Electronic Structure and Covalent Bonding
... -Aufbau principle: An electron goes into the available atomic orbital with the lowest energy. -Pauli exclusion principle: No more than two electrons can occupy each atomic orbital. -Hund’s rule: An electron goes into an empty degenerate orbital rather than pairing up. ...
... -Aufbau principle: An electron goes into the available atomic orbital with the lowest energy. -Pauli exclusion principle: No more than two electrons can occupy each atomic orbital. -Hund’s rule: An electron goes into an empty degenerate orbital rather than pairing up. ...
Unit 2 Assignments Answers
... arrangement was brought on by the hydrogen bonding (a type of strong intermolecular force) water molecules have due to its V-shape structure with two sets of exposed lone-pairs, which makes water molecules very polar. As ice forms, the hexagonal structure takes up more space than its liquid counterp ...
... arrangement was brought on by the hydrogen bonding (a type of strong intermolecular force) water molecules have due to its V-shape structure with two sets of exposed lone-pairs, which makes water molecules very polar. As ice forms, the hexagonal structure takes up more space than its liquid counterp ...
this PDF file - Publications of the Serbian Chemical Society
... their cluster size distributions21 have been studied based on static crystalline properties and using ab initio potential respectively. Gupta proposed a semi-empirical potential to study the metallic fluids by molecular dynamics.22 Gupta potential function has been applied successfully by many resea ...
... their cluster size distributions21 have been studied based on static crystalline properties and using ab initio potential respectively. Gupta proposed a semi-empirical potential to study the metallic fluids by molecular dynamics.22 Gupta potential function has been applied successfully by many resea ...
SOLUBILITY OF GASES AT 25 C AND HIGH PRESSURES: THE
... versus of a certain property of the gas (for example the force constant or critical temperature) don’t lead to a curve with a regular aspect. This aspect is given by the fact that the solubility of gas depends not only of solvit-solvent interaction but on the fugacity of pure solvit in condense stat ...
... versus of a certain property of the gas (for example the force constant or critical temperature) don’t lead to a curve with a regular aspect. This aspect is given by the fact that the solubility of gas depends not only of solvit-solvent interaction but on the fugacity of pure solvit in condense stat ...
Flame Temperature and Chemical Equilibrium
... • This indicates that at high temperatures equilibrium NO-‐levels exceed by far those that are accepted by modern emission standards which are around 100 ppv or lower. • Equilibrium consideraEons therefore ...
... • This indicates that at high temperatures equilibrium NO-‐levels exceed by far those that are accepted by modern emission standards which are around 100 ppv or lower. • Equilibrium consideraEons therefore ...
Classical Thermodynamics I: Sublimation of Solid Iodine
... about 1 atm to provide pressure broadening of the extremely sharp and intense absorption lines of the rotational fine structure (which can be individually resolved only by special techniques of laser spectroscopy). The reason lies in the logarithmic form of Eq. (34). Within the slit width or resolut ...
... about 1 atm to provide pressure broadening of the extremely sharp and intense absorption lines of the rotational fine structure (which can be individually resolved only by special techniques of laser spectroscopy). The reason lies in the logarithmic form of Eq. (34). Within the slit width or resolut ...
Detecting Individual Electrons Using a Carbon Nanotube Field
... gate voltage. This is especially interesting for future studies on organic and biological molecules because the large energy separation between the levels often has limited access to only one level.20,21 We will now compare our work to other existing singleelectron detectors, which are devices micro ...
... gate voltage. This is especially interesting for future studies on organic and biological molecules because the large energy separation between the levels often has limited access to only one level.20,21 We will now compare our work to other existing singleelectron detectors, which are devices micro ...
Chapter 15
... See Example 12.16 (Hill, pp. 511) Practical Applications of Osmosis Patients are usually given intravenous fluids that are isotonic— these solutions have the same osmotic pressure as blood. There are three scenarios: (1) if the external solution is hypertonic, its osmotic pressure > Π(internal), and ...
... See Example 12.16 (Hill, pp. 511) Practical Applications of Osmosis Patients are usually given intravenous fluids that are isotonic— these solutions have the same osmotic pressure as blood. There are three scenarios: (1) if the external solution is hypertonic, its osmotic pressure > Π(internal), and ...
