Organic Chemistry Review
... 1. Circle the letter of each sentence that is TRUE about carbs. a. starches and sugars are examples of carbs b. living things use them as their main source of energy c. the monomers of carbs are starch molecules d. plants and some animals use some carbs for strength and rigidity 2. Single sugar mole ...
... 1. Circle the letter of each sentence that is TRUE about carbs. a. starches and sugars are examples of carbs b. living things use them as their main source of energy c. the monomers of carbs are starch molecules d. plants and some animals use some carbs for strength and rigidity 2. Single sugar mole ...
delhi private school
... Q16. (a) Write the reactions of glucose with (i) HI (ii)HNO3 (iii)(CH3CO)2O (b) Discuss the amphoteric nature of amino acid with suitable example Q17. (a)Discuss the following (i) Denaturation (ii) invert sugar (iii) Globular proteins (b) What is glycogen? How is it different from starch? (c) Draw t ...
... Q16. (a) Write the reactions of glucose with (i) HI (ii)HNO3 (iii)(CH3CO)2O (b) Discuss the amphoteric nature of amino acid with suitable example Q17. (a)Discuss the following (i) Denaturation (ii) invert sugar (iii) Globular proteins (b) What is glycogen? How is it different from starch? (c) Draw t ...
more aromatic chemistry
... • Phenols and alcohols both contain hydroxyl groups however they are classified as separate functional groups. • Phenols have different properties than alcohols, most noteworthy is ...
... • Phenols and alcohols both contain hydroxyl groups however they are classified as separate functional groups. • Phenols have different properties than alcohols, most noteworthy is ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ...
... both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ...
Today*s topic is*11 letters long
... : lipid molecule formed by bonding three fatty acids to a glycerol molecule ...
... : lipid molecule formed by bonding three fatty acids to a glycerol molecule ...
Document
... (C. Schiff Test for Aldehydes) The Schiff test (also called the fuchsin-aldehyde test) is based upon the reaction of an aldehyde with a colorless form of a rosaniline dye to yield a violet or purple product. Ketones fail to undergo this reaction. (D. Tollens Test for Aldehydes) The Tollens test is t ...
... (C. Schiff Test for Aldehydes) The Schiff test (also called the fuchsin-aldehyde test) is based upon the reaction of an aldehyde with a colorless form of a rosaniline dye to yield a violet or purple product. Ketones fail to undergo this reaction. (D. Tollens Test for Aldehydes) The Tollens test is t ...
Subject Description Form
... through a study of the basic reaction types, the basic principles and the uses of common spectroscopic techniques available for functional group identification. Illustration will be emphasized on reactions and compounds with structural interest or industrial importance. ...
... through a study of the basic reaction types, the basic principles and the uses of common spectroscopic techniques available for functional group identification. Illustration will be emphasized on reactions and compounds with structural interest or industrial importance. ...
organic reading
... Most inorganic compounds are made from dements other than carbon. Genera11ÿ inorganic molecules contain fewer atoms than organic molecules. Inorganic compounds are the source fqr many elements needed by living things. Iaor example, plants taÿe up inorganic compounds from the soil. Thesÿ inorganid co ...
... Most inorganic compounds are made from dements other than carbon. Genera11ÿ inorganic molecules contain fewer atoms than organic molecules. Inorganic compounds are the source fqr many elements needed by living things. Iaor example, plants taÿe up inorganic compounds from the soil. Thesÿ inorganid co ...
C h e m g u id e –... ACYL CHLORIDES: REACTIONS WITH WATER, ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
... group. Ethanoylation is a particular example of acylation where a CH3C=O group (an ethanoyl group) is substituted into another molecule. ...
... group. Ethanoylation is a particular example of acylation where a CH3C=O group (an ethanoyl group) is substituted into another molecule. ...
102 Lecture Ch14a
... electronegativity of S is the same as that of C (2.5), much less than that of O (3.5), so C-S and S-H bonds are not polar - thiols do not H-bond and have relatively low boiling points • Ethers do not H-bond with themselves, so have boiling points similar to hydrocarbons -ethers are only slightly sol ...
