a team of scientists led by Carl Wieman reported that they had cooled a sample containing 2 × 107 cesium atoms to 1.1 × 10–6 K, about one-millionth of a degree above absolute zero. This record-low temperature was achieved by a technique know as ...
... The latest low-temperature of Colorado in Boulder when a team of scientists led by Carl Wieman reported that they had cooled a sample containing 2 × 107 cesium atoms to 1.1 × 10–6 K, about one-millionth of a degree above absolute zero. This record-low temperature was achieved by a technique know as ...
Thermodynamic course year 99-00
... Two specific points in equation of state should be emphasized: A. The triple point where the solid liquid and gaseous phases coexist in equilibrium. B. The critical point where there is continuous transition between liquid and gas. At the critical point diverges to infinity. Z= ~0.3 at this point. ...
... Two specific points in equation of state should be emphasized: A. The triple point where the solid liquid and gaseous phases coexist in equilibrium. B. The critical point where there is continuous transition between liquid and gas. At the critical point diverges to infinity. Z= ~0.3 at this point. ...
A mechanical model of Markov processes
... of small particles at each time are not independent to each other, nor to the history of the system. This becomes more evident and significant drawback when considering the model of interactions caused by potentials. Actually, since the interactions between molecules and atoms at each time effect not ...
... of small particles at each time are not independent to each other, nor to the history of the system. This becomes more evident and significant drawback when considering the model of interactions caused by potentials. Actually, since the interactions between molecules and atoms at each time effect not ...
chapter10 - AlvarezHChem
... • Pressure has a major effect on the solubility of a gas in a liquid, but little effect on other systems • Henry’s Law - At low to moderate pressure, the concentration of a gas increases with the pressure ...
... • Pressure has a major effect on the solubility of a gas in a liquid, but little effect on other systems • Henry’s Law - At low to moderate pressure, the concentration of a gas increases with the pressure ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... 1 unit of charge is 1.602 x 10-19 coulombs. A proton is given a charge of +1 and an electron a charge of -1. All charges are measured in these units. 1 unit of mass is 1.661 x 10-27 kg. This is also not a convenient number, so we use “atomic mass units”. Since the mass of protons and neutrons varies ...
... 1 unit of charge is 1.602 x 10-19 coulombs. A proton is given a charge of +1 and an electron a charge of -1. All charges are measured in these units. 1 unit of mass is 1.661 x 10-27 kg. This is also not a convenient number, so we use “atomic mass units”. Since the mass of protons and neutrons varies ...
Regents Chemistry
... Determine how soluble a compound is at a given temperature using the solubility traces found in Table G o use solubility curves to predict how much water is required to dissolve a given amount of solute at a given temp or how much solute will dissolve in a given amount of water o be able to predict ...
... Determine how soluble a compound is at a given temperature using the solubility traces found in Table G o use solubility curves to predict how much water is required to dissolve a given amount of solute at a given temp or how much solute will dissolve in a given amount of water o be able to predict ...
un/scetdg/36/wpxx
... This limitation effectively prohibits the use of > 1.25 L non refillable gas cylinders for flammable gases. However, some countries provide exceptions to this rule. E.g. the Department of Transportaation (DOT) in the United States of America effectively allows carriage of liquefied flammable gases i ...
... This limitation effectively prohibits the use of > 1.25 L non refillable gas cylinders for flammable gases. However, some countries provide exceptions to this rule. E.g. the Department of Transportaation (DOT) in the United States of America effectively allows carriage of liquefied flammable gases i ...
Measurement
... Solid – definite volume and shape; particles packed in fixed positions. Liquid – definite volume but indefinite shape; particles close together but not in fixed positions Gas – neither definite volume nor definite shape; particles are at great distances from one another Plasma – high temperature, io ...
... Solid – definite volume and shape; particles packed in fixed positions. Liquid – definite volume but indefinite shape; particles close together but not in fixed positions Gas – neither definite volume nor definite shape; particles are at great distances from one another Plasma – high temperature, io ...
Chapter2
... ideal gas law, the general gas law, or the perfect gas law. This equation has limited practical value since no known gas behaves as an ideal gas; however, the equation does describe the behavior of most real gases at low pressure and gives a basis for developing equations of state which more adequat ...
... ideal gas law, the general gas law, or the perfect gas law. This equation has limited practical value since no known gas behaves as an ideal gas; however, the equation does describe the behavior of most real gases at low pressure and gives a basis for developing equations of state which more adequat ...
Expriment5-labReport-Spring2017
... 4. Calculate the maximum electric work (in kJ/mol of H2) using an experimentally measured open circuit cell potential from the previous table assuming that only the reversible electrical work is performed at constant temperature and pressure. Compare this with the Wel max calculated under standard c ...
... 4. Calculate the maximum electric work (in kJ/mol of H2) using an experimentally measured open circuit cell potential from the previous table assuming that only the reversible electrical work is performed at constant temperature and pressure. Compare this with the Wel max calculated under standard c ...
Entropy - Department of Mathematics
... 5. Describe Boltzmann’s distribution, then how it explains the distribution of speeds of molecules in a gas. ...
... 5. Describe Boltzmann’s distribution, then how it explains the distribution of speeds of molecules in a gas. ...
