Lecture Notes - Academic Home Page
... anions (metals and non-metals) • Only a few elements form common anions (C, N, O, P, S, Cl, F) ...
... anions (metals and non-metals) • Only a few elements form common anions (C, N, O, P, S, Cl, F) ...
Document
... 12.When 20 gm of an acid (C11H8O2) is dissolved in 50 gm benzene (K f=1.72K kg mol‐1) a freezing point depression of 2K is observed.Thevant Hoff’s factor is ...
... 12.When 20 gm of an acid (C11H8O2) is dissolved in 50 gm benzene (K f=1.72K kg mol‐1) a freezing point depression of 2K is observed.Thevant Hoff’s factor is ...
Final Exam A - Answers - San Diego Chemistry Tutor
... 27. Water boils more easily (at lower temperatures) at higher altitudes than it does at sea level. Which factor below best explains why this happens? a) This is a colligative property of water. b) Temperatures cannot be properly measured at higher altitudes. c) The vapor pressure of water increases ...
... 27. Water boils more easily (at lower temperatures) at higher altitudes than it does at sea level. Which factor below best explains why this happens? a) This is a colligative property of water. b) Temperatures cannot be properly measured at higher altitudes. c) The vapor pressure of water increases ...
Unit 1 Atomic Structure, Periodic Properties and Nuclear Chemistry
... 7. How do atoms of neon-20 and neon-22 differ? _______________________________________________________________________ 8. Neon-20 and neon-22 are called __________________________________________ Atomic Mass 9. Why is the atomic mass unit (amu), rather than the gram, usually used to express atomic m ...
... 7. How do atoms of neon-20 and neon-22 differ? _______________________________________________________________________ 8. Neon-20 and neon-22 are called __________________________________________ Atomic Mass 9. Why is the atomic mass unit (amu), rather than the gram, usually used to express atomic m ...
Chemistry COS 2011-2012
... Describe and explain the process of solution formation Discuss factors that effect solubility Relate enthalpy of solution to endothermic and exothermic dissolving processes Solve problems involving molarity, molality, mole fraction and mass percent Distinguish, describe and characterize solutions, c ...
... Describe and explain the process of solution formation Discuss factors that effect solubility Relate enthalpy of solution to endothermic and exothermic dissolving processes Solve problems involving molarity, molality, mole fraction and mass percent Distinguish, describe and characterize solutions, c ...
Word version - White dwarf stars and the Chandrasekhar limit
... Fowler's ideas with Eddington's work on stellar bodies in equilibrium between gravity and their own internal pressure, and had obtained a more detailed picture of a white dwarf star. He concluded that the central density of such a star would be about six times its average density. Then during the lo ...
... Fowler's ideas with Eddington's work on stellar bodies in equilibrium between gravity and their own internal pressure, and had obtained a more detailed picture of a white dwarf star. He concluded that the central density of such a star would be about six times its average density. Then during the lo ...
1 - GENCHEM
... (a) The containers are well insulated and the oxygen gas cannot escape the containers. Thus this system is isolated system. (b) No work or heat is done. Thus the change in internal energy is zero. (c) No work or heat is done. Thus the change in enthalpy is zero. (d) If the volume of one container is ...
... (a) The containers are well insulated and the oxygen gas cannot escape the containers. Thus this system is isolated system. (b) No work or heat is done. Thus the change in internal energy is zero. (c) No work or heat is done. Thus the change in enthalpy is zero. (d) If the volume of one container is ...
Chapter 1 and Sections 3.1-3.3
... Before viewing this powerpoint, go to end of Chapter 1 and read the Chapter Review: 1.1 Chemistry and Chemicals 1.2 Some Fundamental Ideas of Chemistry 1.3 Scientific Method: Think like a Scientist 1.4 A Study Plan for Learning Chemistry ...
... Before viewing this powerpoint, go to end of Chapter 1 and read the Chapter Review: 1.1 Chemistry and Chemicals 1.2 Some Fundamental Ideas of Chemistry 1.3 Scientific Method: Think like a Scientist 1.4 A Study Plan for Learning Chemistry ...
