PPT - kimscience.com
... batteries. The anode is zinc, the cathode is manganese dioxide, and the electrolyte is ammonium chloride or zinc chloride. Alkaline battery: common in AA, C and D dry cell batteries. The cathode is composed of a manganese dioxide mixture, while the anode is a zinc powder. Lithium-ion battery (rechar ...
... batteries. The anode is zinc, the cathode is manganese dioxide, and the electrolyte is ammonium chloride or zinc chloride. Alkaline battery: common in AA, C and D dry cell batteries. The cathode is composed of a manganese dioxide mixture, while the anode is a zinc powder. Lithium-ion battery (rechar ...
Identification - KHAZAR UNIVERSITY
... such as trips, cruises and sporting events (unless you are participating). The exams will all be cumulative. Most of the questions on each exam will be taken from the chapters covered since the last exam. But some will come from the earlier chapters. In general the coverage will reflect the amount o ...
... such as trips, cruises and sporting events (unless you are participating). The exams will all be cumulative. Most of the questions on each exam will be taken from the chapters covered since the last exam. But some will come from the earlier chapters. In general the coverage will reflect the amount o ...
classical notions of heterogeneous freezing
... It is seen from Fig. 3 that for solids or liquids, the change in volume with pressure is small, so V can be treated as a constant and the integral can be considered approximately as ≈ V∆p. Since at normal pressure the value of V∆p is small, we can suppose that the Gibbs energies of solids and liquid ...
... It is seen from Fig. 3 that for solids or liquids, the change in volume with pressure is small, so V can be treated as a constant and the integral can be considered approximately as ≈ V∆p. Since at normal pressure the value of V∆p is small, we can suppose that the Gibbs energies of solids and liquid ...
Neutron Stars
... electrons are not in the lowest-energy level near the nucleus; instead they are arranged in higher-energy-level shells. ...
... electrons are not in the lowest-energy level near the nucleus; instead they are arranged in higher-energy-level shells. ...
4/page
... •Be sure to notice that DENSITY is an INTENSIVE PROPERTY of matter. •INTENSIVE — does not depend on quantity of matter. Examples are density and temperature. •Contrast with EXTENSIVE — depends on quantity of matter. Examples are mass and volume. •Subdividing matter does not change intensive properti ...
... •Be sure to notice that DENSITY is an INTENSIVE PROPERTY of matter. •INTENSIVE — does not depend on quantity of matter. Examples are density and temperature. •Contrast with EXTENSIVE — depends on quantity of matter. Examples are mass and volume. •Subdividing matter does not change intensive properti ...
Physical Science (Properties of Matter)
... Mixtures are materials composed of two or more substances that retain their separate atomic compositions, even when mixed (e.g., water and sugar can be mixed together thoroughly at the molecular level but the water particles and sugar particles remain separate). Elements are organized into groups ba ...
... Mixtures are materials composed of two or more substances that retain their separate atomic compositions, even when mixed (e.g., water and sugar can be mixed together thoroughly at the molecular level but the water particles and sugar particles remain separate). Elements are organized into groups ba ...
Solved problems in Quantum Preliminaries
... finite walls. This affects the wavefunctions and energies to a small extent, but the equations derived earlier will still give reasonably accurate values for the energies. The existence of discrete energy levels is confirmed by the observation of selective absorption of laser light at certain freque ...
... finite walls. This affects the wavefunctions and energies to a small extent, but the equations derived earlier will still give reasonably accurate values for the energies. The existence of discrete energy levels is confirmed by the observation of selective absorption of laser light at certain freque ...
Physical Chemistry: An Indian Journal
... wrong approach because the physical quantity internal energy must depend on two variables (not on one). It must also depend on volume. He argued that equations of state with two variables must be used instead which show that the internal energy of gases, in each situation, is expressed only as a fun ...
... wrong approach because the physical quantity internal energy must depend on two variables (not on one). It must also depend on volume. He argued that equations of state with two variables must be used instead which show that the internal energy of gases, in each situation, is expressed only as a fun ...