18_Testbank - Lick Observatory
... 37) One foolhardy day, a daring major (let's call him Tom) in the space force decides to become the first of his race to cross the event horizon of the black hole. To add to the drama, he decides to go in wearing only a thin space suit, which offers no shielding against radiation, no cushioning aga ...
... 37) One foolhardy day, a daring major (let's call him Tom) in the space force decides to become the first of his race to cross the event horizon of the black hole. To add to the drama, he decides to go in wearing only a thin space suit, which offers no shielding against radiation, no cushioning aga ...
Describing Matter from Text
... substance. A chemical property is a characteristic of a pure substance that describes its ability to change into different substances. To observe the chemical properties of a substance, you must try to change it to another substance. Like physical properties, chemical properties are used to classify ...
... substance. A chemical property is a characteristic of a pure substance that describes its ability to change into different substances. To observe the chemical properties of a substance, you must try to change it to another substance. Like physical properties, chemical properties are used to classify ...
I.5. Periodic properties of the elements
... The elements of Group 18, rare gases, have the configuration ns2 np6, except helium, whose configuration is 1s2. That means the outer shells of the atoms are full. These prove to be very stable configurations and they can be altered with great difficulty. As a result, rare gases have a very low reac ...
... The elements of Group 18, rare gases, have the configuration ns2 np6, except helium, whose configuration is 1s2. That means the outer shells of the atoms are full. These prove to be very stable configurations and they can be altered with great difficulty. As a result, rare gases have a very low reac ...
Міністерство охорони здоров`я України
... Solutions of high molecular weight compounds (HMC) have properties both true solution and colloidal solution (particle size is more than 10-9 m). 2. Mechanism of the dissolution. Energetic effect of the dissolution. There are two theories based on the structure of the substance: physical and chemica ...
... Solutions of high molecular weight compounds (HMC) have properties both true solution and colloidal solution (particle size is more than 10-9 m). 2. Mechanism of the dissolution. Energetic effect of the dissolution. There are two theories based on the structure of the substance: physical and chemica ...
In Situ Raman Spectroscopic Study of Gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O) and
... To demonstrate the potential of the experimental setup, we studied the stepwise dehydration of levitated epsomite (MgSO4·7H2O) and gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O) crystals induced by heating from the carbon dioxide laser. These experiments have important implications for the understanding of our solar system. T ...
... To demonstrate the potential of the experimental setup, we studied the stepwise dehydration of levitated epsomite (MgSO4·7H2O) and gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O) crystals induced by heating from the carbon dioxide laser. These experiments have important implications for the understanding of our solar system. T ...
Chemistry - Chap 12 Homework Answers 2014
... small amount of liquid? What processes are going on in the flask? pressure exerted by vapor above a liquid. High energy particles at surface escape and exert the pressure 8. Which substance in each pair would be expected to show the largest vapor pressure at a given temperature? The largest vapor pr ...
... small amount of liquid? What processes are going on in the flask? pressure exerted by vapor above a liquid. High energy particles at surface escape and exert the pressure 8. Which substance in each pair would be expected to show the largest vapor pressure at a given temperature? The largest vapor pr ...
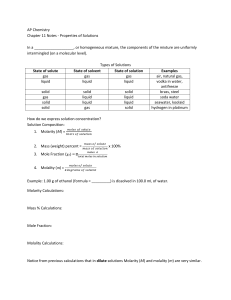
AP Chemistry Chapter 11 Notes - Properties of Solutions In a , or
... membrane. The diluted solution travels up the thistle tube until the osmotic pressure is balanced by the gravitational pull. ...
... membrane. The diluted solution travels up the thistle tube until the osmotic pressure is balanced by the gravitational pull. ...
- Form when atoms SHARE electrons instead of transferring them
... closer to one another than they would if they were sharing one or two pairs of electrons. Triple bonds have the shortest BOND DISTANCE of all covalent bonds. - It takes more energy to break a triple bond between two atoms than it would to break either a single or double bond between the same two ato ...
... closer to one another than they would if they were sharing one or two pairs of electrons. Triple bonds have the shortest BOND DISTANCE of all covalent bonds. - It takes more energy to break a triple bond between two atoms than it would to break either a single or double bond between the same two ato ...
C1403_Lecture9_10110..