Problem Set 3 Solutions
... final pressure inside the tank and (b) the work, heat, and ΔU of the process. Assume that the nitrogen gas behaves ideally and that the constant volume heat capacity of diatomic nitrogen is 21.0 J/mol-K. Part (a) To get the final pressure, the ideal gas equation may be employed, ...
... final pressure inside the tank and (b) the work, heat, and ΔU of the process. Assume that the nitrogen gas behaves ideally and that the constant volume heat capacity of diatomic nitrogen is 21.0 J/mol-K. Part (a) To get the final pressure, the ideal gas equation may be employed, ...
a) octane, a chain of 8 C atoms: C8H18 b) benzene, a ring of 6 C
... a) Still 80.1°C, because the vapour pressure doesn’t depend on external pressure. b) Less than 80.1°C, because a lower temperature is needed for the vapour pressure to reach 120 torr c) There will be no boiling point, because 120 torr is above the critical pressure. d) More than 80.1°C, because a ...
... a) Still 80.1°C, because the vapour pressure doesn’t depend on external pressure. b) Less than 80.1°C, because a lower temperature is needed for the vapour pressure to reach 120 torr c) There will be no boiling point, because 120 torr is above the critical pressure. d) More than 80.1°C, because a ...
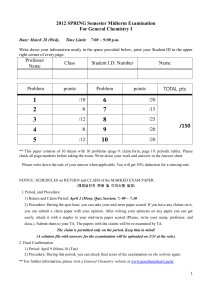
semester 1 examination 2009 the university of the
... There are 10 questions. Each question is worth 3 marks. 1) (a) Students in different class sections attempted to measure the mass of a 100.0 g object. Describe the series of measurements as precise, precise and accurate, or ...
... There are 10 questions. Each question is worth 3 marks. 1) (a) Students in different class sections attempted to measure the mass of a 100.0 g object. Describe the series of measurements as precise, precise and accurate, or ...
0 Quarter Three Assessment Review - SRHSchem
... the solid is completely dissolve, the water temperature drops to 15.2°C. a. Is this process endothermic or exothermic? Explain. – The temperature of the water decreases, so the dissolving process must have absorbed that heat, ...
... the solid is completely dissolve, the water temperature drops to 15.2°C. a. Is this process endothermic or exothermic? Explain. – The temperature of the water decreases, so the dissolving process must have absorbed that heat, ...
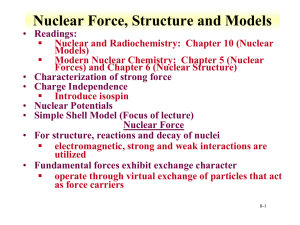
Nuclear Structure - UNLV Radiochemistry
... level order given is to be applied independently to neutrons and protons proton levels increasingly higher than neutron levels as Z increases Coulomb repulsion effect order given within each shell essentially schematic and may not represent exact order of filling • Ground States of Nuclei f ...
... level order given is to be applied independently to neutrons and protons proton levels increasingly higher than neutron levels as Z increases Coulomb repulsion effect order given within each shell essentially schematic and may not represent exact order of filling • Ground States of Nuclei f ...
General Chemistry
... • polar solvents dissolve polar solutes. • Non-polar solvents dissolve non-polar solutes. Water is polar (because it’s bent). It will therefore tend to dissolve other polar molecules or ions. For example, most salts, alcohols and sugars dissolve in water. Alcohols and sugars all contain the O-H part ...
... • polar solvents dissolve polar solutes. • Non-polar solvents dissolve non-polar solutes. Water is polar (because it’s bent). It will therefore tend to dissolve other polar molecules or ions. For example, most salts, alcohols and sugars dissolve in water. Alcohols and sugars all contain the O-H part ...
Document
... you to a birthday party! 50 years ago, Illinois alumnus Nick Holonyak Jr. demonstrated the first visible light-emitting diode (LED) while working at GE. Holonyak returned to Illinois as a professor in 1963, and has been unveiling new inventions on our campus ever since. Today, the LED he demonstrate ...
