physical chemistry - University Science Books
... 1.1 Nature of Physical Chemistry Physical chemistry can be described as a set of characteristically quantitative approaches to the study of chemical problems. A physical chemist seeks to predict and/ or explain chemical events using certain models and postulates. Because the problems encountered in ...
... 1.1 Nature of Physical Chemistry Physical chemistry can be described as a set of characteristically quantitative approaches to the study of chemical problems. A physical chemist seeks to predict and/ or explain chemical events using certain models and postulates. Because the problems encountered in ...
Dynamics and particle uxes in atmospheric
... Besides the obvious difference in terms of size, the discharge dynamics in microplasmas differ from conventional low-pressure large-scale reactors. In microplasmas, sheaths can become comparable to the source size,5,6 enabling interesting possibilities such as electrode/sample bombardment by energet ...
... Besides the obvious difference in terms of size, the discharge dynamics in microplasmas differ from conventional low-pressure large-scale reactors. In microplasmas, sheaths can become comparable to the source size,5,6 enabling interesting possibilities such as electrode/sample bombardment by energet ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... of matter: gases, liquids, solids, etc.; are there more states there? Yes – think of the chicken soup (suspension) you are warming up on the gas flame (plasma) while checking your watch display (liquid crystal), or think of the peanut butter (emulsion)–jam (gel) sandwich you had this morning. You may ...
... of matter: gases, liquids, solids, etc.; are there more states there? Yes – think of the chicken soup (suspension) you are warming up on the gas flame (plasma) while checking your watch display (liquid crystal), or think of the peanut butter (emulsion)–jam (gel) sandwich you had this morning. You may ...
Chapter 13
... 24. For an ideal gas, volume and temperature described in kelvins are directly proportional if the number of gas particles and pressure are constant. This is a statement of Charles’ Law. 26. If the temperature and volume of an ideal gas are held constant, the number of gas particles in a container a ...
... 24. For an ideal gas, volume and temperature described in kelvins are directly proportional if the number of gas particles and pressure are constant. This is a statement of Charles’ Law. 26. If the temperature and volume of an ideal gas are held constant, the number of gas particles in a container a ...
Role of Pressure in Transport of F
... The swarm is ensemble of charged particles travelling through the neutral gas and balancing between the energy and momentum gained from the external (electric) field and dissipating the energy and momentum in collisions with the background gas [13]. Assuming that probability of collisions of swarm p ...
... The swarm is ensemble of charged particles travelling through the neutral gas and balancing between the energy and momentum gained from the external (electric) field and dissipating the energy and momentum in collisions with the background gas [13]. Assuming that probability of collisions of swarm p ...
2017 Chemistry Exam Review Compounds and Reactions 1. Know
... 60. In an aqueous solution, how is [H+] calculated from [OH-] (or vice versa)? 61. Define pH. How is it calculated from [H+] or [H3O+]? How is [H+] calculated from pH? 62. What is pH and [H+] for pure water? 63. How is pOH calculated from pH (or vice versa)? 64. What happens to acidity ([H+]) for ea ...
... 60. In an aqueous solution, how is [H+] calculated from [OH-] (or vice versa)? 61. Define pH. How is it calculated from [H+] or [H3O+]? How is [H+] calculated from pH? 62. What is pH and [H+] for pure water? 63. How is pOH calculated from pH (or vice versa)? 64. What happens to acidity ([H+]) for ea ...
Chapter 6 - Department of Chemical Engineering
... Vapor pressure of liquids depends on the temperature and the nature of the liquid. The forces causing the vaporization of a liquid are derived from the kinetic energy of translation of its molecules. An increase in kinetic energy of molecular translation increases the rate of vaporization and vapor ...
... Vapor pressure of liquids depends on the temperature and the nature of the liquid. The forces causing the vaporization of a liquid are derived from the kinetic energy of translation of its molecules. An increase in kinetic energy of molecular translation increases the rate of vaporization and vapor ...