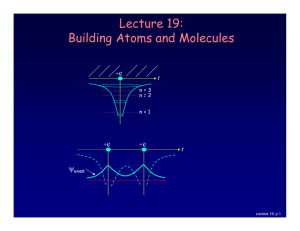
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... there is more than one electron: • 2 electrons (two neutral H atoms): Both electrons occupy the bonding state (with different ms). This is neutral H2. • 4 electrons (two neutral He atoms). Two electron must be in the anti-bonding state. The repulsive force cancels the bonding, and the atoms don’t st ...
... there is more than one electron: • 2 electrons (two neutral H atoms): Both electrons occupy the bonding state (with different ms). This is neutral H2. • 4 electrons (two neutral He atoms). Two electron must be in the anti-bonding state. The repulsive force cancels the bonding, and the atoms don’t st ...
11.3 GAS VOLUMES AND THE IDEAL GAS LAW
... In 1811, Amedeo Avogadro explained Gay-Lussac’s law of combining volumes of gases without violating Dalton’s idea of indivisible atoms. Avogadro reasoned that, instead of always being in monatomic form when they combine to form products, gas molecules can contain more than one atom. He also stated a ...
... In 1811, Amedeo Avogadro explained Gay-Lussac’s law of combining volumes of gases without violating Dalton’s idea of indivisible atoms. Avogadro reasoned that, instead of always being in monatomic form when they combine to form products, gas molecules can contain more than one atom. He also stated a ...
Article3-Dirac - Inframatter Research Center
... approximated this non-relativistically, and Dirac adjusted Bohr’s work to account for relativity. Unfortunately, this does not match what the astronomers were doing. The electron’s motion produces a centripetal effect pushing the electron outward counterbalancing the electro-dynamic pull inward. Cla ...
... approximated this non-relativistically, and Dirac adjusted Bohr’s work to account for relativity. Unfortunately, this does not match what the astronomers were doing. The electron’s motion produces a centripetal effect pushing the electron outward counterbalancing the electro-dynamic pull inward. Cla ...
Chapter 4 The First Law - Physics | Oregon State University
... All thermodynamic state variables are true (exact) differentials with a change in state defined as in Eq.4.5. Moreover, state variables are not independent and can be functionally expressed in terms of other state variables. Usually only a few are needed to completely specify any state of a system. ...
... All thermodynamic state variables are true (exact) differentials with a change in state defined as in Eq.4.5. Moreover, state variables are not independent and can be functionally expressed in terms of other state variables. Usually only a few are needed to completely specify any state of a system. ...
... of conventional quantum mechanics, as it applies in atoms and molecules, in solids, the associated distance has marginal consequence. This is because except within the immediate vicinity of each surface or interface, the substrate effectively “behaves” as if it is neutral. For this reason, electrost ...
Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding
... In 1916, Gilbert Lewis used this fact to explain why atoms form certain kinds of ions and molecules The Octet Rule: in forming compounds, atoms tend to achieve a noble gas configuration; 8 in the outer level is stable Each noble gas (except He, which has 2) has 8 electrons in the outer level ...
... In 1916, Gilbert Lewis used this fact to explain why atoms form certain kinds of ions and molecules The Octet Rule: in forming compounds, atoms tend to achieve a noble gas configuration; 8 in the outer level is stable Each noble gas (except He, which has 2) has 8 electrons in the outer level ...
Physical Chemistry Lab (Real Gas Behavior)
... The more negative B value from the experiment could come from a couple errors. The most likely error is due to a leak in the vessel. A leak would mean that less pressure and less CO2 would be in the vessel at the time of weighing, which would ultimately increase the Z value. This explains why the y- ...
... The more negative B value from the experiment could come from a couple errors. The most likely error is due to a leak in the vessel. A leak would mean that less pressure and less CO2 would be in the vessel at the time of weighing, which would ultimately increase the Z value. This explains why the y- ...
1a) Charged particles in matter :-
... Defects of Rutherford’s model of the atom :Any particle in a circular orbit would undergo acceleration and during acceleration the charged particle would radiate energy. So the revolving electrons would lose energy and fall into the nucleus and the atom would be unstable. We know that atoms are stab ...
... Defects of Rutherford’s model of the atom :Any particle in a circular orbit would undergo acceleration and during acceleration the charged particle would radiate energy. So the revolving electrons would lose energy and fall into the nucleus and the atom would be unstable. We know that atoms are stab ...