... you to a birthday party! 50 years ago, Illinois alumnus Nick Holonyak Jr. demonstrated the first visible light-emitting diode (LED) while working at GE. Holonyak returned to Illinois as a professor in 1963, and has been unveiling new inventions on our campus ever since. Today, the LED he demonstrate ...
Neutron Stars
... additional periodicity imposed on the pulse stream. A straightforward application of Kepler’s Law The Doppler shift of the pulses, together with the orbital period, revealed that the combined masses of the two stars was about 2.8 M . The fact that no tidal distortions were apparently affecting the ...
... additional periodicity imposed on the pulse stream. A straightforward application of Kepler’s Law The Doppler shift of the pulses, together with the orbital period, revealed that the combined masses of the two stars was about 2.8 M . The fact that no tidal distortions were apparently affecting the ...
a. Matter First Day of Class
... ALL PURE SUBSTANCES are HOMOGENEOUS pure substance - overall composition consists of only one substance. Examples are: a. elements - the fundamental unit of all matter which combines to form compounds. b. compounds - two or more elements combined in a fixed ratio or proportion. ...
... ALL PURE SUBSTANCES are HOMOGENEOUS pure substance - overall composition consists of only one substance. Examples are: a. elements - the fundamental unit of all matter which combines to form compounds. b. compounds - two or more elements combined in a fixed ratio or proportion. ...
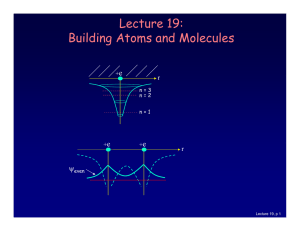
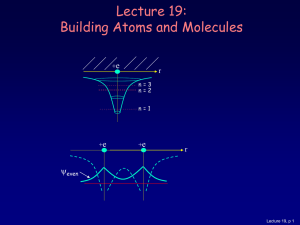
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... there is more than one electron: • 2 electrons (two neutral H atoms): Both electrons occupy the bonding state (with different ms). This is neutral H2. • 4 electrons (two neutral He atoms). Two electron must be in the anti-bonding state. The repulsive force cancels the bonding, and the atoms don’t st ...
... there is more than one electron: • 2 electrons (two neutral H atoms): Both electrons occupy the bonding state (with different ms). This is neutral H2. • 4 electrons (two neutral He atoms). Two electron must be in the anti-bonding state. The repulsive force cancels the bonding, and the atoms don’t st ...
LECTURE NOTES ON PHS 222 (THERMAL PHYSICS) BY DR. V.C.
... Where Pext = external pressure applied in order to perform work, which causes a change in volume dV. The negative sign implies compression (dV<0) when dw should be positive ...
... Where Pext = external pressure applied in order to perform work, which causes a change in volume dV. The negative sign implies compression (dV<0) when dw should be positive ...
PPT
... Example: Nuclear Spin and MRI Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) depends on the absorption of electromagnetic radiation by the nuclear spin of the hydrogen atoms in our bodies. The nucleus is a proton with spin ½, so in a magnetic field B there are two energy states. The proton’s magnetic moment is m ...
... Example: Nuclear Spin and MRI Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) depends on the absorption of electromagnetic radiation by the nuclear spin of the hydrogen atoms in our bodies. The nucleus is a proton with spin ½, so in a magnetic field B there are two energy states. The proton’s magnetic moment is m ...
Matter Notes
... Eg: density, melting temp; pure gold will always have the same density and melting temp, regardless of amount. Intensive properties are used to identify substances. ...
... Eg: density, melting temp; pure gold will always have the same density and melting temp, regardless of amount. Intensive properties are used to identify substances. ...
******************Q***********Q*******Q****** Q***Q***Q***Q***Q***Q
... Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann. Maxwell's calculation (1859) of the distribution law of molecular velocities in thermal equilibrium can be considered as the starting point of statistical mechanics, the first time a ...
... Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann. Maxwell's calculation (1859) of the distribution law of molecular velocities in thermal equilibrium can be considered as the starting point of statistical mechanics, the first time a ...