Factors Affecting the Rate of a Chemical Reaction
... We can follow this reaction by measuring the volume of carbon dioxide produced as the reaction proceeds. Gas being collected ...
... We can follow this reaction by measuring the volume of carbon dioxide produced as the reaction proceeds. Gas being collected ...
Allowed and forbidden transitions in artificial hydrogen and helium
... orbital, while the first excited state is a spin triplet (labelled T) with two parallel-spin electrons, one each occupying the 1s and 2p orbitals4,5. Because of Coulomb interactions, the energy spacing between the two states, 1 S–T (,0.6 meV at B ¼ 0 T), is smaller than 1 1s–2p. Energy relaxation fr ...
... orbital, while the first excited state is a spin triplet (labelled T) with two parallel-spin electrons, one each occupying the 1s and 2p orbitals4,5. Because of Coulomb interactions, the energy spacing between the two states, 1 S–T (,0.6 meV at B ¼ 0 T), is smaller than 1 1s–2p. Energy relaxation fr ...
Lectures 5
... decreasing solubility of most gases due to greater tendency of the gas to expand at higher temperature. Therefore we should use caution when opening containers of gas at high temperature. e.g., ethyl nitrite vessel should be immersed in cold water or ice before opening. 3) Addition of salts (salting ...
... decreasing solubility of most gases due to greater tendency of the gas to expand at higher temperature. Therefore we should use caution when opening containers of gas at high temperature. e.g., ethyl nitrite vessel should be immersed in cold water or ice before opening. 3) Addition of salts (salting ...
Oxidation-Reduction (REDOX) Reactions
... In a redox reaction, at least one element is oxidized, and at least one element is reduced. An element cannot be oxidized in a chemical reaction unless some other element is reduced, and vice-versa. (After all, the electrons have to come from somewhere, and they have to go somewhere.) oxidizing agen ...
... In a redox reaction, at least one element is oxidized, and at least one element is reduced. An element cannot be oxidized in a chemical reaction unless some other element is reduced, and vice-versa. (After all, the electrons have to come from somewhere, and they have to go somewhere.) oxidizing agen ...
Ch#1 Introduction - Seattle Central College
... to change lead into gold. The major results of their experiments were to prove most of the Greek ideas of chemistry to be false and to show a clear distinction between science and ...
... to change lead into gold. The major results of their experiments were to prove most of the Greek ideas of chemistry to be false and to show a clear distinction between science and ...
Acids and Bases Acids and Bases Conjugate Pair Question
... He is ~half as soluble as nitrogen and so less must be released avoiding this problem. He also has a higher rate of diffusion in the blood which makes He more acceptable. ...
... He is ~half as soluble as nitrogen and so less must be released avoiding this problem. He also has a higher rate of diffusion in the blood which makes He more acceptable. ...
ChemQuiz_QntativeChem
... Dividing all by 2 gives a ratio of C:H:O = 1:2:1 The empircal formula is CH2O ...
... Dividing all by 2 gives a ratio of C:H:O = 1:2:1 The empircal formula is CH2O ...
Document
... • Physically, such processes are accompanied by a very small change in volume, the system does negligible work on the surroundings when the process occurs, so the energy supplied as heat stays entirely within the system. ...
... • Physically, such processes are accompanied by a very small change in volume, the system does negligible work on the surroundings when the process occurs, so the energy supplied as heat stays entirely within the system. ...
lect1f
... rH = 2Hm(H2O) - 2Hm(H2) - Hm(O2) The heat of reaction defined this way depends on T, p and the concentrations of the reactants and products. ...
... rH = 2Hm(H2O) - 2Hm(H2) - Hm(O2) The heat of reaction defined this way depends on T, p and the concentrations of the reactants and products. ...
The absorption spectra of very small CdS or ZnS particles (1
... The first studies on the photochemistry of inorganic particles in aqueous suspension were made with zinc sulfide some fifty years ago (Ref. 1,2). Zinc sulfide, a component of the white pigment lithophone, was shown not only to photolyse but also to catalyse redox processes including the photo-decomp ...