Chapter 13 Notes Types of Solutions Saturated Solution: contains
... The Effect of Temperature on Solubility *In most cases, the solubility of a solid substance increases with temperature Fractional Crystallization: the separation of a mixture of substances into pure components on the basis of their differing solubility (Works well if the substances involved have gre ...
... The Effect of Temperature on Solubility *In most cases, the solubility of a solid substance increases with temperature Fractional Crystallization: the separation of a mixture of substances into pure components on the basis of their differing solubility (Works well if the substances involved have gre ...
experiment 7 - (canvas.brown.edu).
... g. Calculate the % error between both experimental values in part f and the accepted value of the Faraday constant of 96,485 C/mol. ...
... g. Calculate the % error between both experimental values in part f and the accepted value of the Faraday constant of 96,485 C/mol. ...
Chemistry 3510: Physical Chemistry Midterm Exam 1 19 February 2007 Name:
... Calculate the work, heat, change in internal energy, change in enthalpy, and change in entropy of both system and surroundings for each of the legs and for the cycle. Fill in the table provided with these results. ...
... Calculate the work, heat, change in internal energy, change in enthalpy, and change in entropy of both system and surroundings for each of the legs and for the cycle. Fill in the table provided with these results. ...
2.00atm x 1 .00L 0.0821 L.atm.mol K 298.15 = 8.17x10 mol. U = 8
... Answers: At a depth h, the pressure p = hρg, in which ρ is the liquid density and g = 9.8 m s–2. The density of sea water is about 1027 kg/m3. Hence the pressure: p = 1.5x103m (1027 kg/m3) (9.8 m s–2) = 1.5x107 Pa. = 149. 5 atm ( 1.0 atm = 101.3 kPa). In the oceans, the pressure increases by about 1 ...
... Answers: At a depth h, the pressure p = hρg, in which ρ is the liquid density and g = 9.8 m s–2. The density of sea water is about 1027 kg/m3. Hence the pressure: p = 1.5x103m (1027 kg/m3) (9.8 m s–2) = 1.5x107 Pa. = 149. 5 atm ( 1.0 atm = 101.3 kPa). In the oceans, the pressure increases by about 1 ...
Decomposition Reactions
... The reaction you will investigate in this experiment is the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. You may be familiar with this compound; hydrogen peroxide solution can be commonly purchased in any pharmacy and it is found in most home medicine cabinets. In fact, the reaction you will be studying take ...
... The reaction you will investigate in this experiment is the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. You may be familiar with this compound; hydrogen peroxide solution can be commonly purchased in any pharmacy and it is found in most home medicine cabinets. In fact, the reaction you will be studying take ...
Chapter 6-States of Matter: Gases, Liquids, and Solids
... absorbs a portion of the radiation from the sun, preventing it from reaching the planet's surface. Most importantly, it absorbs the portion of ultraviolet light called UVB(UltraViolet-B). UVB is particularly effective at damaging DNA. It is a cause of melanoma and other types of skin cancer. UVB has ...
... absorbs a portion of the radiation from the sun, preventing it from reaching the planet's surface. Most importantly, it absorbs the portion of ultraviolet light called UVB(UltraViolet-B). UVB is particularly effective at damaging DNA. It is a cause of melanoma and other types of skin cancer. UVB has ...
che-20028 QC lecture 1 - Rob Jackson`s Website
... How the experiment is performed • Using a variable frequency light source, shine light onto a metal surface. • Determine the light frequency which causes electrons to be emitted. • Measure the energy of the emitted electrons, by applying a voltage across the cell in the opposite direction to balanc ...
... How the experiment is performed • Using a variable frequency light source, shine light onto a metal surface. • Determine the light frequency which causes electrons to be emitted. • Measure the energy of the emitted electrons, by applying a voltage across the cell in the opposite direction to balanc ...
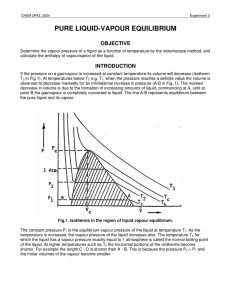
pure liquid-vapour equilibrium - Theoretical and Computational
... = G , the molar Gibbs free energy. ...
... = G , the molar Gibbs free energy. ...
Electronic Structure - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... electrons of an element are located. The Aufbau Principle states that electrons will fill orbitals starting with the orbital of lowest energy. For degenerate orbitals, electrons fill each orbital singly before any orbital gets a second electron (Hund’s Rule of Maximum Multiplicity). The Pauli Exclus ...
... electrons of an element are located. The Aufbau Principle states that electrons will fill orbitals starting with the orbital of lowest energy. For degenerate orbitals, electrons fill each orbital singly before any orbital gets a second electron (Hund’s Rule of Maximum Multiplicity). The Pauli Exclus ...
Acta Polytechnica
... into the HF (high-frequency) fields and plasma particles energy [12, 5, 1]. The phenomenon of beam instability is in the effective initiation of fluctuations and waves in plasma by means of electron beam, which came into being after publication of the fundamental works by Akhiyezer and Faynberg, Bom ...
... into the HF (high-frequency) fields and plasma particles energy [12, 5, 1]. The phenomenon of beam instability is in the effective initiation of fluctuations and waves in plasma by means of electron beam, which came into being after publication of the fundamental works by Akhiyezer and Faynberg, Bom ...