... The energy of an orbital of a hydrogen atom or any one electron atom only depends on the value of n shell = all orbitals with the same value of n subshell = all orbitals with the same value of n and l an orbital is fully defined by three quantum numbers, n, l, and ml Each shell of QN = n contains n ...
... The energy of an orbital of a hydrogen atom or any one electron atom only depends on the value of n shell = all orbitals with the same value of n subshell = all orbitals with the same value of n and l an orbital is fully defined by three quantum numbers, n, l, and ml Each shell of QN = n contains n ...
Unit Powerpoint
... Cu(s) + 2Ag+ (aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag (s) Copper began as a neutral atom with no charge but changes into an ion with a 2+ charge. This happens when it loses 2 electrons. Cu (s) Cu2+ (aq) + 2 eCopper was oxidized because it lost electrons. Silver went from an ion Ag+ to a neutral atom Ag. The only way ...
... Cu(s) + 2Ag+ (aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag (s) Copper began as a neutral atom with no charge but changes into an ion with a 2+ charge. This happens when it loses 2 electrons. Cu (s) Cu2+ (aq) + 2 eCopper was oxidized because it lost electrons. Silver went from an ion Ag+ to a neutral atom Ag. The only way ...
script
... heavy elements is so large that the ionization of these levels cannot be detected. In general, the lifetime of an ionized state is short if there are several electronic states with smaller EB which can fill the state. These channels are numerous for heavy elements. For slow Auger processes, i.e., lo ...
... heavy elements is so large that the ionization of these levels cannot be detected. In general, the lifetime of an ionized state is short if there are several electronic states with smaller EB which can fill the state. These channels are numerous for heavy elements. For slow Auger processes, i.e., lo ...
ECE final exam_fall 2013
... all these papers when you are finished. A separate packet has a page of equations, a periodic table, and a phase diagram. Make sure that you have both packets. Use a pen with blue or black ink for the entire exam. Be sure to follow ALL directions. In working the problems, you MUST SHOW ALL WORK. Wri ...
... all these papers when you are finished. A separate packet has a page of equations, a periodic table, and a phase diagram. Make sure that you have both packets. Use a pen with blue or black ink for the entire exam. Be sure to follow ALL directions. In working the problems, you MUST SHOW ALL WORK. Wri ...
Document
... We start with the reactants, decompose them into elements, then rearrange the elements to form products. The overall enthalpy change is the sum of the ...
... We start with the reactants, decompose them into elements, then rearrange the elements to form products. The overall enthalpy change is the sum of the ...
Cold Fusion By Plasma Electrolysis of Water
... was formed from mass mF = 4,270602 ⋅10 −31 kg and flew away in the unknown direction; the second one – there were no conditions for the formation of the photons in the process being considered, and mass mF , which failed to be formed as a particle, “was dissolved” in the ether. Which variant is clos ...
... was formed from mass mF = 4,270602 ⋅10 −31 kg and flew away in the unknown direction; the second one – there were no conditions for the formation of the photons in the process being considered, and mass mF , which failed to be formed as a particle, “was dissolved” in the ether. Which variant is clos ...
Stoichiometry
... d. Ice consists of water molecules in a hexagonal arrangement. 2. Compare a polar water molecule with a less-polar molecule, such as formaldehyde, CH2O. Both are liquids at room temperature and 1 atm pressure. a. Which liquid should have the higher boiling point? b. Which liquid is more volatile? c. ...
... d. Ice consists of water molecules in a hexagonal arrangement. 2. Compare a polar water molecule with a less-polar molecule, such as formaldehyde, CH2O. Both are liquids at room temperature and 1 atm pressure. a. Which liquid should have the higher boiling point? b. Which liquid is more volatile? c. ...
Unit 1 review
... Real gas equation (P+a(n/V)’2)(V-bn)= nRT First part = The factor that the regular PV=nRT value is off because of the fact that IMFA was not included Second part = The factor that the regular PV=nRT value is off because it now does not include the molecules themselves ...
... Real gas equation (P+a(n/V)’2)(V-bn)= nRT First part = The factor that the regular PV=nRT value is off because of the fact that IMFA was not included Second part = The factor that the regular PV=nRT value is off because it now does not include the molecules themselves ...