... electronegativity of S is the same as that of C (2.5), much less than that of O (3.5), so C-S and S-H bonds are not polar - thiols do not H-bond and have relatively low boiling points • Ethers do not H-bond with themselves, so have boiling points similar to hydrocarbons -ethers are only slightly sol ...
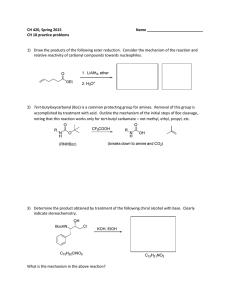
CH 420, Spring 2015 Name ___________________________ CH 18 practice problems
... 3) Determine the product obtained by treatment of the following chiral alcohol with base. Clearly indicate stereochemistry. ...
... 3) Determine the product obtained by treatment of the following chiral alcohol with base. Clearly indicate stereochemistry. ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... effective if electronegative elements such as chlorine are present. Thus the chloroethanoic acids become increasingly more acidic as more chlorine atoms are present in the molecule. The reagent of preference is SOCl2, since both by-products are gases. Other possibilities are PCl3 and PCl5. The react ...
... effective if electronegative elements such as chlorine are present. Thus the chloroethanoic acids become increasingly more acidic as more chlorine atoms are present in the molecule. The reagent of preference is SOCl2, since both by-products are gases. Other possibilities are PCl3 and PCl5. The react ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... effective if electronegative elements such as chlorine are present. Thus the chloroethanoic acids become increasingly more acidic as more chlorine atoms are present in the molecule. The reagent of preference is SOCl2, since both by-products are gases. Other possibilities are PCl3 and PCl5. The react ...
... effective if electronegative elements such as chlorine are present. Thus the chloroethanoic acids become increasingly more acidic as more chlorine atoms are present in the molecule. The reagent of preference is SOCl2, since both by-products are gases. Other possibilities are PCl3 and PCl5. The react ...
Organic Notes #5 - RX`ns - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... increased attraction from the hydrogen bonding between molecules. Solubility in Water - Is determined by the polarity of the molecule from the presence of functional groups and on the chain length. Shorter chains of most functional groups are soluble. Longer chains much less so. Compounds with non-p ...
... increased attraction from the hydrogen bonding between molecules. Solubility in Water - Is determined by the polarity of the molecule from the presence of functional groups and on the chain length. Shorter chains of most functional groups are soluble. Longer chains much less so. Compounds with non-p ...
Organic Polymer Workshee t /16
... 2. The bonds that are broken when water vaporizes are: a. ionic b. bonds between water molecules c. bonds between atoms of individual water molecules d. polar covalent bonds e. nonpolar covalent bonds 3. Which of the following terms includes all other in the list? a. monosaccharide b. disaccharide c ...
... 2. The bonds that are broken when water vaporizes are: a. ionic b. bonds between water molecules c. bonds between atoms of individual water molecules d. polar covalent bonds e. nonpolar covalent bonds 3. Which of the following terms includes all other in the list? a. monosaccharide b. disaccharide c ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... Main storage molecules in plants – Chains of simple sugars that must be broken down before they can be used ...
... Main storage molecules in plants – Chains of simple sugars that must be broken down before they can be used ...
File
... Ar-OH Phenols are compounds with an –OH group attached to an aromatic carbon. Although they share the same functional group with alcohols, where the –OH group is attached to an aliphatic carbon, the chemistry of phenols is very different from that of alcohols. ...
... Ar-OH Phenols are compounds with an –OH group attached to an aromatic carbon. Although they share the same functional group with alcohols, where the –OH group is attached to an aliphatic carbon, the chemistry of phenols is very different from that of alcohols. ...
Ch 13 vitamins and Minerals
... Colors and Pigments • Extracted from natural and / or synthetic sources- added to foods – Carotenoids: – red in tomatoes (lycopene) – Carrots ( beta carotene) ...
... Colors and Pigments • Extracted from natural and / or synthetic sources- added to foods – Carotenoids: – red in tomatoes (lycopene) – Carrots ( beta carotene) ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.