Name _____Mr. Perfect________________________________ Date __F 14_______ n l of
... 9. The first ionization energies of As and Se are 0.947 MJ/mol for As and 0.941 MJ/mol for Se. Explain this result using orbital diagrams. (5 pts) As [Ar] [↑↓] [↑↓][↑↓][↑↓][↑↓][↑↓] [↑ ][ ↑ ][↑ ] 4s 3d 4p Se [Ar] [↑↓] [↑↓][↑↓][↑↓][↑↓][↑↓] [↑↓][↑ ][↑ ] 4s 3d 4p The periodic trend would predict Se to h ...
... 9. The first ionization energies of As and Se are 0.947 MJ/mol for As and 0.941 MJ/mol for Se. Explain this result using orbital diagrams. (5 pts) As [Ar] [↑↓] [↑↓][↑↓][↑↓][↑↓][↑↓] [↑ ][ ↑ ][↑ ] 4s 3d 4p Se [Ar] [↑↓] [↑↓][↑↓][↑↓][↑↓][↑↓] [↑↓][↑ ][↑ ] 4s 3d 4p The periodic trend would predict Se to h ...
Electron Configuration
... introduced the concept of energy levels, where the electrons orbited similar to the way the planets orbit the sun. ...
... introduced the concept of energy levels, where the electrons orbited similar to the way the planets orbit the sun. ...
Chapter 10: Gases
... • Simply put, if a gas's temperature increases then so does its pressure, if the mass and volume of the gas are held constant. The law has a particularly simple mathematical form if the temperature is measured on an absolute scale, such as in Kelvin. • Since pressure and temperature are directly rel ...
... • Simply put, if a gas's temperature increases then so does its pressure, if the mass and volume of the gas are held constant. The law has a particularly simple mathematical form if the temperature is measured on an absolute scale, such as in Kelvin. • Since pressure and temperature are directly rel ...
Document
... * A gas always becomes more ordered when dissolved in a liquid and gas. 5. Complexity of the element or compound. ...
... * A gas always becomes more ordered when dissolved in a liquid and gas. 5. Complexity of the element or compound. ...
AP 3rd 9 weeks notes
... * A gas always becomes more ordered when dissolved in a liquid and gas. 5. Complexity of the element or compound. ...
... * A gas always becomes more ordered when dissolved in a liquid and gas. 5. Complexity of the element or compound. ...
FALL Final Review KEY
... 31. Elements in the same GROUP (vertical column) have the same number of electrons in the outer energy level (valence electron) 32. (A) 1s2 2s2 2p6 Noble gas is the most stable and will have a general formula of ns2 np6 (where n=1, 2,3,4…7) 33. Check in your notes for the Electronegativity Trend Dia ...
... 31. Elements in the same GROUP (vertical column) have the same number of electrons in the outer energy level (valence electron) 32. (A) 1s2 2s2 2p6 Noble gas is the most stable and will have a general formula of ns2 np6 (where n=1, 2,3,4…7) 33. Check in your notes for the Electronegativity Trend Dia ...
Solid State Physics
... filled with electrons, while all levels above EF are empty. • Electrons are free to move into “empty” states of conduction band with only a small electric field E, leading to high electrical conductivity! • At T > 0, electrons have a probability to be thermally “excited” from below the Fermi energy ...
... filled with electrons, while all levels above EF are empty. • Electrons are free to move into “empty” states of conduction band with only a small electric field E, leading to high electrical conductivity! • At T > 0, electrons have a probability to be thermally “excited” from below the Fermi energy ...
Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding
... lose electrons to attain a noble gas configuration. They make positive ions (cations) If we look at the electron configuration, it makes sense to lose electrons: Na 1s22s22p63s1 1 valence electron Na1+ 1s22s22p6 This is a noble gas configuration with 8 electrons in the outer level. ...
... lose electrons to attain a noble gas configuration. They make positive ions (cations) If we look at the electron configuration, it makes sense to lose electrons: Na 1s22s22p63s1 1 valence electron Na1+ 1s22s22p6 This is a noble gas configuration with 8 electrons in the outer level. ...