... The first studies on the photochemistry of inorganic particles in aqueous suspension were made with zinc sulfide some fifty years ago (Ref. 1,2). Zinc sulfide, a component of the white pigment lithophone, was shown not only to photolyse but also to catalyse redox processes including the photo-decomp ...
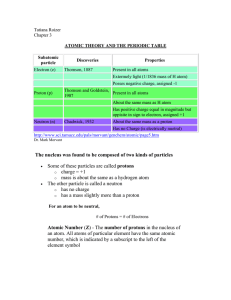
atomic theory and the periodic table
... 3s, 4s (etc) orbitals get progressively further from the nucleus. p orbitals Not all electrons inhabit s orbitals (in fact, very few electrons live in s orbitals). At the first energy level, the only orbital available to electrons is the 1s orbital, but at the second level, as well as a 2s orbital, ...
... 3s, 4s (etc) orbitals get progressively further from the nucleus. p orbitals Not all electrons inhabit s orbitals (in fact, very few electrons live in s orbitals). At the first energy level, the only orbital available to electrons is the 1s orbital, but at the second level, as well as a 2s orbital, ...
T h - Website Staff UI
... The Nernst Theorem The entropy change accompanying any physical or chemical transformation approaches zero as the temperature approaches zero. S 0 as T0 ...
... The Nernst Theorem The entropy change accompanying any physical or chemical transformation approaches zero as the temperature approaches zero. S 0 as T0 ...
Lecture Slides - School of Chemical Sciences
... http://www.scs.uiuc.edu/~makri/444-web-page/chem-444.html/444-course-planner.html ...
... http://www.scs.uiuc.edu/~makri/444-web-page/chem-444.html/444-course-planner.html ...
Lowering of the L10 ordering temperature of FePt
... a micellar technique on Si substrates. The phase transition of these magnetic particles towards the chemically ordered L10 phase is tracked for 350 kV He+ ion irradiated samples and compared to a nonirradiated reference. Due to the large separation of the magnetically decoupled particles the array c ...
... a micellar technique on Si substrates. The phase transition of these magnetic particles towards the chemically ordered L10 phase is tracked for 350 kV He+ ion irradiated samples and compared to a nonirradiated reference. Due to the large separation of the magnetically decoupled particles the array c ...
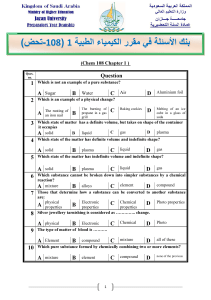
ض ( ا ء ا ط ك ا رر 108 1) -
... Which state of the matter has definite volume and indefinite shape? solid B plasma C liquid D gas Which state of the matter has indefinite volume and indefinite shape? ...
... Which state of the matter has definite volume and indefinite shape? solid B plasma C liquid D gas Which state of the matter has indefinite volume and indefinite shape? ...
1 The modern model of the atom is based on the work of (1) one
... In 1897, J. J. Thomson demonstrated in an experiment that cathode rays were deflected by an electric field. This suggested that cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles found in all atoms. Thomson concluded that the atom was a positively charged sphere of almost uniform density in ...
... In 1897, J. J. Thomson demonstrated in an experiment that cathode rays were deflected by an electric field. This suggested that cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles found in all atoms. Thomson concluded that the atom was a positively charged sphere of almost uniform density in ...
Mr Alasdair Ross at Southpointe Academy
... The Vapour Pressure of a liquid is the partial pressure exerted by its vapor in dynamic equilibrium with liquid at a constant temperature. The Vapour Pressure of a liquid increases with temperature. At a higher temperature more molecules have enough kinetic energy to escape from the liquid state. At ...
... The Vapour Pressure of a liquid is the partial pressure exerted by its vapor in dynamic equilibrium with liquid at a constant temperature. The Vapour Pressure of a liquid increases with temperature. At a higher temperature more molecules have enough kinetic energy to escape from the liquid state. At ...